Method of asymmetrically reducing p-propiophenone compound with rice callus
A technology of callus and propiophenone, which is applied in the field of rice callus to change the chirality of drugs, can solve the problems of different catalytic activities of plant cells, expensive synthetic drugs, etc., achieve great economic and ecological significance, and easy to obtain Economical and low-cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
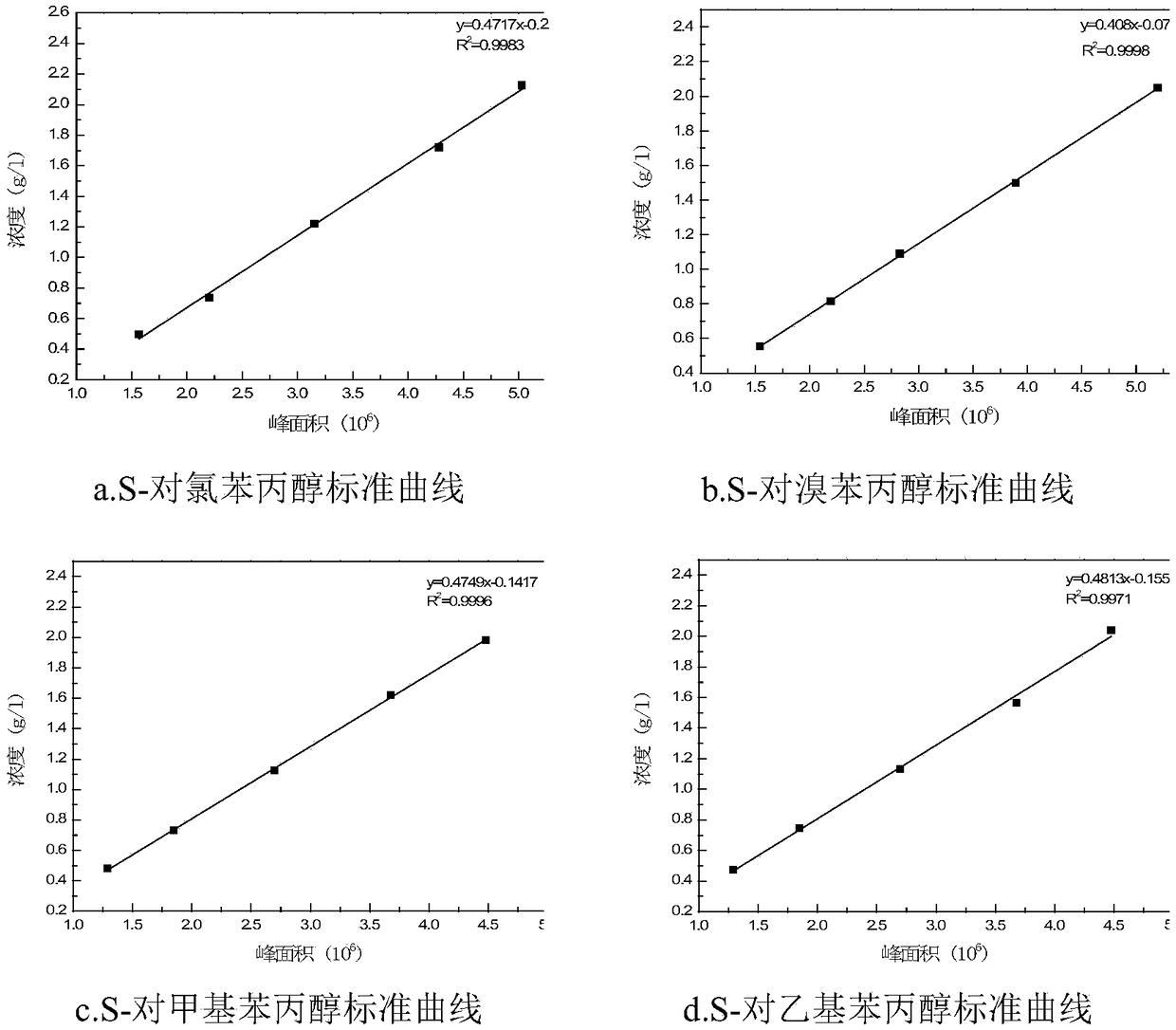
[0054] Embodiment 1: the preparation of standard substance.
[0055] Dissolve 5g of p-chloropropiophenone in 50ml of methanol and add KBH several times 4 The one-pot method was carried out in an ice-water bath, using petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 9:1 as the developing agent to spot the plate, until the reaction was complete, adding an appropriate amount of ice water to remove excess KBH 4 , and then adjust the pH value to neutral with dilute HCl, and extract the product with anhydrous ether about 20ml each time, and extract three times. After adding anhydrous MgSO 4 After drying, filtration and rotary evaporation, the standard substance of p-chlorophenylpropanol was obtained.
[0056] P-bromopropiophenone, p-methylpropiophenone, p-ethylpropiophenone can adopt the same method to obtain the corresponding standard substance. The standard curves for the four substrates are as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Consider the influence of different sampling sites on the yield and ee value.
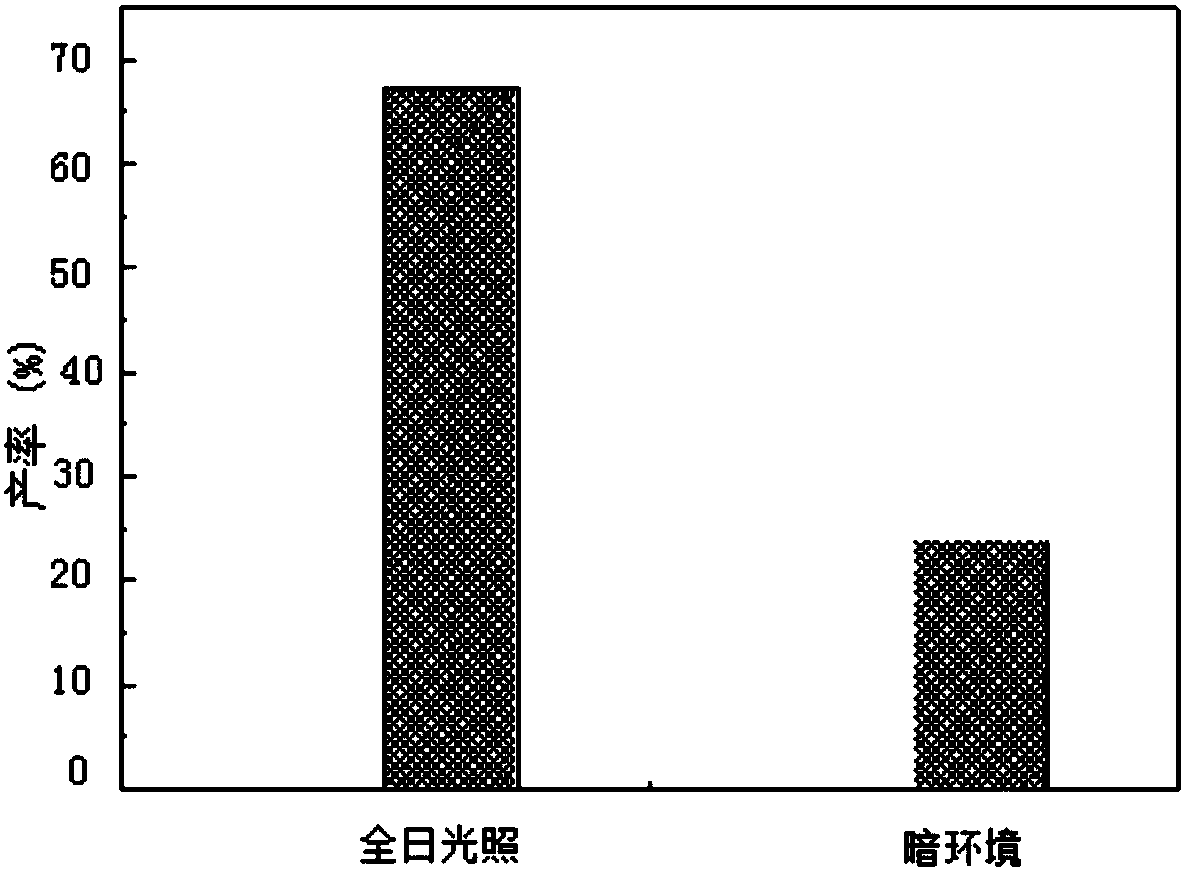
[0058]Rinse the rice seeds with clean water to remove surface stains, soak them in 75% ethanol for 0.5 min, take them out, rinse them twice with sterile water, soak them in 10% NaClO solution for 20 min, take them out, rinse them several times with sterile water, and put Get 5g rice seed (wet weight) and put into the medium of 20mlpH 5.8 (adjust pH with NaOH or Tris) and add 0.5g / l different (p-methylpropiophenone, p-ethylpropiophenone, p-chloropropiophenone, p-bromopropiophenone) reacted for 5 days, centrifuged, extracted, rotary evaporated, constant volume, liquid chromatography detection. In the same way, rooted rice seedlings were taken to investigate the reducing ability of leaves, roots and stems to different substrates.
[0059] The results are shown in Table 2:
[0060] Table 2: Effects of different parts of rice on the reaction
[0061]
[0062] It can be seen from ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: Cultivation of rice callus and asymmetric reduction of substrates.
[0064] 3.1 Culture of rice callus
[0065] The sterilized rice seeds were placed in the AA solid medium, and after being put into an all-weather climate incubator to cultivate for one week, seedlings were formed.
[0066] After the seedlings were taken out, the leaves were cut into small pieces and put into AA, MS, N6 solid medium (3 mg / l NAA) with auxin, and after two weeks of culture, callus cells were generated, and they were transferred to the subsequent culture medium. Substituted medium (half the auxin content) for re-cultivation, ready to use. At the same time, the roots and stems of rice were carried out in the same method as above for callus culture.
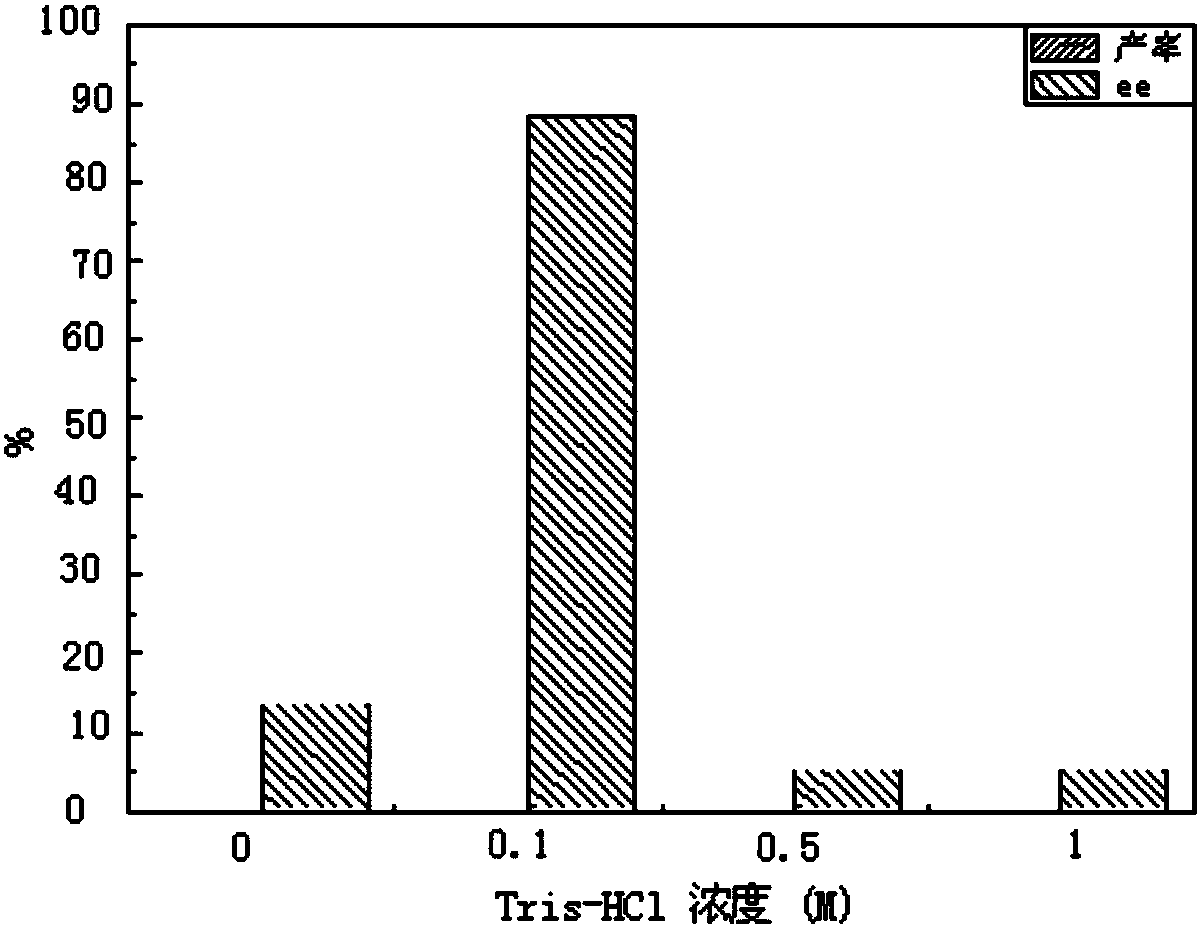
[0067] 3.2 Asymmetric reduction of substrates by calluses from different parts of rice
[0068] Take 2g of rice callus cells from leaves, roots, and stems and add them to 20ml MS liquid medium for shaking for 2 days, then add 10mg ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com