Permanent magnet, rotary electric machine, and vehicle
A technology of permanent magnets and rotating motors, applied in the manufacture of inductors/transformers/magnets, circuits, magnetic materials, etc., which can solve problems such as increased copper loss and reduced efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
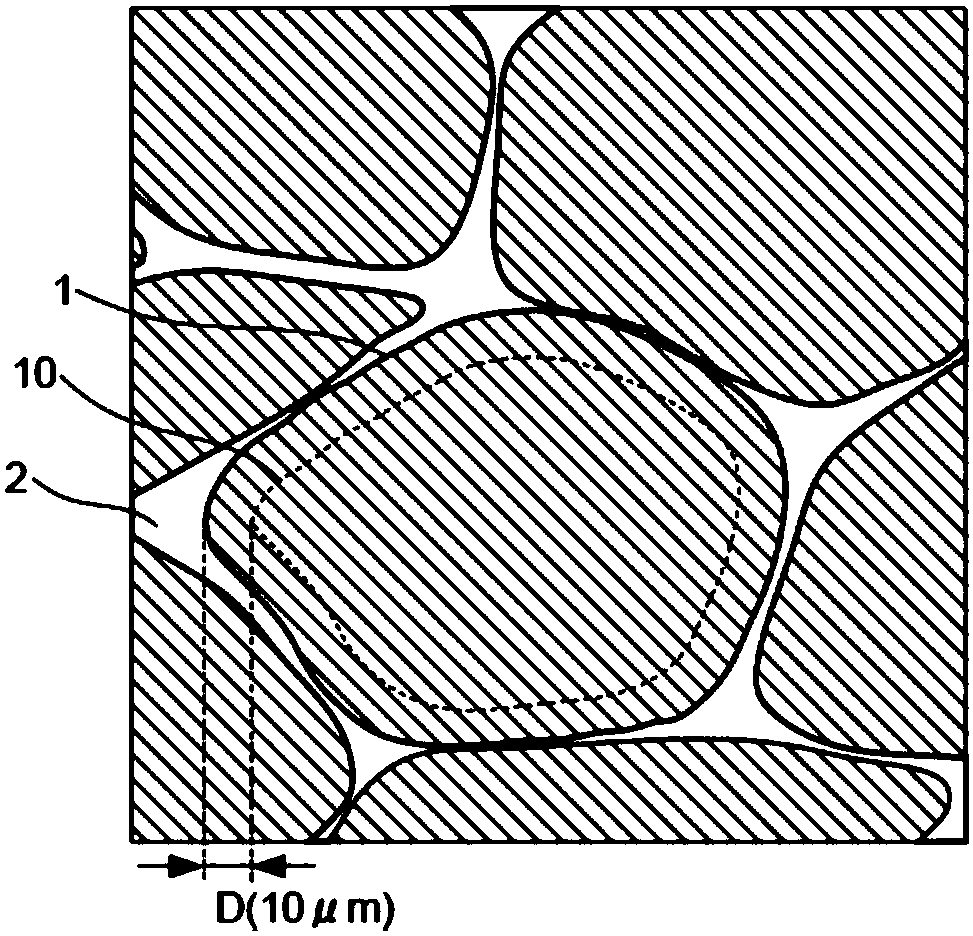
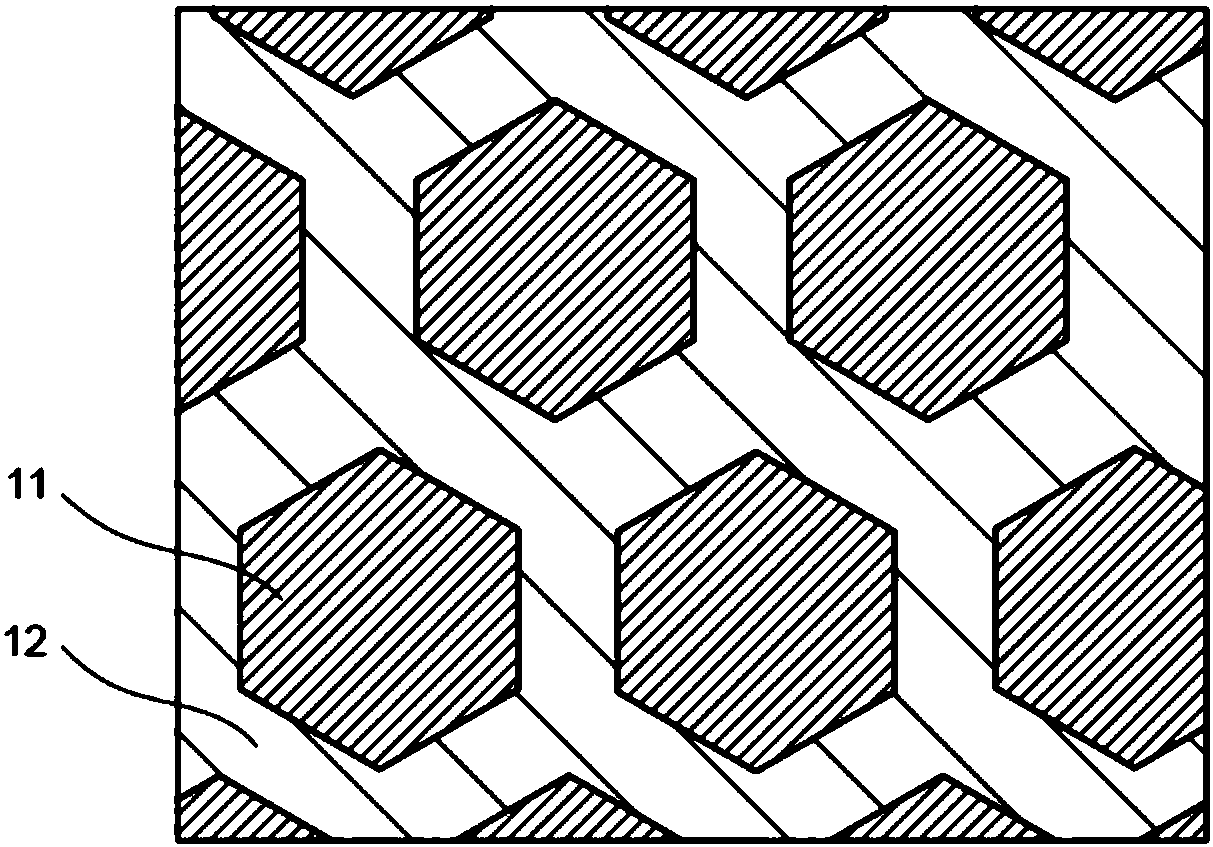
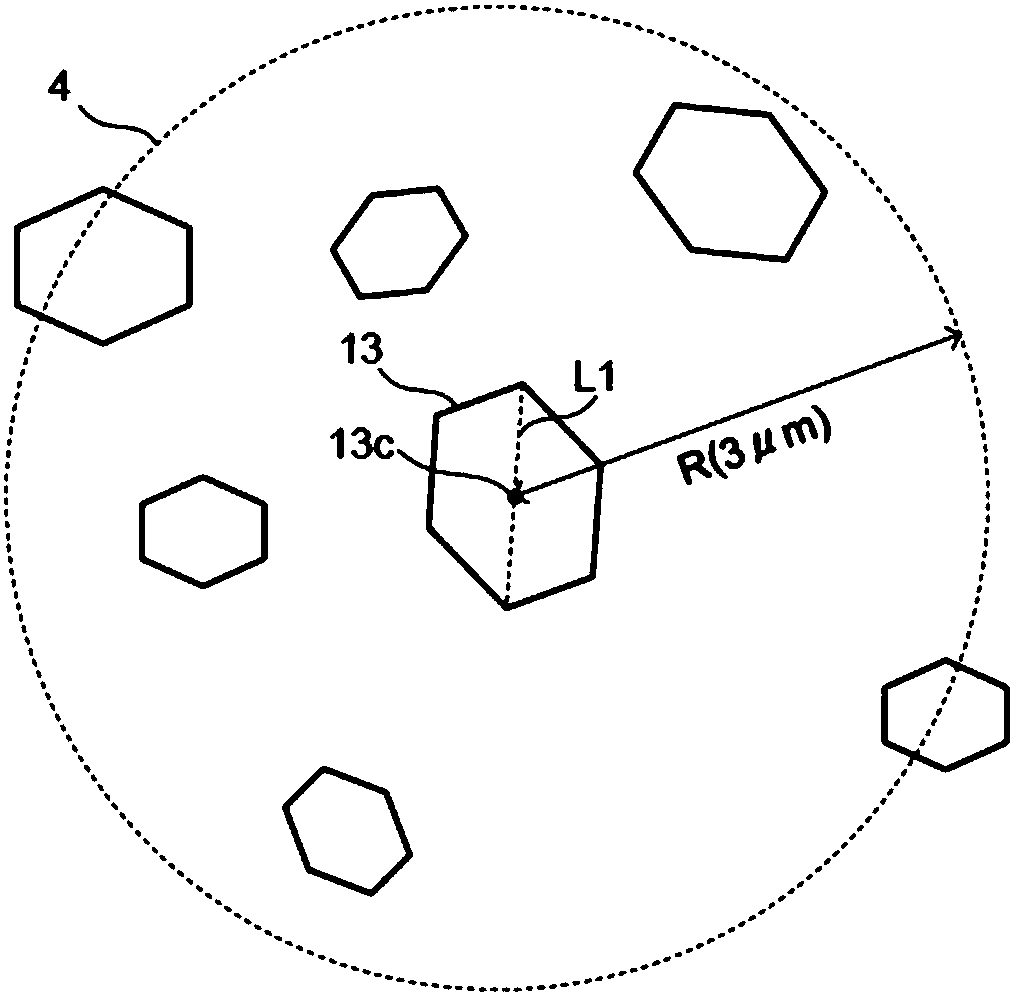
[0036] The permanent magnet of this embodiment has a composition formula: R p Fe q M r Cu t Co 100-p-q-r-t (In the formula, R is more than one rare earth element, M is at least one element selected from Ti, Zr and Hf, p is a number that satisfies 10.8≤p≤11.6 atomic %, and q is a number that satisfies 24≤q≤40 atomic The number of %, r is a number satisfying 0.88≤r≤4.5 at%, and t is a number satisfying 0.88≤t≤13.5at%). The atomic ratio of the above composition formula is the atomic ratio when the sum of R, Fe, M, Cu, and Co is 100 atomic %, and the permanent magnet may contain trace amounts of oxygen and carbon.
[0037] R in the above composition formula is an element that increases the magnetic anisotropy of the magnet material. As an example of the element R, for example, one or more elements selected from rare earth elements including yttrium (Y) can be used. For example, samarium (Sm), cerium (Ce), neodymium (Nd), praseodymium ( Pr) and the like, Sm is particularly preferably...
no. 2 approach
[0103] The permanent magnet of the first embodiment can be used for rotating electric machines such as various motors and generators provided in automobiles and railway vehicles. In addition, it can also be used as a fixed magnet and a variable magnet for variable flux motors and variable flux generators. By using the permanent magnet of the first embodiment, various motors and generators can be constructed. When the permanent magnet of the first embodiment is applied to a variable-flux motor, in the structure and drive system of the variable-flux motor, for example, Japanese Patent Laid-Open 2008-29148 or 2008-43172 can be applied Technology disclosed in.
[0104] Next, a rotating electric machine having the above-mentioned permanent magnets will be described with reference to the drawings. Figure 4 It is a diagram showing an example of an embedded permanent magnet synchronous motor (IPMSM: Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, hereinafter referred to as an IPM motor) i...
Embodiment 1-3
[0119] The raw materials were weighed and mixed according to the composition shown in Table 1, and then arc-melted in an Ar gas atmosphere to form an alloy ingot. The obtained ingot was vacuum-sealed in a quartz tube, and kept at a holding temperature of 1160°C for 20 hours to perform homogenization. Then, coarse pulverization and jet mill pulverization are performed on the alloy to prepare the alloy powder of the magnet. The obtained alloy powder is press-molded while applying a magnetic field to form a compact.
[0120] Next, the powder compact is placed in the sintering furnace so that the vacuum degree in the furnace reaches 3.2×10 -3 After Pa, the temperature was increased to 1165°C, and the temperature was maintained for 40 minutes. Then, Ar gas was introduced into the furnace, the temperature was raised to 1225° C. in an Ar atmosphere at a gas flow rate of 2.0 L / min, and the temperature was maintained at the reached temperature for 6 hours to perform sintering.
[0121] Ne...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coercivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com