A kind of composite microbial culture and its application in the production of carotenoids
A technology of compounding microorganisms and carotene, applied in the field of microorganisms, to achieve the effect of low raw materials and reducing enterprise costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A composite microbial culture, which includes Bacillus subtilis, Rhodopseudomonas capsulata and Rhodotorula glutinis;
[0035] First crush the rice straw to 2cm, and then put it under the conditions of 1.5MPa pressure and 10min residence time for steam explosion pretreatment;
[0036] Pass the steam-blasted rice straw through a 50-mesh sieve, collect the under-sieve, and mix it with distiller’s grains in a mass ratio of 3:1 to obtain a mixture, then add it to water that accounts for 2 times the weight of the mixture, and heat it to 60°C. Stir at 100 rpm for 90 min, then heat to 121°C, keep for 5 min, and cool to room temperature naturally to obtain a culture solution;
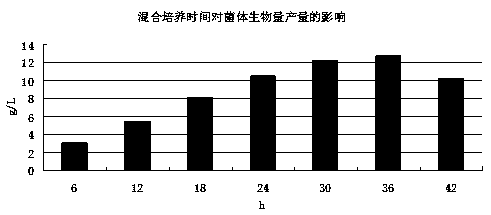
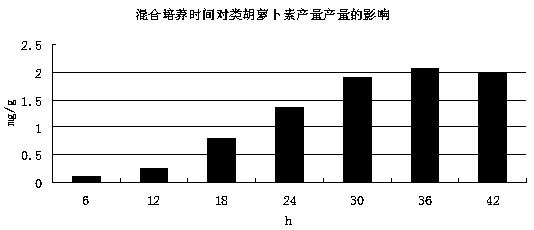
[0037] The Bacillus subtilis seed solution was cultured in a photosynthetic culture fermenter containing the culture solution at an inoculum of 7% (volume ratio). The temperature was 30°C, the dissolved oxygen concentration was 1 mg / L, the light intensity was 2000 lux, and the culture time For 36h, then inocul...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A composite microbial culture, which includes Bacillus subtilis, Rhodopseudomonas capsulata and Rhodotorula glutinis;
[0043] First crush the rice straw to 5cm, and then put it under the conditions of pressure 1.8MPa and residence time of 5min for steam explosion pretreatment;
[0044] Pass the steam-blasted rice straw through a 50-mesh sieve, collect the under-sieve, and then mix it with distiller’s grains in a mass ratio of 3:1 to obtain a mixture, then add it to water that accounts for 3 times the weight of the mixture, and heat to 70°C. Stir at 100 rpm for 80 minutes, then heat to 121°C, keep for 4 minutes, and naturally cool to room temperature to obtain a culture solution;
[0045] The Bacillus subtilis seed solution was cultured in a photosynthetic culture fermenter containing the culture solution at an inoculum of 6% (volume ratio), the temperature was 30℃, the dissolved oxygen concentration was 2mg / L, the light intensity was 3000lux, and the culture time For 24h, th...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The changes of main components of rice straw by blasting are shown in Table 1:
[0051] Table 1
[0052] index Before blasting After blasting Hemicellulose and cellulose%53.740.5 Lignin%27.922.1 Xylooligosaccharides%03.4
[0053] Conclusion: Blasting damages the cell wall of the straw, and part of the hemicellulose and cellulose are degraded and dissolved out, which is conducive to the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose by cellulase; the cellulose crystallinity and degree of polymerization decrease during the pre-blasting process, and the hemicellulose passes through Autohydrolysis degrades into monosaccharides and oligosaccharides, which can be used as a carbon source for strains.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com