Preparation method of ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer
A technology of styrene derivatives and copolymers, applied in the field of preparation of ethylene-styrene derivatives copolymers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] A kind of preparation method of ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer provided by the invention, concrete steps are as follows:
[0037] a) under the protection of an inert gas such as nitrogen or argon, dissolving the rare earth catalyst composition in an organic solvent to obtain a rare earth catalyst composition solution;
[0038] b) using ethylene and styrene derivative monomers as raw materials, using the rare earth catalyst composition solution to catalyze the polymerization reaction, sedimenting the product, and drying to obtain an ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer;
[0039] Polymerization The solution polymerization is carried out in the presence of a solvent. The organic solvent is selected from one or a mixture of saturated alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons and cycloalkanes. Preferred is one or a mixture of n-hexane, n-heptane, petroleum ether, cyclohexane, benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, xylene, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenz...
Embodiment 12
[0104] Example 12: Under anhydrous and oxygen-free conditions, the rare earth complex 1 (6.0 mg, 10 μmol) and [Ph 3 C][B(C 6 f 5 ) 4 ] (9.2mg, 10μmol) of toluene solution 5mL, at 70 ° C, was added to 100mL filled with styrene (4.16g, 40mmol) monomer and Ai i Bu 3 (0.4mL×0.5M) in ethylene-saturated toluene (25mL). Then keep the ethylene pressure constant and react for 1 hour, add a small amount of ethanol solution to terminate the polymerization reaction. Then the reaction solution was poured into 100 mL ethanol containing a small amount of hydrochloric acid and stabilizer (BHT) for sedimentation. The obtained polymer was dried in a vacuum oven at 50° C. for 48 hours to obtain a polymer with a net weight of 1.26 g.
Embodiment 1~47
[0105] Examples 1-47: The experimental procedure of this series of examples is the same as that of Example 12, and the polymerization reaction conditions and the change conditions of the catalytic system are described in Table 1 in detail.
[0106] Table 1 Composition of Rare Earth Complex 1 Catalyzes Copolymerization of Ethylene and Styrene
[0107]
[0108]
[0109] Table 2 Different types of rare earth complex composition composition catalyzed copolymerization of ethylene and styrene derivatives
[0110]
[0111] Note: a p-methylstyrene, b p-fluorostyrene; A is [Ph 3 C][B(C 6 f 5 ) 4 ], B is [PhNMe 2 H][B(C 6 f 5 ) 4 ], C is [NEt 3 H][B(C 6 f 5 ) 4 ].
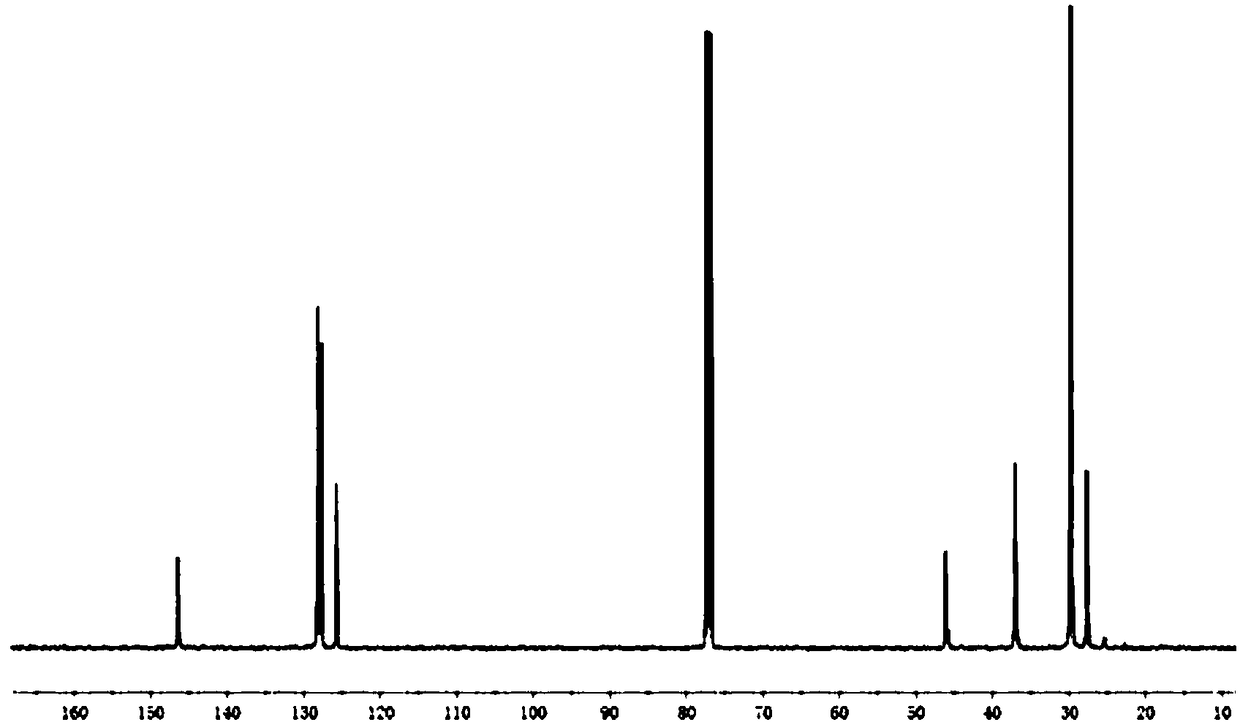
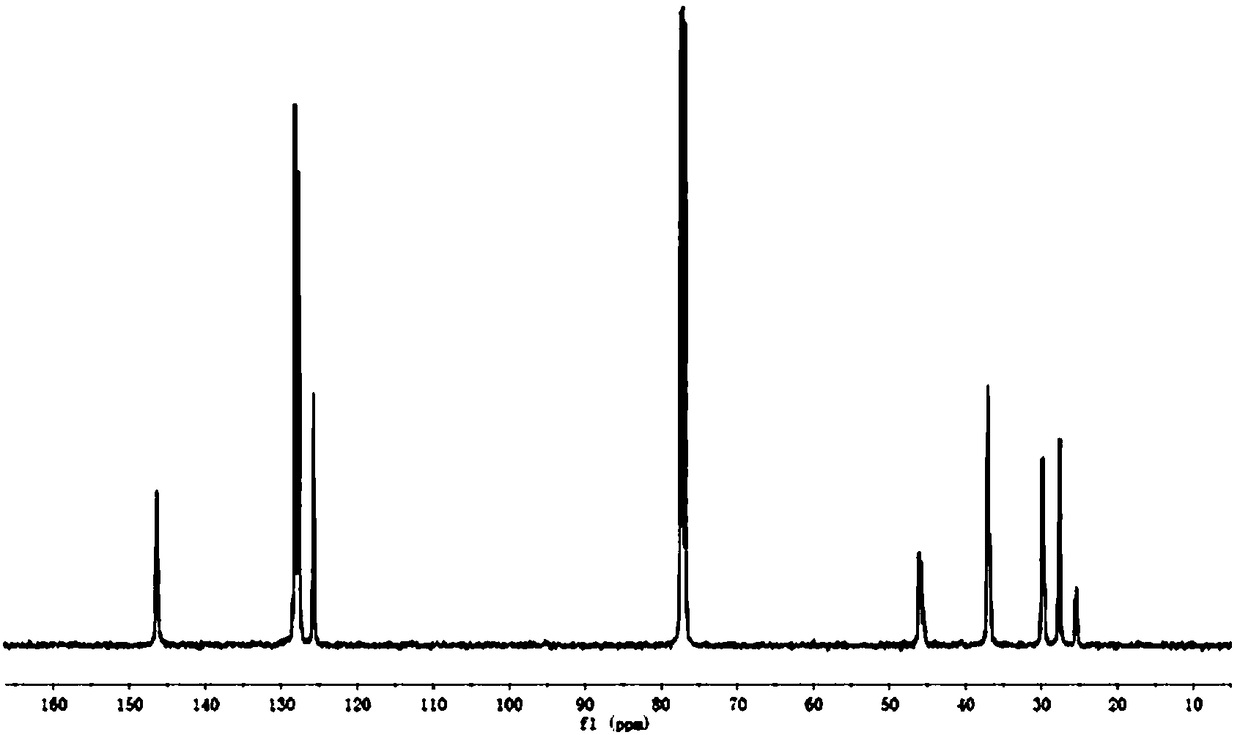
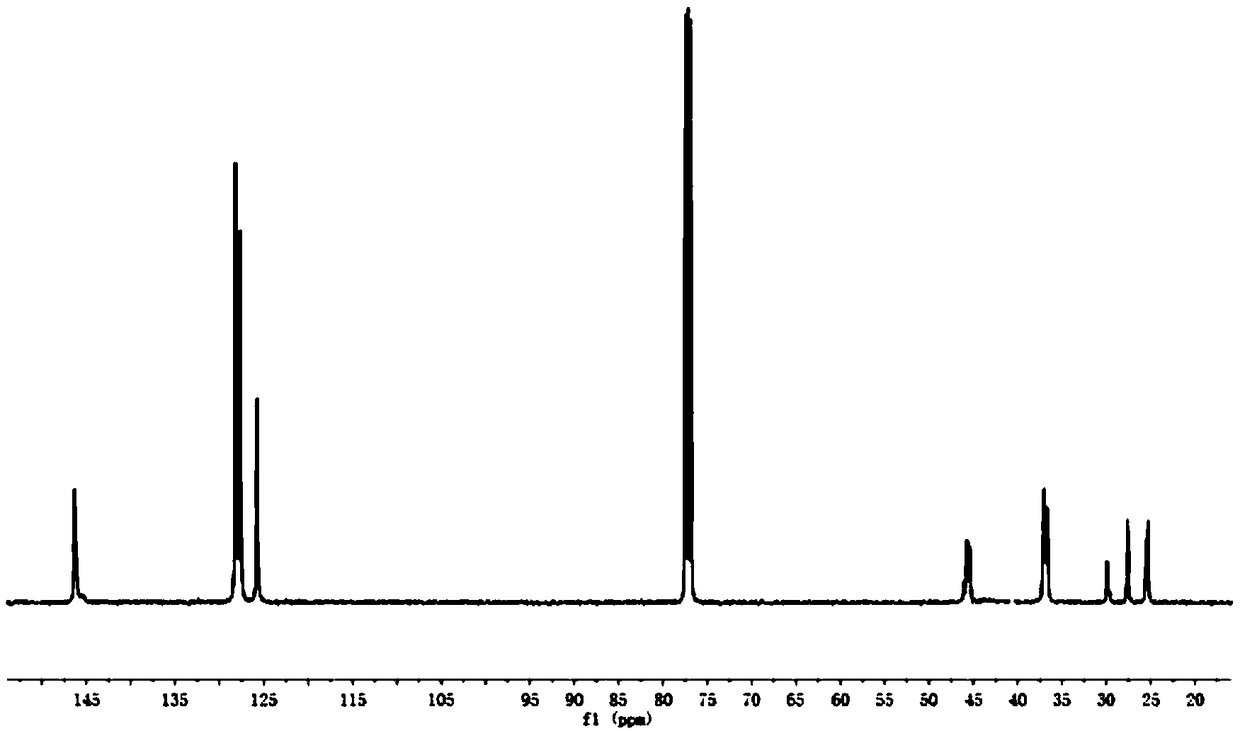
[0112] Carry out carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis to above-mentioned ethylene-styrene derivative copolymer, as Figure 1~3 shown. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the ethylene-styrene copolymer chain microstructure prepared in Example 9 does not contain styrene continuous struct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com