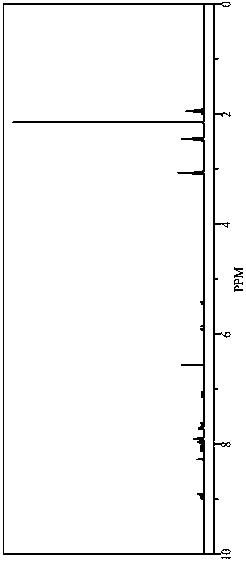
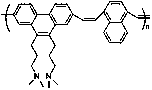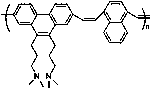Similar material for simulating rock mass and preparation method thereof
A technology for similar materials and simulating rock mass, which is applied in the field of similar materials and their preparation in geomechanical models, and can solve the problems of inability to prepare similar materials and inability to meet simulation requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1) Add 3,8-dibromophenanthrene (0.01 mol) into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and add DMSO to dissolve the solid under a nitrogen atmosphere. A hydrochloride solution dissolved with 0.01 mol of 3-dimethylaminopropyl chloride was added dropwise to the mixture, and stirred at room temperature for 6 hours to stop the reaction. Water was added to the reaction to dissolve any salts. After extraction, the combined organic layers were washed with NaOH solution, water and concentrated brine. The washed solution was dried with anhydrous MgSO4, filtered under reduced pressure, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a yellow solid crude product, which was recrystallized in methanol / water to obtain white crystals.
[0037] 2) Add 0.02 mol of N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) and 0.001 g of benzoyl peroxide to a 100 mL three-necked flask, and add 1,4-dimethylbiphenyl (0.01 mol) in a nitrogen atmosphere and CCl4. Stir magnetically to dissolve all solids. Heat to reflux ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] First mix 100 parts of barite powder with a particle size of 300 mesh and 0.014 parts of formula I polymer, then dry at 90°C for 3 hours to remove water, take it out and cool to room temperature; add 4 parts of No. 32 hydraulic oil to the dried Mix the barite powder and the polymer of formula I evenly, and then pulverize the mixed material until its particle size is ≤1mm; add 0.17 part of cement marked as 525 to the barite powder, the polymer of formula I and No. 32 hydraulic machine oil In the mixture, continue to mix evenly; finally add 2 parts of water to the above mixture, and mix evenly. The compressive strength of the material is 31.6MPa, the tensile strength is 2.91MPa, and the deformation modulus is 132.6MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0044] First mix 100 parts of barite powder with a particle size of 300 mesh and 0.012 parts of formula I polymer, then dry at 90°C for 3 hours to remove water, take it out and cool to room temperature; add 4 parts of No. 32 hydraulic oil to the dried Mix the barite powder and the polymer mixture of formula I evenly, and then crush the mixed material until its particle size is ≤1mm; add 0.1 part of cement marked 425 to the barite powder, the polymer formula I and No. 32 hydraulic press In the oil mixture, continue to mix well; finally add 2.5 parts of water to the above mixture, and mix well. The compressive strength of the material is 22.6MPa, the tensile strength is 3.12MPa, and the deformation modulus is 32.8MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com