Gene ZmNL4 for controlling corn leaf width and application thereof
A maize leaf and maize technology, applied in the field of molecular genetics, can solve the problem of not yet clearly controlling the main function gene of maize leaf width and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
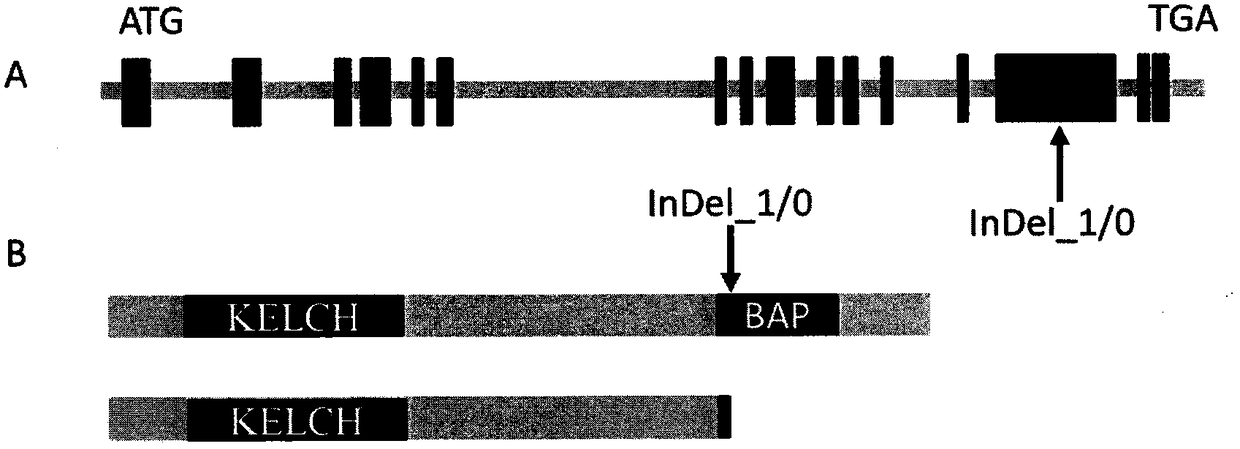
[0060] The structure of embodiment 1ZmNL4 gene and InDel functional site
[0061] The functional gene ZmNL4 controlling maize leaf width, numbered GRMZM2G070553, is located at chr4: 3,464,429-3,471,840, with a total length of 7,412bp and 16 exons. The length of the coding region is 2153bp. Its genetic structure is as figure 1 As shown in A. Exon 14 of the ZmNL4 gene has a molecular marker highly correlated with leaf width phenotypic variation, which is located at the 6,606th base of SEQID NO.1 (ie chr4: 3465235), which is a 1bp indel (InDel_1 / 0)( figure 1 A). Wherein, the sequence of the InDel_0 genotype is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the sequence of the InDel_1 genotype is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. By Sanger sequencing, comparing 70 population materials from different genetic backgrounds, it was found that the leaf width of maize materials with InDel_1 was significantly smaller than that of InDel_0 maize materials (Table 1). The results showed that InDel_1 / 0 located at the 6,606b...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2 Development of Molecular Markers Based on InDel Sites
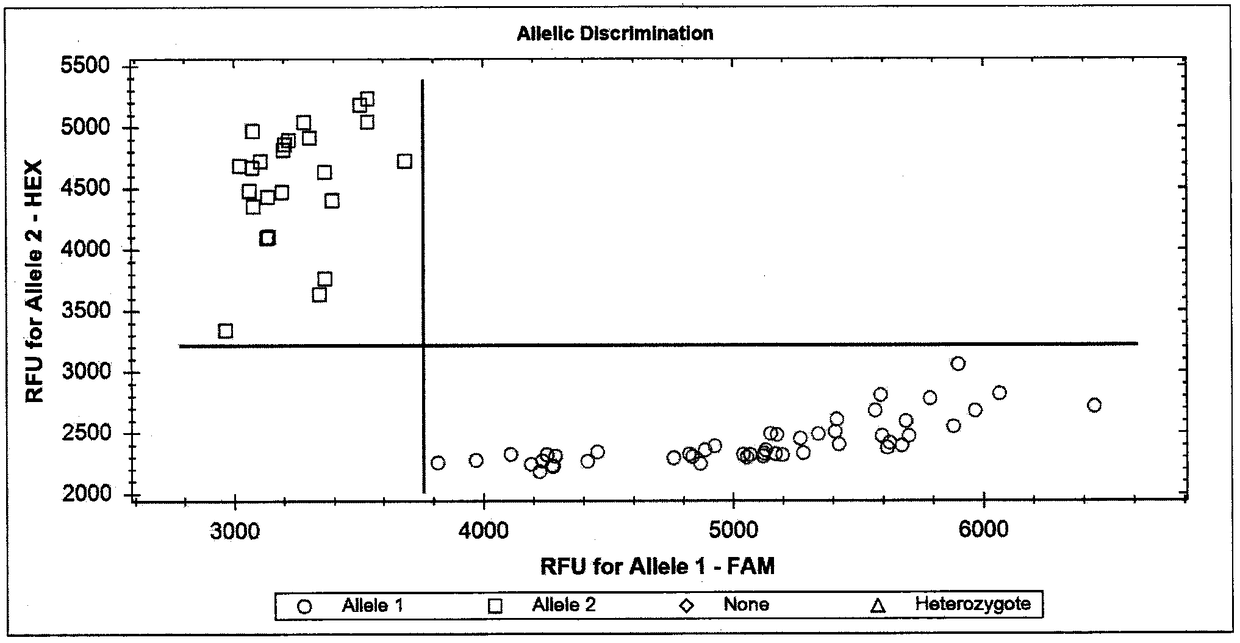
[0066] Competitive allele-specific PCR (KompetitiveAlell Specific PCR) primers, referred to as KASP primers, were designed according to the InDel functional sites described in Example 1. Include the forward primer G0553-K1F (SEQ ID NO.5): gaaggtgaccaagttcatgctGTGGCGCTGGAAGAGCAGCT for detecting the InDel_0 marker site, wherein gaaggtgaccaagttcatgct is the nucleotide sequence of the FAM tag; G0553-K2F (SEQ ID NO.6): gaaggtcggagtcaacggattGTGGCGCTGGAAGAGCAGCG To detect the InDel_1 marker site, wherein gaaggtcggagtcaacggatt is the nucleotide sequence of the HEX tag; reverse primer: G0553-KR (SEQ ID NO.7): GTCGATGACCAGGGACAGGTTC.
[0067] The utility of molecular markers was evaluated by the association analysis between different genotypes and maize leaf width traits.
[0068] 1. Extract the genomic DNA of the corn to be tested. The specific process is as follows:
[0069] (1) Take an appropriate amount of l...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3 ZmNL4 protein structure and identity protein thereof
[0085] Further analysis of the protein sequence encoded by the ZmNL4 gene found that the gene encodes a total of 716 amino acids (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.8), and its protein has two functional domains, namely KELCH-domain and BAP-domain ( figure 1 B). There is an allele InDel_1 genotype with a 1bp deletion, which leads to a frameshift mutation at position 566 and early termination of protein coding, resulting in a truncated protein with only 603 amino acids (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.9). The short protein contains a KELCH-domain and a very small part of the BAP-domain. It can be seen that the deletion of the BAP domain has an important impact on protein function and may lead to variation in leaf phenotypes. Further use of the BLASTP tool in the NCBI database (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) found that the protein encoded by the ZmNL4 gene was expressed in sorghum, millet, millet, palmarosa, Brach...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com