Extraction technology of flavonoid pigments from dillenia indica fruits
An extraction process, the technology of sycamores, which is applied in food extraction, the function of food ingredients, food science, etc., can solve the problems of unstudied extraction process optimization, antioxidant capacity, and less sycamores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A process for extracting flavonoid pigments from sycamore quinces, comprising the following steps:
[0024] 1. Pretreatment of raw materials of samosa fruit
[0025] The sycamore fruit was picked from Lvchun County, Honghe Prefecture, Yunnan Province. The fruit of the sycamore fruit was ground with the skin, sealed and placed in a -18°C refrigerator for later use.
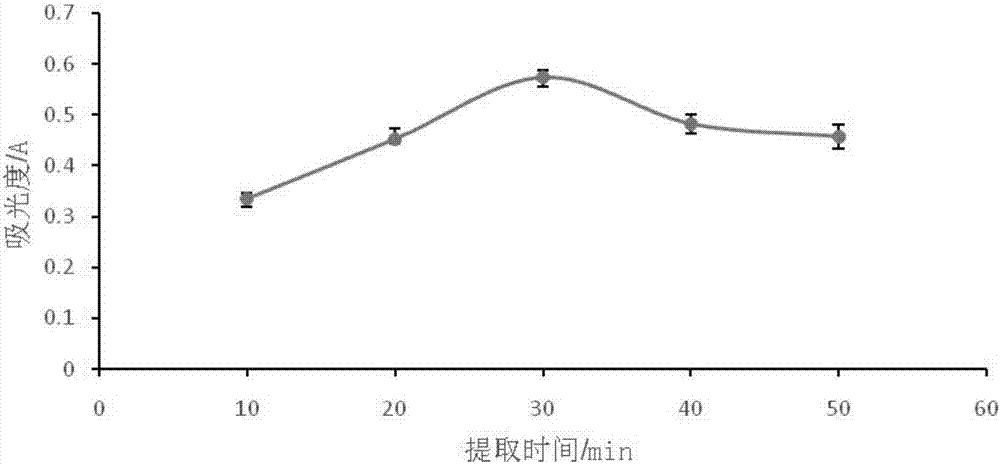
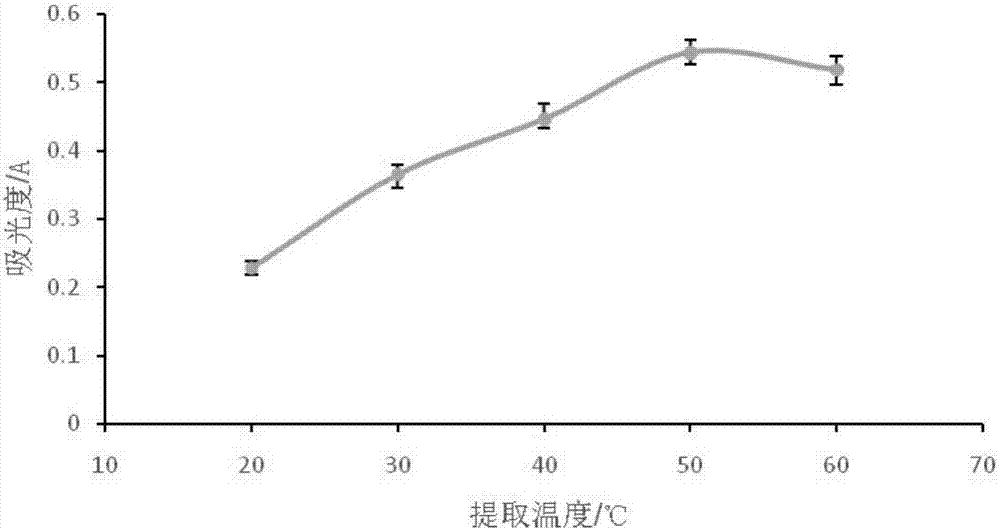
[0026] 2. Preliminary qualitative determination of flavonoid pigments to determine the best extraction solvent and maximum absorption wavelength
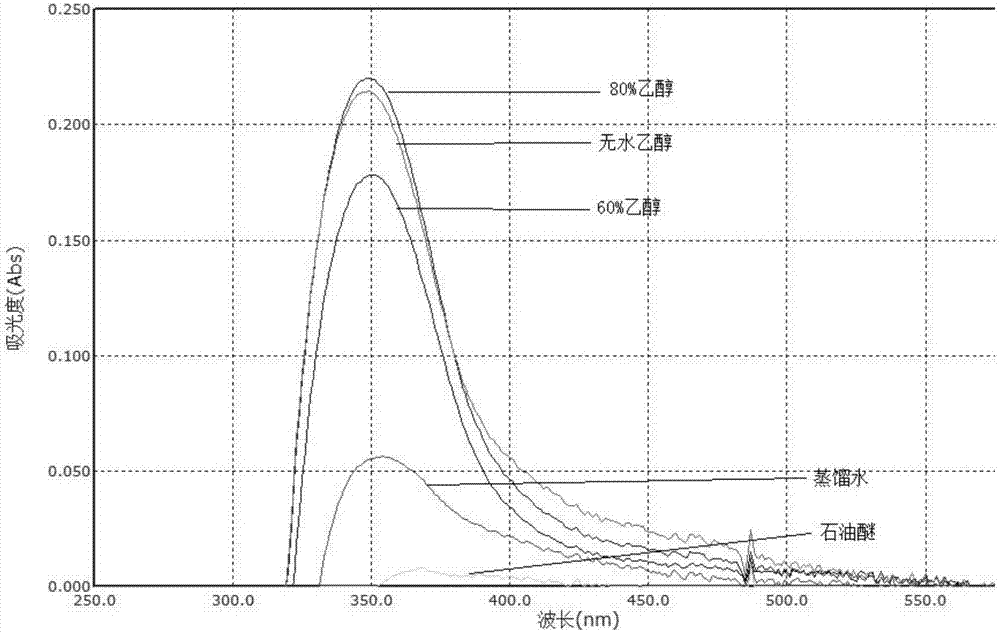
[0027] Accurately weigh 5 samples, each 1g, put them in a beaker, add 10mL to prepare 60% ethanol, 80% ethanol, distilled water, absolute ethanol, and petroleum ether respectively. Oscillate, filter, and dilute to 50mL volumetric flasks with different extraction solvents, measure the absorbance in the range of 200nm-1000nm, and determine the maximum absorption wavelength;
[0028] pass figure 1 It can be seen that the flavonoids in Wuxia fruit are insoluble in ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The mensuration of the in vitro antioxidant activity of the flavonoid pigment in the flavonoid pigment extracted by the process described in Example 1 comprises the following steps:
[0057] 1. Preparation of flavonoid extraction solution
[0058] Accurately weigh 1g of fresh sycamore fruit, extract flavonoid pigments under optimal conditions, and then set the volume in a 50mL volumetric flask for later use.
[0059] 2. Determination of DPPH free radical scavenging ability
[0060] Draw 1mL of flavonoid pigment solution and 4mL of DPPH methanol solution and mix, vortex shake, place in dark place at room temperature for 10min, perform colorimetric measurement at 517nm, and calculate the scavenging ability of DPPH free radicals according to the standard curve. Utilize ferulic acid to draw standard curve, standard equation is y=0.9406x+28.698 (R 2 =0.969)
[0061] Free radical scavenging ability (%) = [(A 0 -A 1 ) / A 0 ]×100
[0062] A 0 Absorbance for the control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com