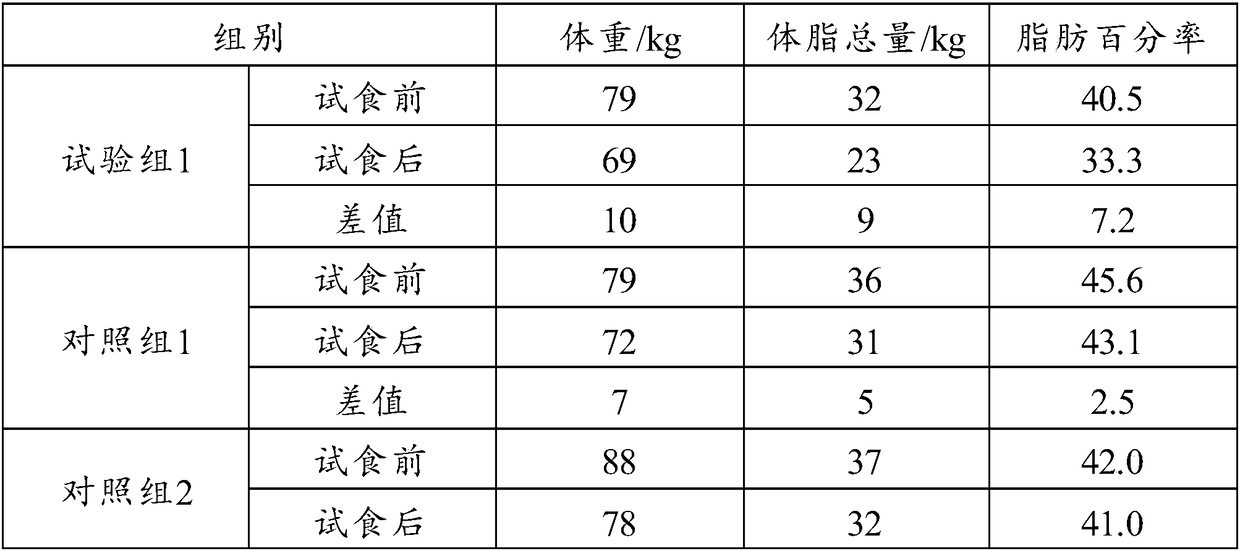
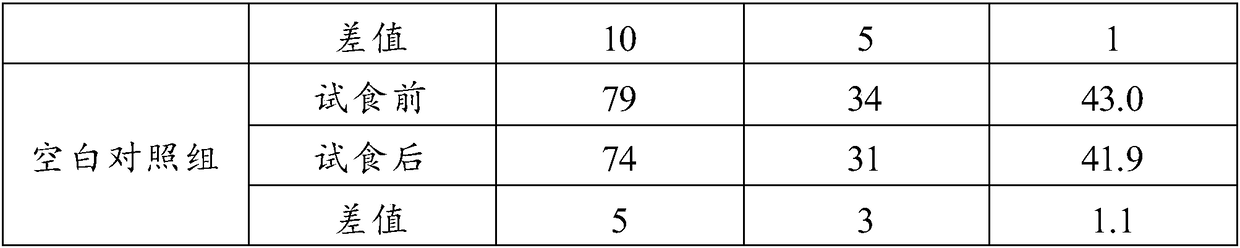
Low-fat high-protein high-fiber food composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composition, high-protein technology, applied in the fields of application, food science, food ingredients, etc., to achieve the effects of simple preparation process, convenient eating and good taste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The preparation of embodiment 1 low-fat high-protein high-fiber food
[0041] Preparation: Lotus leaves are routinely planted in the field. When the lotus leaves are 3 leaf years old, the population of apple snail eggs is artificially sown on the lotus leaves. After about 60 days, the density of apple snail eggs on the lotus leaves reaches 3 nests per square meter, together with the apple snail eggs. Harvest the tender lotus leaves together, and be careful not to shake off the apple snail eggs. When the peanuts were at the third leaf age, artificially sow large and small bridge-building insect populations on the peanut leaves, and harvest when they reached 33 per square meter. Pick and select the young leaves and apple snail eggs of more than 5 branches in the upper part of the lotus leaf plant, and select the intact lotus leaf leaves and apple snail eggs without rot and diseases and insect pests. There are also tender peanut leaves eaten by large and small bridge-buil...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The preparation of embodiment 2 low-fat high-protein high-fiber food
[0050] The raw materials and preparation method are the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that the ratio of each raw material is different from that in Example 1. In this example, the mass ratio of lotus leaf leaves, apple snail eggs, tender peanut leaves, and large and small bridge builders is 40:8 :30:15.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3 Preparation of low-fat, high-protein, high-fiber food
[0052] The raw materials and preparation method are the same as in Example 1. The only difference is that the ratio of each raw material is different from that in Example 1. In this example, the mass ratio of lotus leaf leaves, apple snail eggs, tender peanut leaves, and large and small bridge builders is 60:2 :50:5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com