PC (polycarbonate) alloy material as well as preparation method and application thereof
An alloy material and uniform mixing technology, applied in the field of PC alloy material and its preparation, can solve problems such as insufficient fluidity, warpage performance, internal stress performance, mold release performance, and color and luster that fail to achieve good results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0104] In embodiment and comparative example, the preparation method of described PC alloy material, comprises the steps:
[0105] 1) Weigh each component according to the formula content, and mix the polycarbonate, polyethylene terephthalate-1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene ester, fibrous filler, and other additives that need to be pre-dried Perform pre-drying treatment at 120°C to 130°C, and set the pre-drying time to 4h to 6h to obtain pre-dried polycarbonate, polyethylene terephthalate-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol Esters, fibrous fillers, other additives;
[0106] 2) Mix the pre-dried polycarbonate, polyethylene terephthalate-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, fibrous fillers, and other additives through a high-speed mixer, and the mixing temperature is 30℃~50℃, the mixing time is set at 5min~15min;
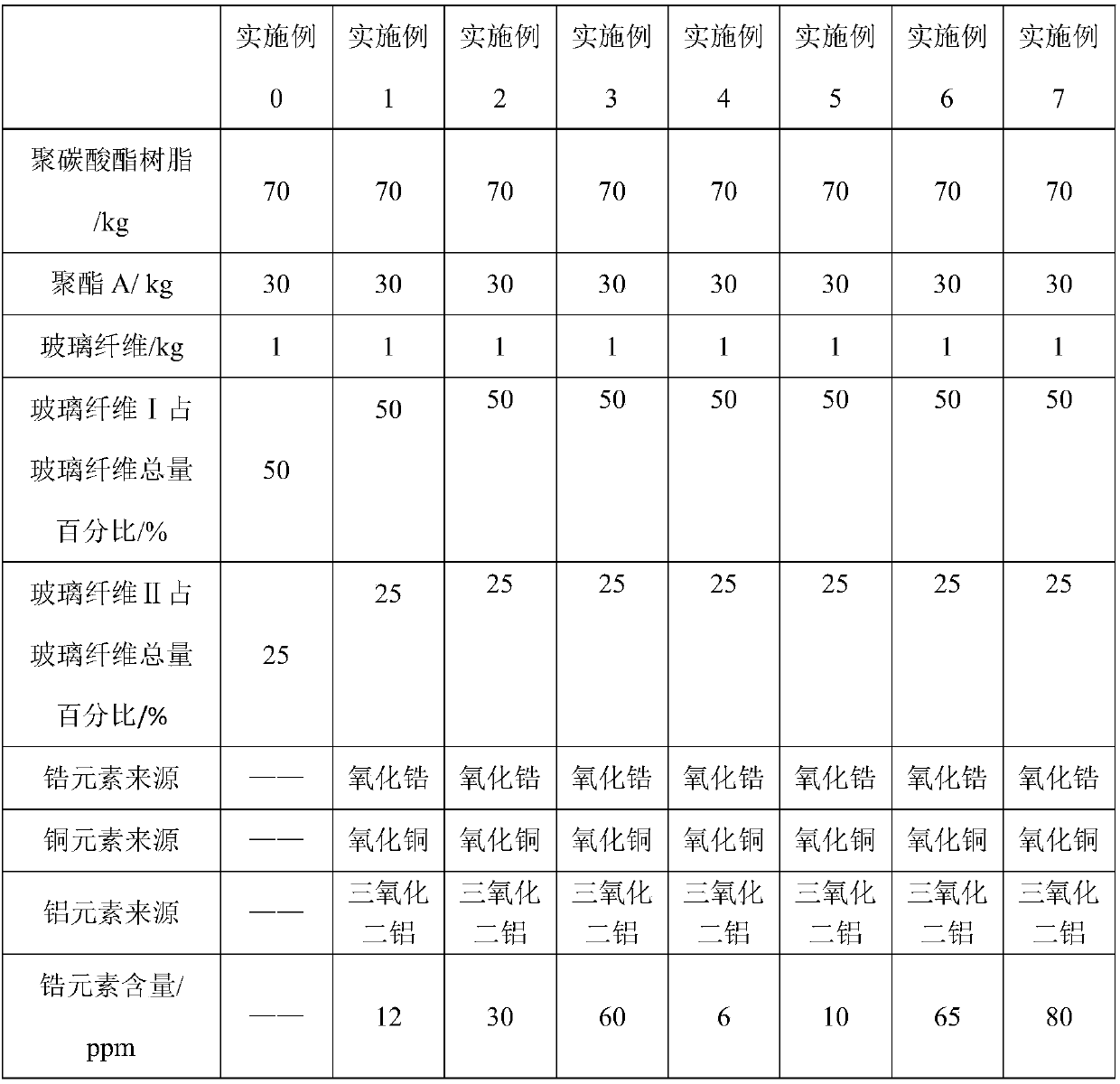
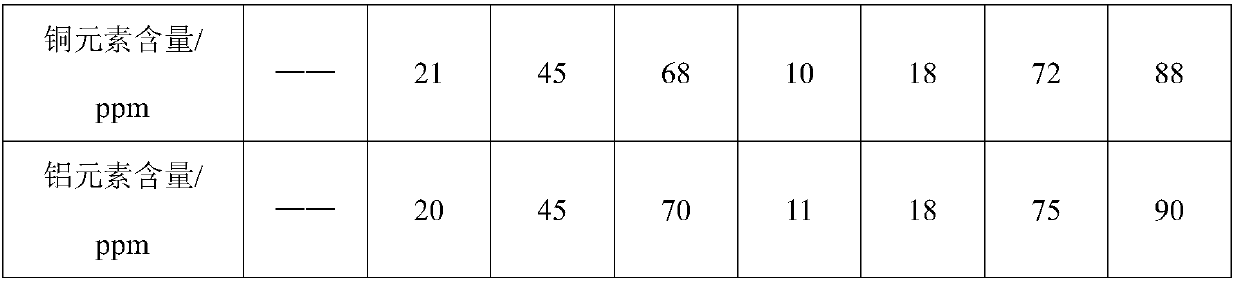
[0107] 3) Mix homogeneously mixed polycarbonate, polyethylene terephthalate-1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol, other additives, aluminum salt or aluminum oxide, copper salt or copper oxide, Zircon...
Embodiment 33
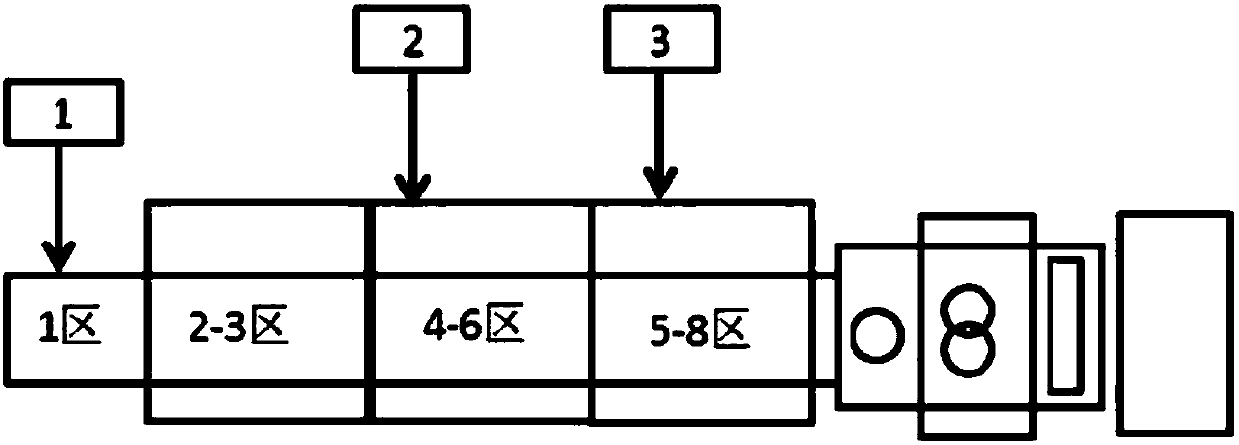
[0116] Embodiment 33: The way of adding glass fibers in 3) is: based on the total weight of glass fibers, the glass fibers accounting for 40% of the total weight of glass fibers are added from the feeding port 1 in the figure, based on the total weight of glass fibers, accounting for 40% of the total weight of glass fibers. The glass fiber of 35% of the total weight of the glass fiber is added from the feed port 2, based on the total weight of the glass fiber, the glass fiber accounting for 25% of the total weight of the glass fiber is added from the feed port 3. In the obtained pellets, glass fibers with a length of 100um to 300um account for 40% by weight of glass fibers; glass fibers with a length greater than 300um but not more than 500um account for 25% by weight of glass fibers.
Embodiment 34
[0117] Example 34: The glass fiber is added in the following manner in 3): based on the total weight of the glass fiber, the glass fiber accounting for 20% of the total weight of the glass fiber is added from the feeding port 1 in the figure, based on the total weight of the glass fiber, accounting for 20% of the total weight of the glass fiber. The glass fiber of 35% of the total weight of the glass fiber is added from the feed port 2, based on the total weight of the glass fiber, the glass fiber accounting for 45% of the total weight of the glass fiber is added from the feed port 3. The glass fibers with a length of 100um to 300um in the obtained pellets account for 60% by weight of the glass fibers; the glass fibers with a length greater than 300um but not more than 500um account for 25% by weight of the glass fibers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com