Genetically engineered bacterium for production of beta-ionone and construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and ionone, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of less bio-heterogeneous synthesis of β-ionone, and achieve good industrial application prospects , good application prospects, and the effect of shortening the construction cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1 experimental scheme and primer design
[0049] The experimental scheme design of this embodiment is as follows:
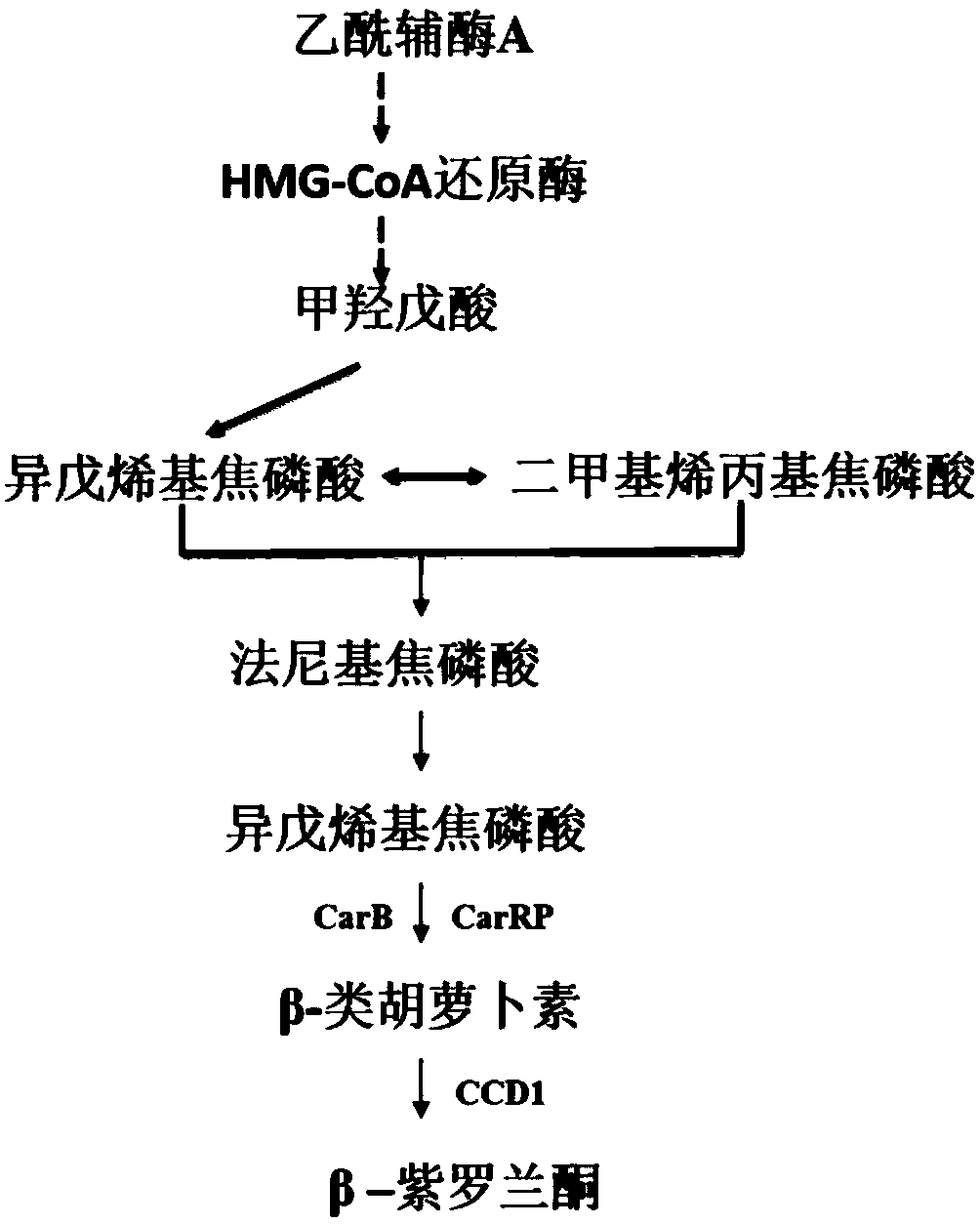
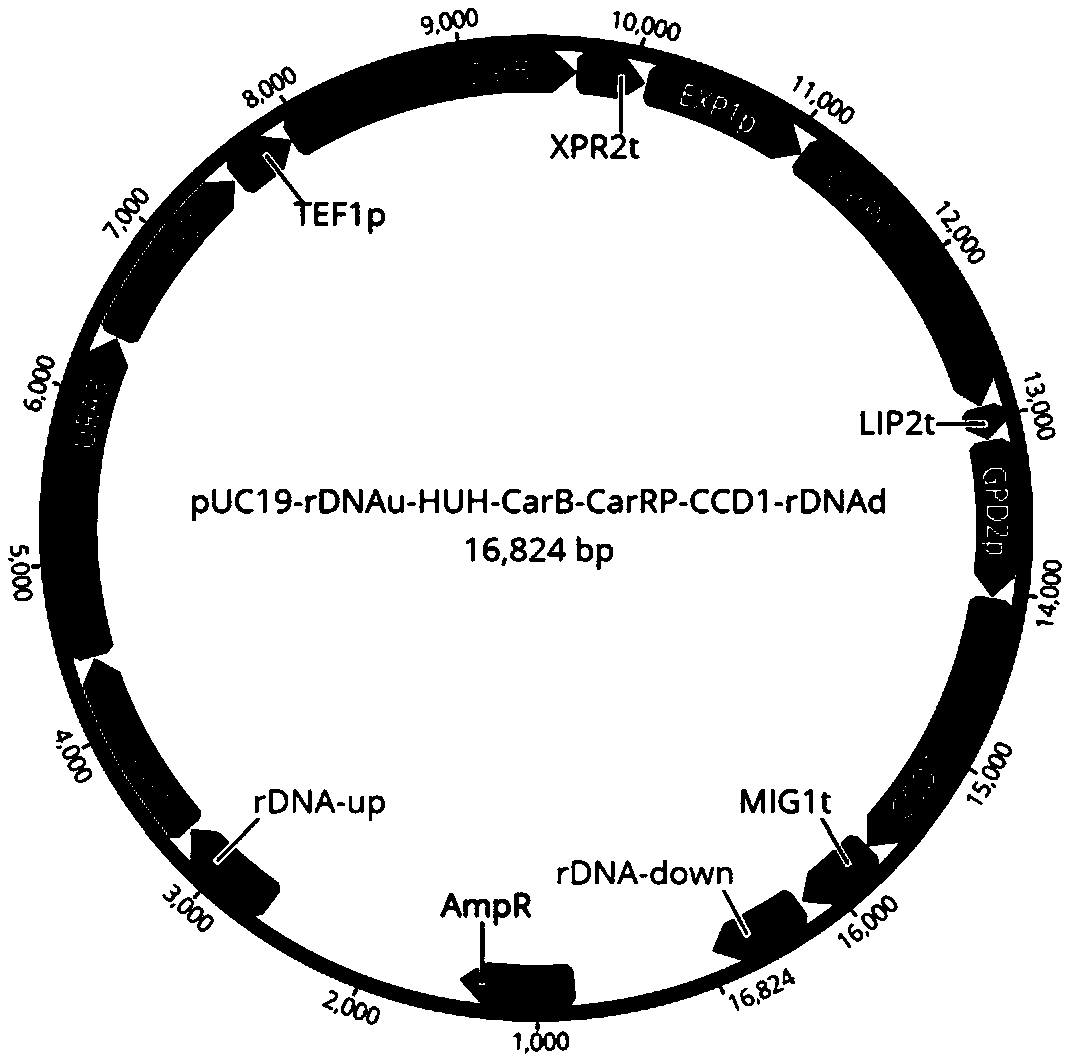
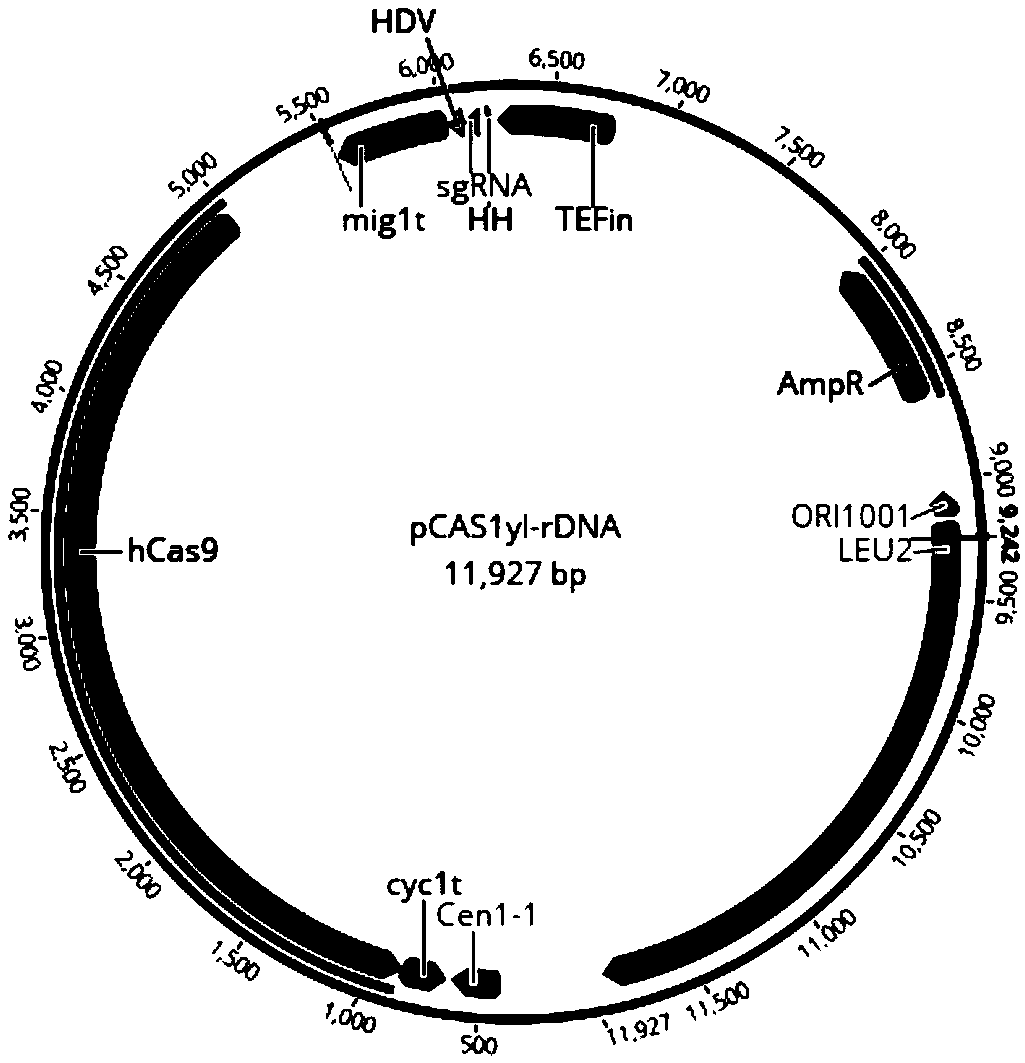
[0050] In Yarrowia lipolytica po1f (purchased from YEASTERN BIOTECH company, strain information: MatA, leu2-270, ura3-302, xpr2-322, axp1-2, Leu - , Ura - ΔAEP, ΔAXP, Suc + ) to express CarB and CarRP from Mucor circinosa and CCD1 gene from Petunia to construct the synthesis pathway of β-ionone, and at the same time use the Ura3 gene as a screening marker to select the yeast chromosome rDNA site as the integration site , the assembly sequence of each gene module is as follows figure 2 shown. The CRISPR / cas9 operation vector, using pCAS1yl (ADDGENE No. 73226) as the starting vector, was constructed as image 3 shown.
[0051] The following gene expression modules and CRISPR / cas9 operation vectors were constructed using the method of gibson assembly:
[0052] rDNAup-hisG-Ura3-hisG, TEF1p-CarB-XPR2t, EXP1p-CarRP-LIP2t, GPD2p-CCD1-MIG1t-rDNA...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The construction of embodiment 2 genetically engineered bacteria
[0057] 2.1 Acquisition of β-ionone gene:
[0058] The genes were selected from CarB, CarRP from Mucor volvulus and CCD1 from Petunia. After codon optimization, they were synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.; using the primers in the sequence list, they were respectively amplified and obtained CarB, CarRP, CCD1 gene fragments.
[0059] 2.2 Extraction of yeast genomic DNA
[0060] The extraction method of the Yarrowia lipolytica po1f genome is as follows: Pick a single clone colony from a freshly recovered plate and inoculate it in a 5mL YPD liquid medium test tube, culture it at 28°C and 250rpm for 24 hours, collect 1mL of the bacterial liquid, and use the yeast genome to extract Kit (purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) to extract the genome.
[0061] The extraction method of the plasmid is as follows: inoculate the DH5α bacteria containing the corres...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Fermentation of embodiment 3 genetically engineered bacteria and the detection of β-ionone
[0078] 3.1 Fermentation
[0079] Seed liquid cultivation method is as follows:
[0080] The single colonies of the positive clones screened from the culture plate Tianqu Example 2 were connected to 10mL YPD culture solution (50mL centrifuge tube), cultivated to OD at 28°C and 250rpm 600 2 to 3.
[0081] The fermentation culture methods at different temperatures are as follows:
[0082] Inoculate the seed liquid into 20mL YPD medium (50mL shake flask), initial OD 600 The value is 0.1, the organic phase is n-dodecane (10% V / V), placed in shakers at different temperatures (15-30° C.) at 250 rpm, and cultivated for 12 days.
[0083] The fermentation and cultivation methods of different carbon sources are as follows:
[0084] Inoculate the seed liquid into 20mL YP medium (50mL shake flask) containing various carbon sources (20g / L), initial OD 600 The value is 0.1, the organic p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com