Method for authenticating and distinguishing fusarium culture causing soybean root rot
A technology for soybean root rot and Fusarium spp. is applied in the measurement/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., which can solve the problem of high cost of pathogen identification, achieve good application value and reduce costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
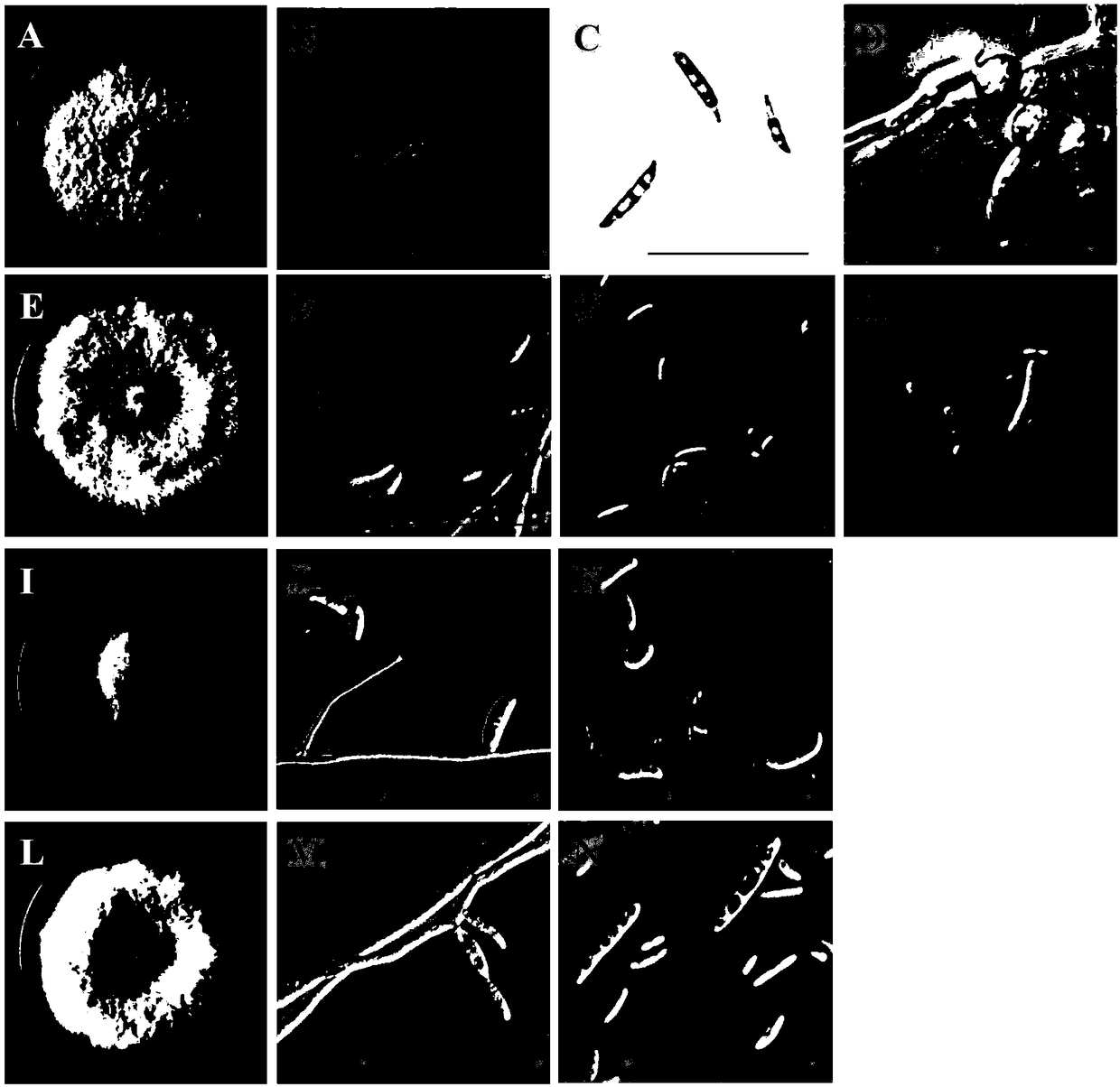
[0042] Embodiment 1: the morphological characteristic of fusarium
[0043] Isolation and purification of pathogenic bacteria
[0044] The wilted diseased plants were collected from the soybean planting field and stored in dry ice for future use. Separation and purification of pathogenic bacteria in the laboratory: rinse the sample with tap water; disinfect with 2% sodium hypochlorite for 10 minutes, rinse with 75% alcohol for 2-3 times, and use sterile water. Rinse several times. Use a sterile knife to cut out the junction of stem disease and health, about 1 cm, inoculate it on a PDA solid medium (containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin) plate, and culture at 25 ° C. After 3 days, with ddH 2 O (containing 100 μ g / mL ampicillin) rinses the colony surface, observes the concentration of the bacterium amount under the electron microscope, and the bacterium amount is diluted to only 3-5 spores in the visual field under the 10-fold microscope, draws an appropriate amount of spore liquid ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2: the molecular identification of Fusarium
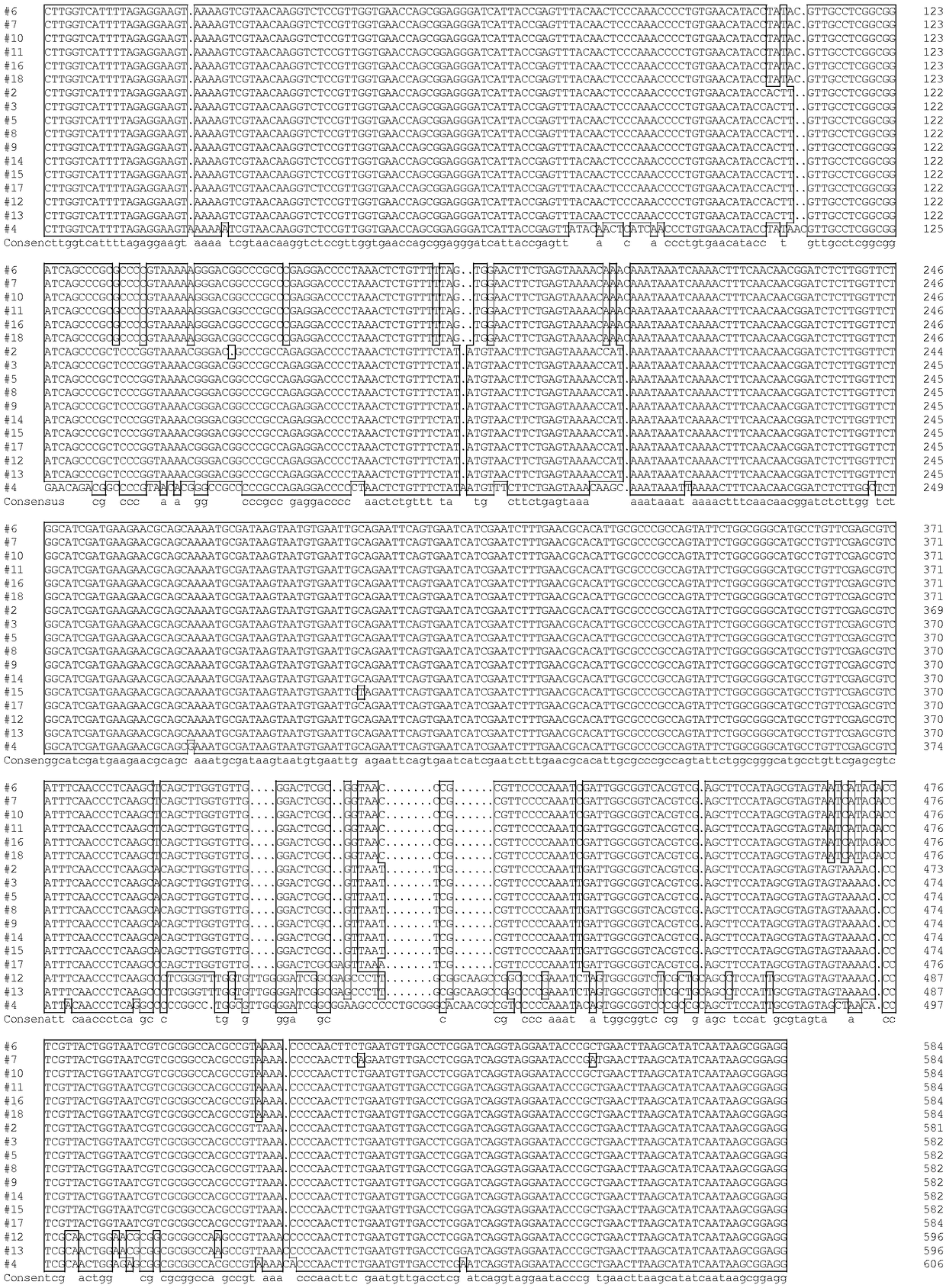
[0052] DNA extraction
[0053] Nearly 1 g of mycelium was suspended in 650 μL of 2×CTAB extract (add 0.2% β-mercaptoethanol before use), then 4 μL of RNase enzyme was added, and ground in a mortar. The ground tissue fluid was incubated in a water bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, and extracted with an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1). Precipitate DNA with two volumes of absolute ethanol, wash with 75% ethanol, ddH 2 O was dissolved and stored at -20°C for later use. DNA quality was detected by spectrophotometer and agarose gel electrophoresis.
[0054] PCR amplification
[0055] Fungal universal primer ITS1F (5'-CTTGGTCATTTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3', Gardes M, Bruns TD. ITSprimers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes—application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 1993, 2, 113-118) and ITS4 (5'-TCCTATCCGCTTATTG -3', White TJ, Bruns TD, Lee SB, TaylorJW. Amplification an...
Embodiment 3
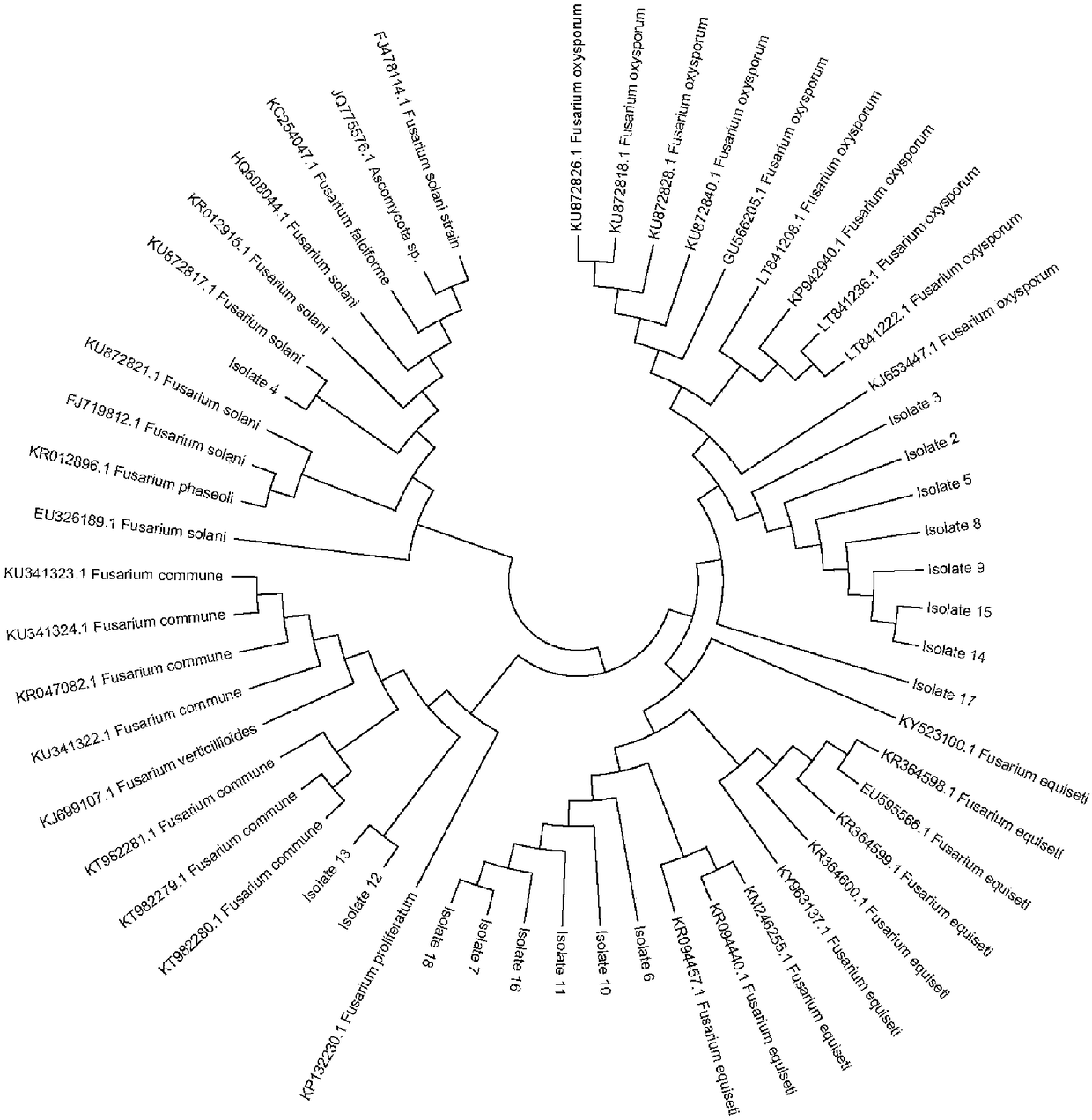
[0060] Embodiment 3: CAPS molecular marker development and strain distinction
[0061] Select one Fusarium from each of the four types of Fusarium, use ITS1F and ITS4 primers, and use DNA as a template to carry out PCR amplification, and the PCR products are separated by electrophoresis on 3% agarose gel. From the results of electrophoresis, it can be seen that the amplified band of Fusarium solanifolia runs significantly slower than that of the other three species of bacteria, while the amplified bands of the other three species of bacteria move at the same speed. spp. can be directly distinguished from the other 3 species of Fusarium ( Figure 4 -A). Then, compare the restriction endonuclease restriction endonuclease site difference of the ITS sequence of other 3 kinds of Fusarium, find 3 kinds of specific restriction endonucleases, BspCNI, AvaI and PstI (New England BioLabs, USA), Develop specific CAPS molecular markers. The ITS PCR amplification products of the four Fus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com