Raman spectroscopy-heavy water isotope labeling based rapid detection method for drug susceptibility of drug-resistant bacteria and judgment method for rational drug use
A technology of isotope labeling and Raman spectroscopy, which is applied in the field of rapid detection of drug-resistant bacteria susceptibility and judgment of rational drug use, can solve the problems of lack of rapid detection technology of drug-resistant bacteria susceptibility, to curb the spread of bacterial resistance, analyze Simple, easy-to-operate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Raman-heavy water isotope labeling method to quickly distinguish antibiotic-resistant and sensitive Escherichia coli
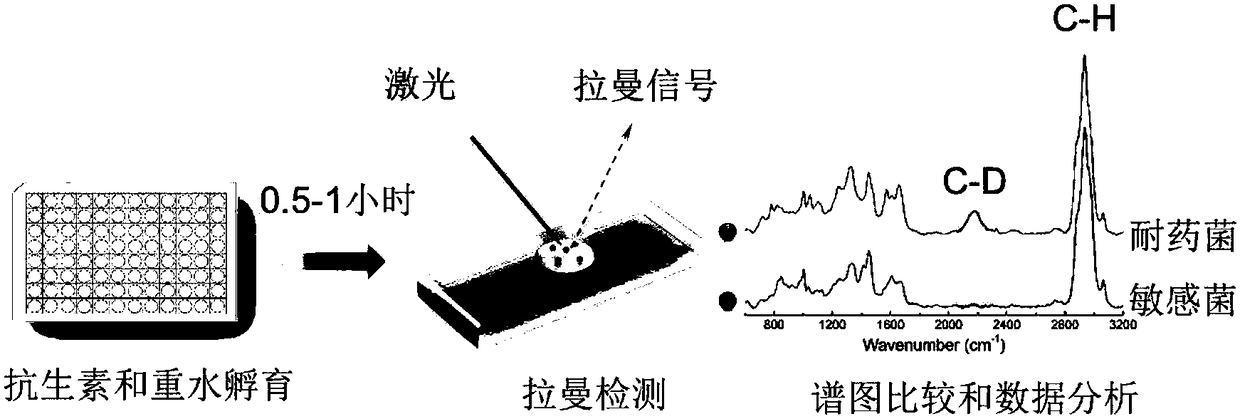
[0044] attached figure 1 The detection process of the Raman-heavy water isotope labeling method is given, including:
[0045] Add 200 μL of 10×~60×MIC antibiotics and 30%-100% (vol / vol) heavy water D in a 96-well plate 2 O (99.9atom% D; Sigma-Aldrich) LB broth, 200 μL without antibiotics but with heavy water D 2 O's LB medium was used as a control. Inoculate 5uL overnight cultured sensitive and drug-resistant bacteria in the culture medium. After incubating for 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2 hours at different times, the bacterial solution was taken out and washed by centrifugation with deionized water or 70% ethanol. The conditions were: 5000 rpm, 3 min each time, twice in total. Drop 2 μL of the cleaned bacterial solution on aluminum foil paper, dry it in the air, and perform Raman detection. Raman detection can be performed at the single-cell ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Raman-heavy water isotope labeling method to quickly detect the drug susceptibility of Escherichia coli to different antibiotics and guide rational drug use
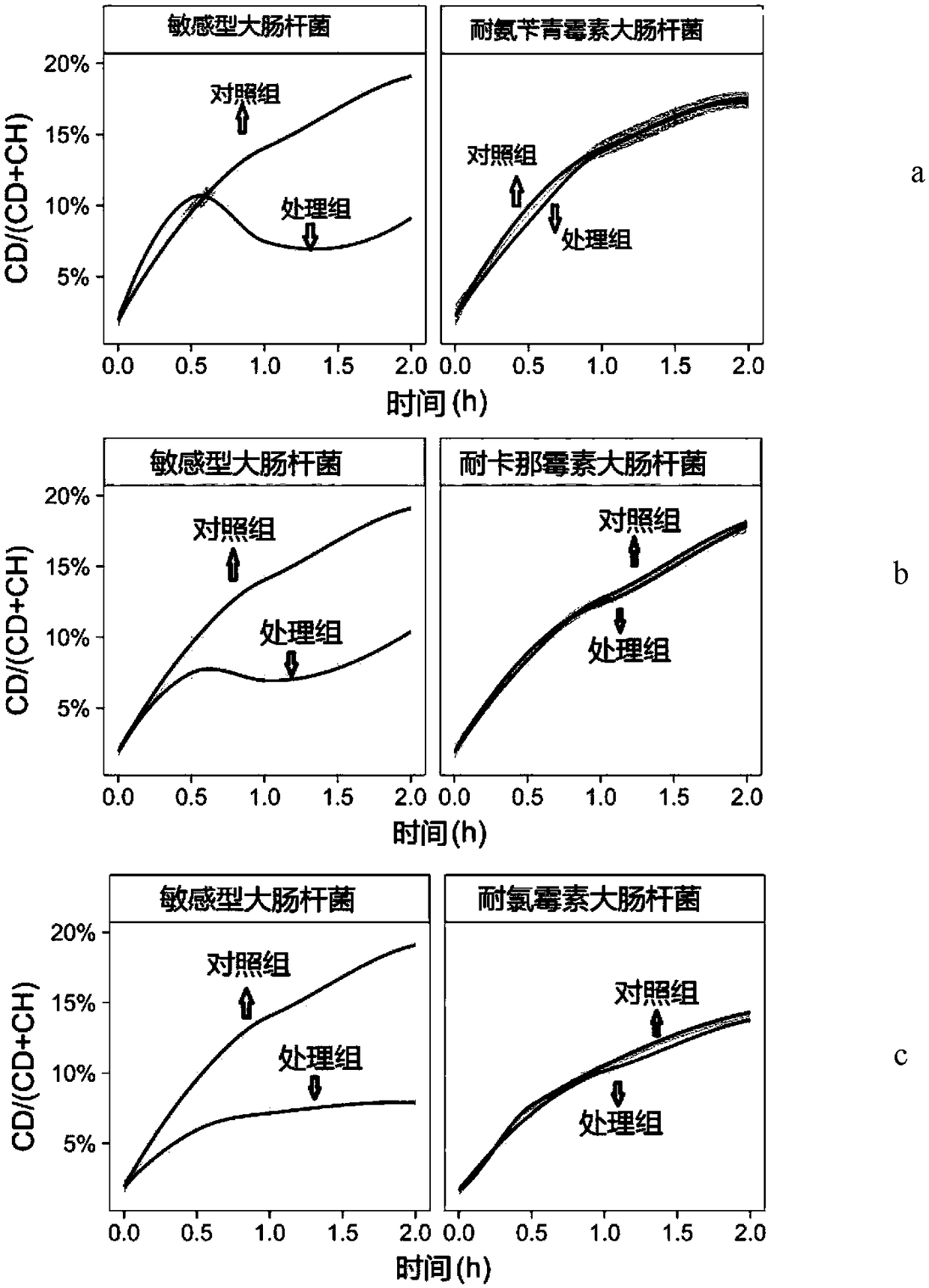
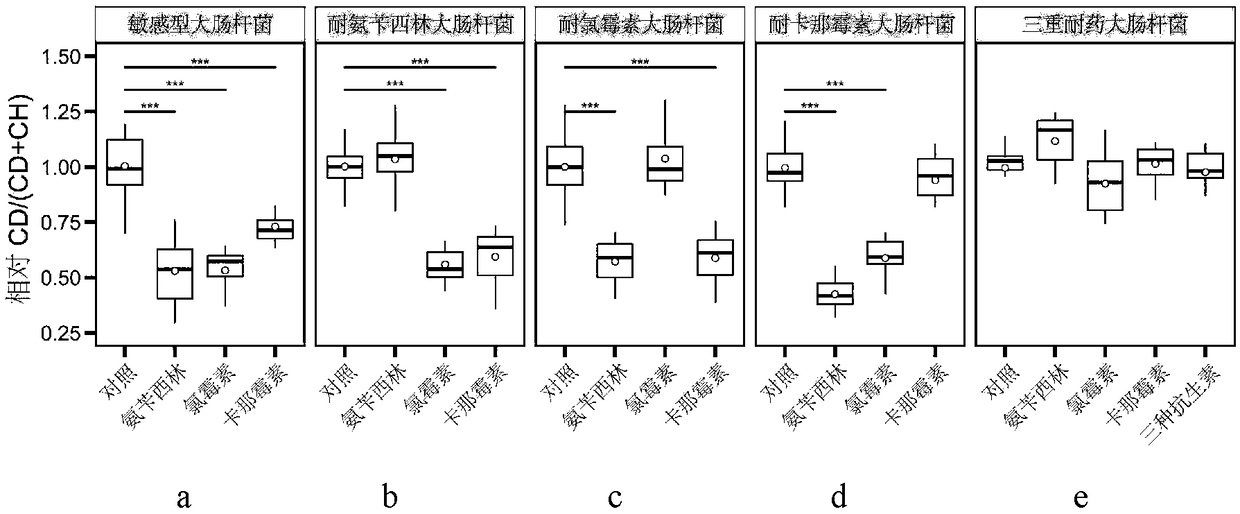
[0048] Here, four different types of drug-resistant E. coli are used as examples, including ampicillin-resistant E. coli Escherichiacoli Amp R , Kanamycin-resistant Escherichia coli Kan R , Chloramphenicol-resistant Escherichiacoli Chl R , and the multidrug-resistant Escherichia coliT that is resistant to all three antibiotics R . The drug susceptibility of the above four bacteria has been tested by using the standard zone of inhibition test. The test results show that the sensitive Escherichia coli DH5α is sensitive to the three antibiotics, and Amp R Resistant to ampicillin, sensitive to kanamycin and chloramphenicol, Chl R Resistant to chloramphenicol, sensitive to ampicillin and kanamycin, Kan R Resistant to kanamycin, sensitive to ampicillin and chloramphenicol, T R Resistant to all three ant...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Rapid detection of drug susceptibility of other pathogenic bacteria to different antibiotics by Raman-heavy water isotope labeling method
[0051] Three other pathogenic bacteria are used here as examples, including Salmonella enterica, Shigella flexneri, and Proteus vulgaris. In order to ensure the effectiveness of antibiotics and the accuracy of the discrimination results, Raman detection was also performed on a strain of quality control bacteria Escherichia coli 25922. Shigella flexneri and Proteus vulgaris were extracted from fresh chicken manure. The experimental procedure is basically the same as in Example 2, except that the incubation time is 1 hour. The results are attached Figure 4 as shown, Figure 4 It is above-mentioned four kinds of bacteria in 100% (vol / vol) heavy water D without antibiotics (control), and ampicillin, chloramphenicol, kanamycin, meropenem containing 10×MIC concentration 2 Relative C-D peak intensity ratio obtained by Raman...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com