Method for preparing carbon fiber by co-spinning biomass extract and polyacrylonitrile and carbon fiber
A polyacrylonitrile and extractive technology, applied in the chemical characteristics of fibers, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of poor spinnability and high cost, and achieve the effects of developed surface pore structure, high quality carbon fiber, and reduced production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
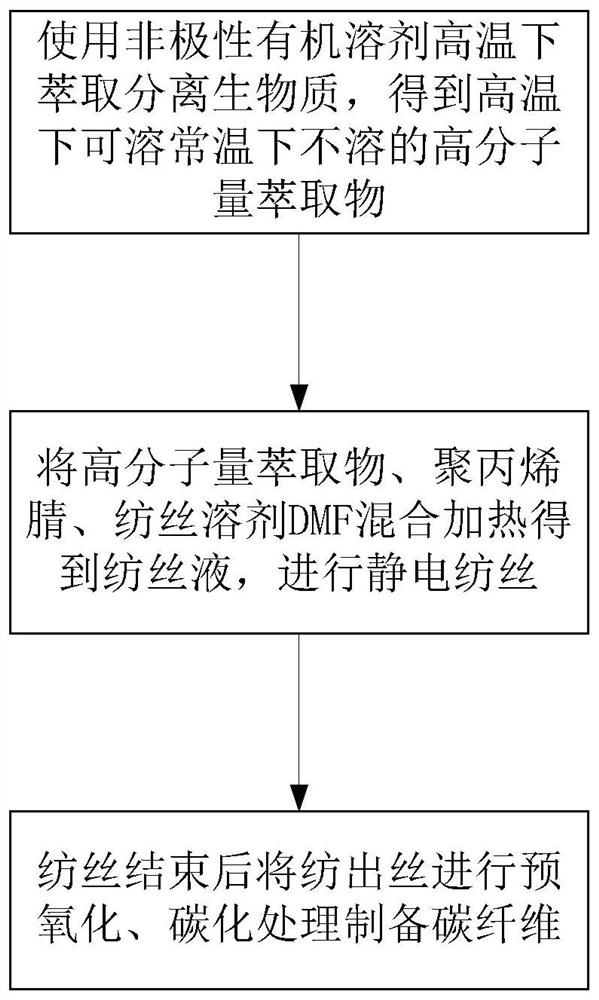
[0040]Using sawdust (pine wood) as raw material, put it and 300ml 1-methylnaphthalene in a reaction kettle to carry out hot-solution extraction experiment at 350°C, the reaction residence time is 60min, Deposit (precipitate) in the obtained high molecular weight extract The carbon content is increased to 75.04%, the aroma is 58.70%, the ash content is 0.40%, and the softening point is 230°C. After the obtained high molecular weight extract and polyacrylonitrile were mixed in equal proportions for electrospinning, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 280°C at a heating rate of 1.0°C / min in the air atmosphere and kept for two hours for pre-oxidation, and then switched The nitrogen atmosphere was heated up to 800°C at a rate of 8°C / min and held for two hours for carbonization treatment to obtain carbon fibers. The surface pore structure of the obtained carbon fibers was developed, mainly micropores aggregated, and the specific surface area reached 714.20m 2 / g, the...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Using sawdust (pine wood) as raw material, put it and 300ml 1-methylnaphthalene in a reaction kettle for hot-solution extraction experiment at 350°C, the reaction residence time is 60min, the carbon content of Deposit in the obtained high molecular weight extract Increased to 75.04%, the aroma is 58.70%, the ash content is 0.40%, and the softening point is 230°C. After the obtained high molecular weight extract and polyacrylonitrile were mixed in equal proportions for electrospinning, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 280°C at a rate of 0.5°C / min in the air atmosphere and kept for two hours for pre-oxidation, and then switched The nitrogen atmosphere is heated up to 1000°C at a rate of 10°C / min and held for two hours for carbonization treatment to obtain carbon fibers. The surface pore structure of the obtained carbon fibers is developed, mainly micropores are aggregated, and the specific surface area reaches 836.82m 2 / g, the specific volume reaches 1...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Using sawdust (pine wood) as raw material, put it and 300ml 1-methylnaphthalene in a reaction kettle to carry out hot-solution extraction experiment at 350°C, the reaction residence time is 30min, and the carbon content in the obtained high molecular weight extract increases To 73.53%, the aroma is 56.90%, the ash content is 0.16%, and the softening point is 210°C. After the obtained high molecular weight extract and polyacrylonitrile were mixed in equal proportions for electrospinning, the temperature was raised from room temperature to 280°C at a heating rate of 2°C / min in an air atmosphere and kept for two hours for pre-oxidation, and then switched In the nitrogen atmosphere, the temperature was raised to 800°C at a rate of 8°C / min and held for two hours for carbonization treatment to obtain carbon fibers. The surface pore structure of the obtained carbon fibers was developed, mainly micropores aggregated, and the specific surface area reached 656.42m 2 / g, the speci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com