Polymer capable of responding to acid and oxidation-reduction environment in cells as well as preparation and application thereof
A reaction and derivative technology, applied in the field of pharmacy, can solve problems such as hindering the effective release of drugs, and achieve the effect of improving tumor treatment effect and increasing drug concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
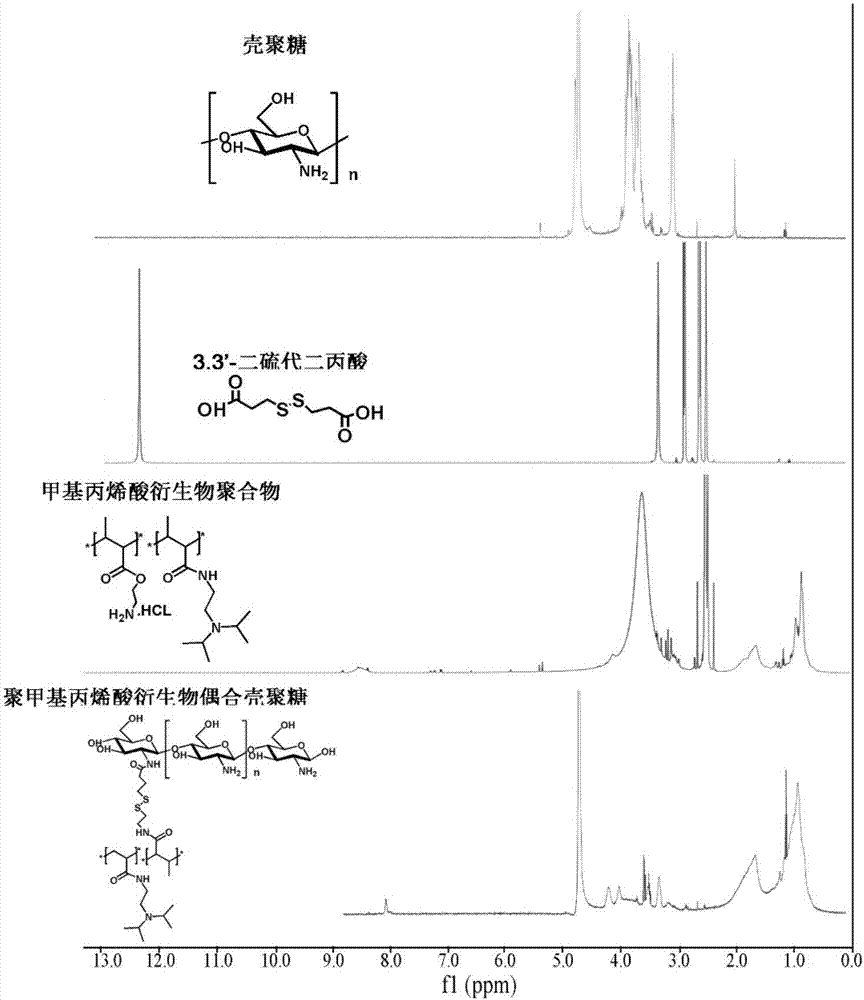
[0033] Take 6.4mL of N,N-diisopropylethylenediamine, 16mL of triethylamine, 3mL of methacrylic acid, 1.9g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 3.0g of carbodiimide, dissolve in 30mL of dichloromethane, and protect with nitrogen 40°C for 12 hours. The product was passed through an aluminum oxide column while it was hot, extracted with water, and after rotary evaporation, the methacrylic acid derivative monomer was obtained, which was stored at -20°C.
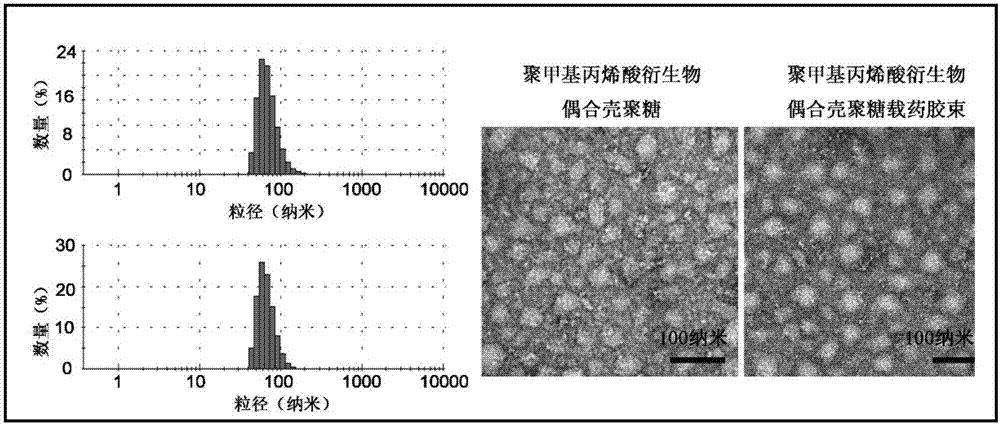
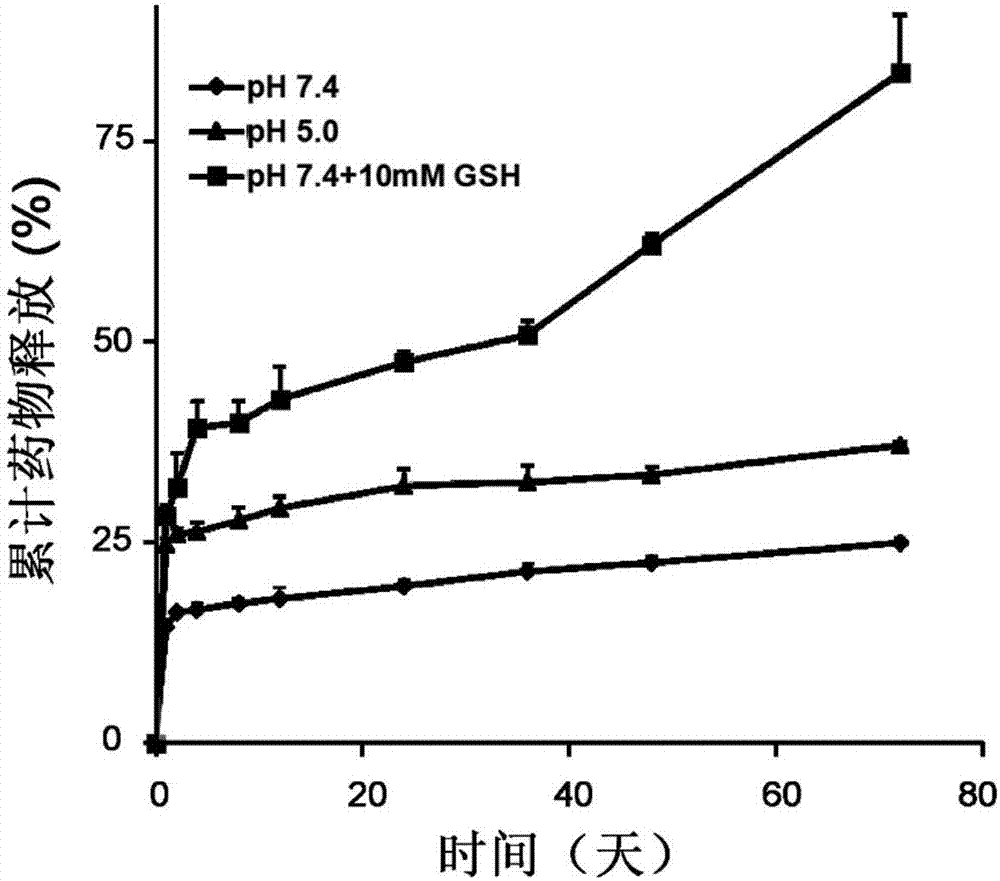
[0034] Take 500 mg of methacrylic acid derivative monomer, 50 mg of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylate, and 8.8 mg of azobisisobutyronitrile, dissolve them in 3 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and react at 60°C under nitrogen protection 0.5 hours. Terminate the reaction, extract with glacial ethyl acetate, and centrifuge to obtain polymethacrylic acid derivatives. By gel permeation chromatography (PLgel MIXED-C columns, particle size: 5 μm; dimensions: 7.5 mm×300 mm), the molecular weight of the polymethacrylic acid derivative was calculated to b...
Embodiment 2
[0040]Take N,N-diisopropylethylenediamine 6.4mL, triethylamine 16mL, methacrylic acid 4.5mL, 1.9g 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 3.0g carbodiimide, dissolve in 30mL dichloromethane, nitrogen Under protection, react at 40°C for 12 hours. The product was passed through an aluminum oxide column while it was hot, extracted with water, and after rotary evaporation, the methacrylic acid derivative monomer was obtained, which was stored at -20°C.
[0041] Take 500 mg of methacrylic acid derivative monomer, 50 mg of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylate, and 8.8 mg of azobisisobutyronitrile, dissolve them in 3 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and react at 60°C under nitrogen protection 1 hour. Terminate the reaction, extract with glacial ethyl acetate, and centrifuge to obtain polymethacrylic acid derivatives. By gel permeation chromatography (PLgel MIXED-C columns, particlesize: 5 μm; dimensions: 7.5 mm×300 mm), the molecular weight of the polymethacrylic acid derivative was calculated to be 6500 Da a...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Take N,N-diisopropylethylenediamine 6.4mL, triethylamine 16mL, methacrylic acid 6.0mL, 1.9g 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 3.0g carbodiimide, dissolve in 30mL dichloromethane, nitrogen Under protection, react at 40°C for 12 hours. The product was passed through an aluminum oxide column while it was hot, extracted with water, and after rotary evaporation, the methacrylic acid derivative monomer was obtained, which was stored at -20°C.
[0049] Take 1 g of methacrylic acid derivative monomer, 50 mg of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylate, and 8.8 mg of azobisisobutyronitrile, dissolve them in 3 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and react at 60°C under nitrogen protection 2.5 hours. Terminate the reaction, extract with glacial ethyl acetate, and centrifuge to obtain polymethacrylic acid derivatives. By gel permeation chromatography (PLgel MIXED-C columns, particlesize: 5 μm; dimensions: 7.5 mm×300 mm), the molecular weight of the polymethacrylic acid derivative was calculated to be 18.8 kDa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com