Preparation and purification method of everolimus intermediate
A purification method, the technology of everolimus, is applied in chemical instruments and methods, compounds of Group 4/14 elements of the periodic table, organic chemistry, etc., and can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, high operational risks, and high costs. Achieving the effect of simple operation and overcoming complex operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
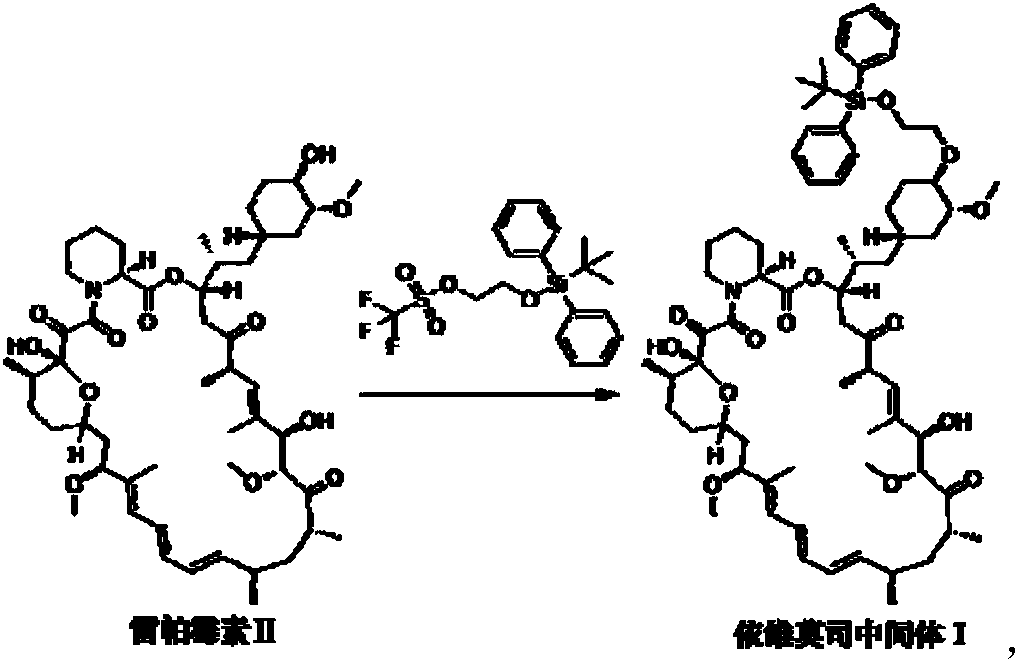
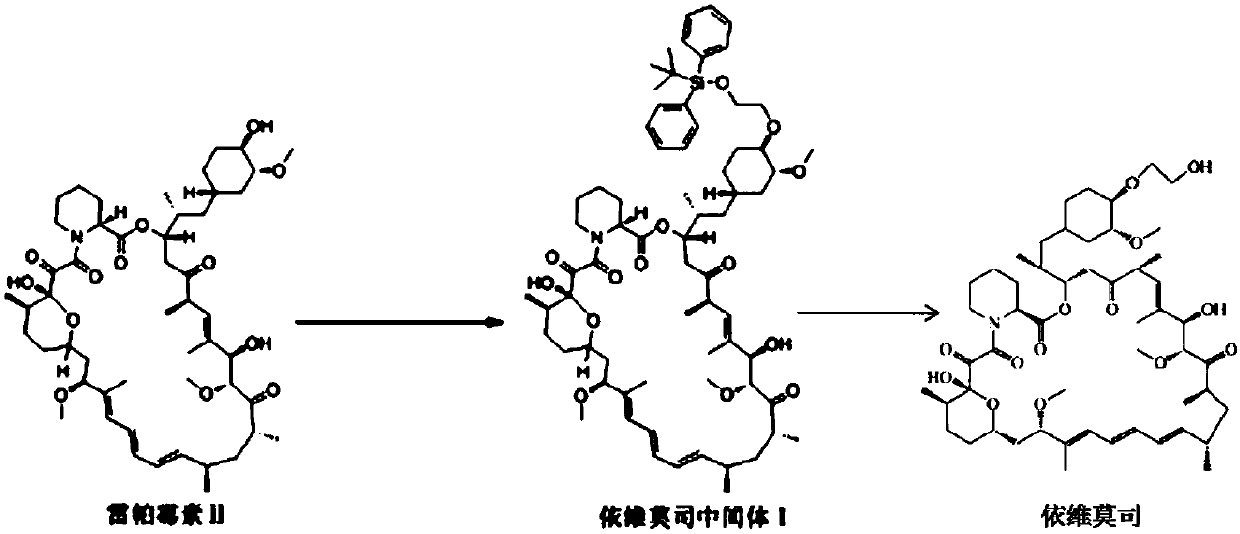
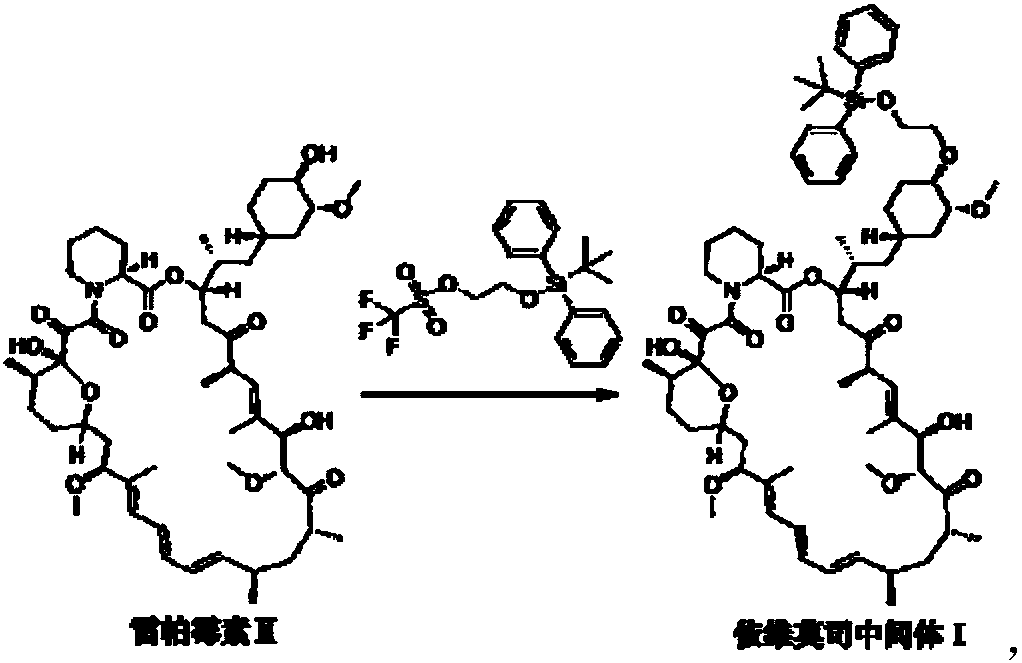
[0027] In a 100ml single-necked flask, add 5.00g of rapamycin and 14.18g of 2-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxyethyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, then add 40ml of toluene solvent, room temperature Stirring, the solution is a milky white suspension. Then add 3.53g of 2,6-lutidine, heat up and stir, control the temperature between 60°C and 70°C, and react for 6 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction solution was a light yellow suspension solution. The solid residue in the reaction solution was removed by filtration to obtain a pale yellow clear toluene solution. Wet loading column chromatography, eluted in three gradients: first use n-hexane as the eluent until the eluent TLC has no toluene absorption point, the volume of the eluent n-hexane used in this gradient and the raw material rapamycin The weight ratio is 100-250mL / g; then the mixed liquid C 1 As the eluent, collect the TLC eluate containing only everolimus intermediate 1 to obtain the intermediate component,...
Embodiment 2
[0033] In a 100ml single-necked flask, add 5.00g of rapamycin and 14.18g of 2-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxyethyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, then add 40ml of toluene solvent, room temperature Stirring, the solution is a milky white suspension. Then add 3.53g of 2,6-lutidine, heat up and stir, control the temperature between 60°C and 70°C, and react for 6 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction solution was a light yellow suspension solution. The solid residue in the reaction solution was removed by filtration to obtain a pale yellow clear toluene solution. Wet loading column chromatography, as the elution conditions shown in Table 2, first separate and elute toluene with eluent n-heptane, and then use eluent n-heptane and ethyl acetate (volume ratio 4:1) , separate and collect the intermediate components, and then use ethyl acetate as the eluent to recover unreacted rapamycin raw material components. The specific elution conditions are shown in Table 2.
[003...
Embodiment 3
[0039] In a 100ml single-necked flask, respectively add 5.00g of rapamycin and 14.18g of 2-(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxyethyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, then add 40ml of toluene solvent, Stirring at room temperature, the solution was a milky white suspension. Then add 3.53g of 2,6-lutidine, heat up and stir, control the temperature between 60°C and 70°C, and react for 6 hours. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction solution was a light yellow suspension solution. The solid residue in the reaction solution was removed by filtration to obtain a pale yellow clear toluene solution. Wet loading column chromatography, first use the eluent as methyl tert-butyl ether to separate and elute toluene, then use the eluent methyl tert-butyl ether and ethyl acetate (volume ratio 15:1), separate and collect Intermediate components, and then use ethyl acetate as the eluent to recover unreacted rapamycin raw material components. The specific elution conditions are shown in Table 3. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com