Method for preparing magnesium diboride superconducting wire rod by using graphite-like phase carbon nitride in-situ coating boron powder
A graphite phase carbon nitride, in-situ coating technology, applied in the usage of superconducting elements, superconducting devices, superconducting/high-conducting conductors, etc., can solve the problem of uneven distribution of doping sources, and achieve low prices. , The coating layer is thin and uniform, and the effect of increasing the connectivity between grains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
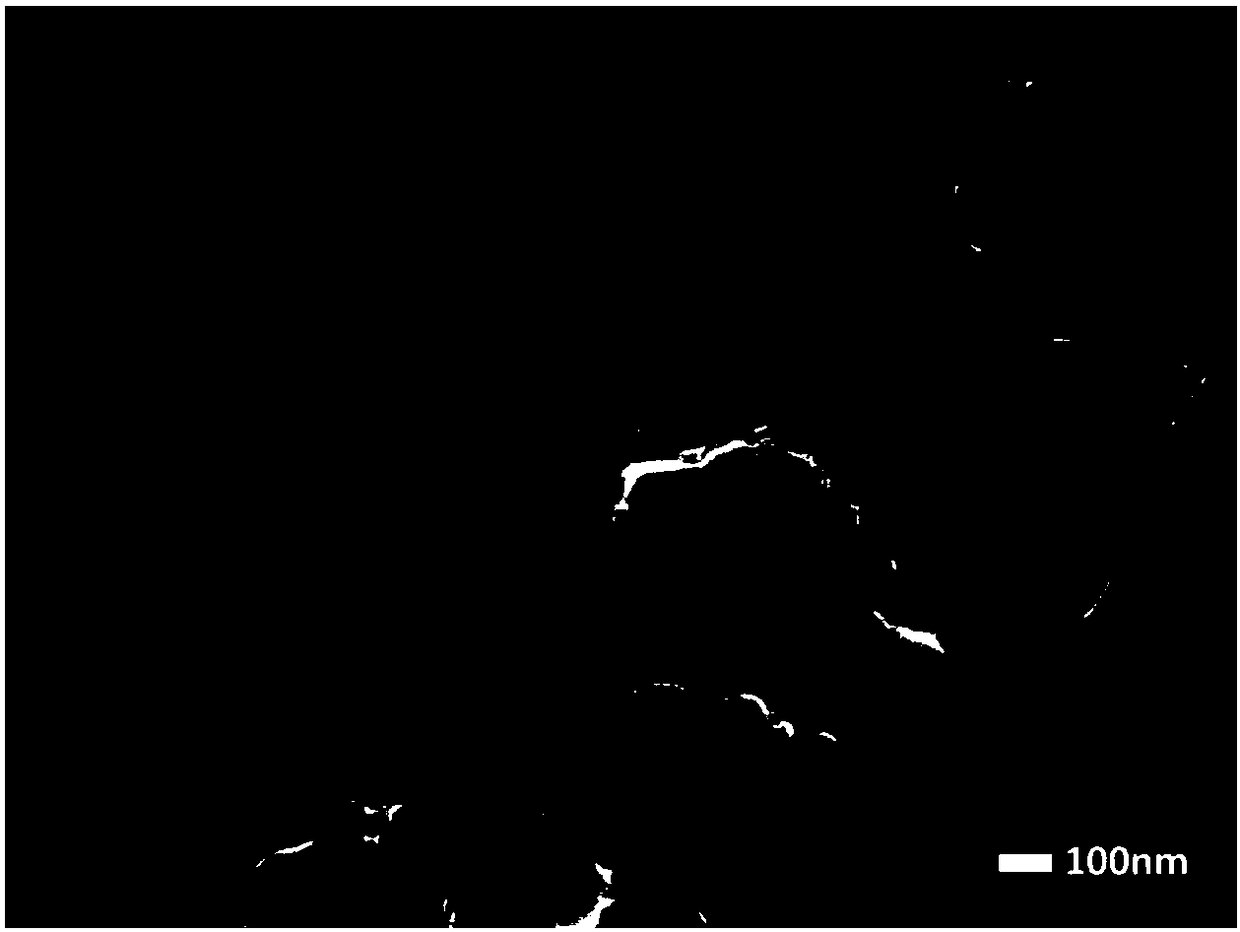
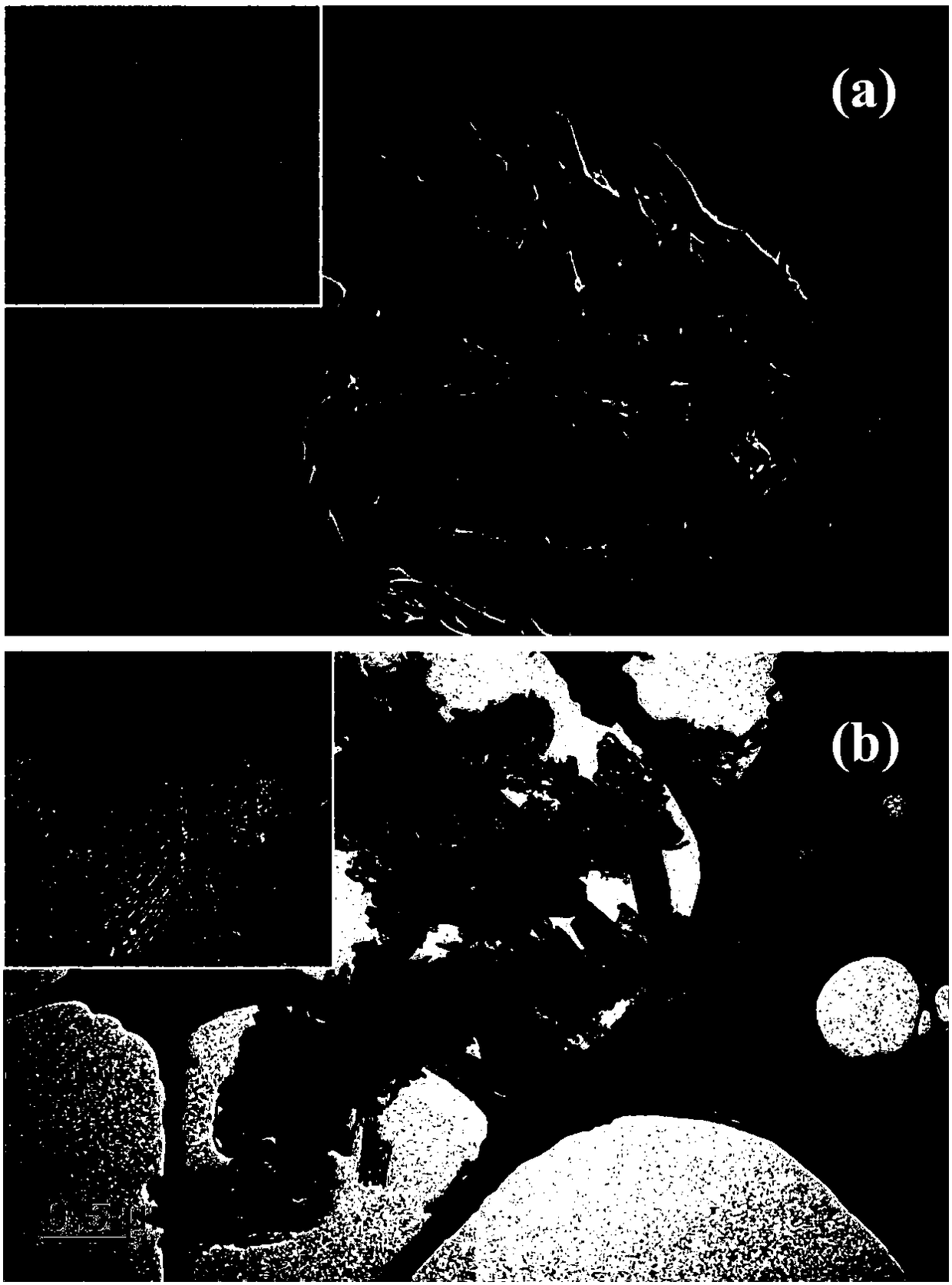
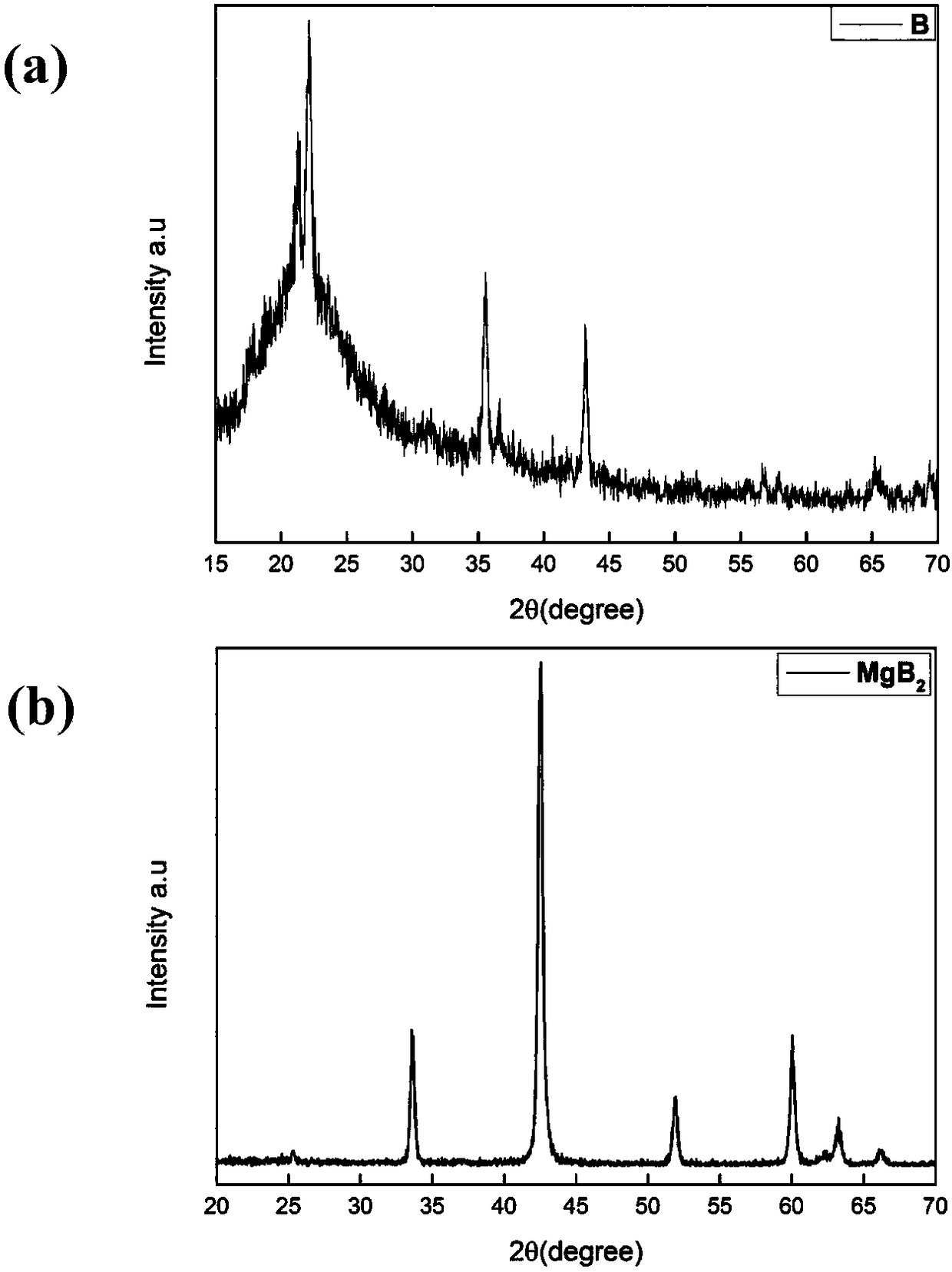
[0029] In this example, see Figure 1~3 , a method for preparing a magnesium diboride superconducting wire by using graphite-like carbon nitride in situ to coat boron powder, comprising the steps of:
[0030] (1) Urea is used as the graphite-like phase carbon nitride precursor material, and the urea and boron powder are ground and mixed for 30 minutes to obtain a mixed powder according to the mass of urea being 1 times the mass of boron powder;
[0031] (2) placing the mixed powder prepared in the step (1) in a crucible, placing the open but not closed crucible into a muffle furnace to be heated evenly, and heat-treating the mixed powder in an air state, and then After cooling down to room temperature in the furnace, uniformly coat graphite-like carbon nitride with controllable thickness on the surface of boron particles in situ to obtain boron powder coated with graphite-like carbon nitride in situ; control the thermal system of heat treatment as follows: heat treatment tempe...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, especially in that:
[0040] In this embodiment, a method for preparing a magnesium diboride superconducting wire by in-situ coating boron powder with graphite-like carbon nitride comprises the following steps:
[0041] (1) Dicyandiamide is used as the graphite-like carbon nitride precursor material, and the mass of dicyandiamide is 3 times that of boron powder, and the dicyandiamide and boron powder are ground and mixed for 40 minutes to obtain a mixed powder ;
[0042] (2) placing the mixed powder prepared in the step (1) in a crucible, putting the open and unclosed crucible into a muffle furnace to be heated evenly, and heat-treating the mixed powder in an air state, and then Cool down to room temperature with the furnace, uniformly coat graphite-like carbon nitride with controllable thickness on the surface of boron particles in situ, and obtain boron powder coated with graphite-like carbon nitride in situ; con...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment is basically the same as the previous embodiment, and the special features are:
[0051] In this embodiment, a method for preparing a magnesium diboride superconducting wire by in-situ coating boron powder with graphite-like carbon nitride comprises the following steps:
[0052] (1) Using melamine as the graphite-like carbon nitride precursor material, according to the mass of melamine being 6 times the mass of boron powder, the melamine and boron powder were ground and mixed for 50 minutes to obtain a mixed powder;
[0053] (2) placing the mixed powder prepared in the step (1) in a crucible, putting the open and unclosed crucible into a muffle furnace to be heated evenly, and heat-treating the mixed powder in an air state, and then Cool down to room temperature with the furnace, uniformly coat graphite-like carbon nitride with controllable thickness on the surface of boron particles in situ, and obtain boron powder coated with graphite-like carbon nitri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| superconducting critical temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com