Preparation method of high-throughput airway inflammatory drug screening cell model based on NF-kappaB signaling pathway, and application of cell model
A technology of airway inflammation and cell model, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low efficiency, error, cumbersome and time-consuming detection steps, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
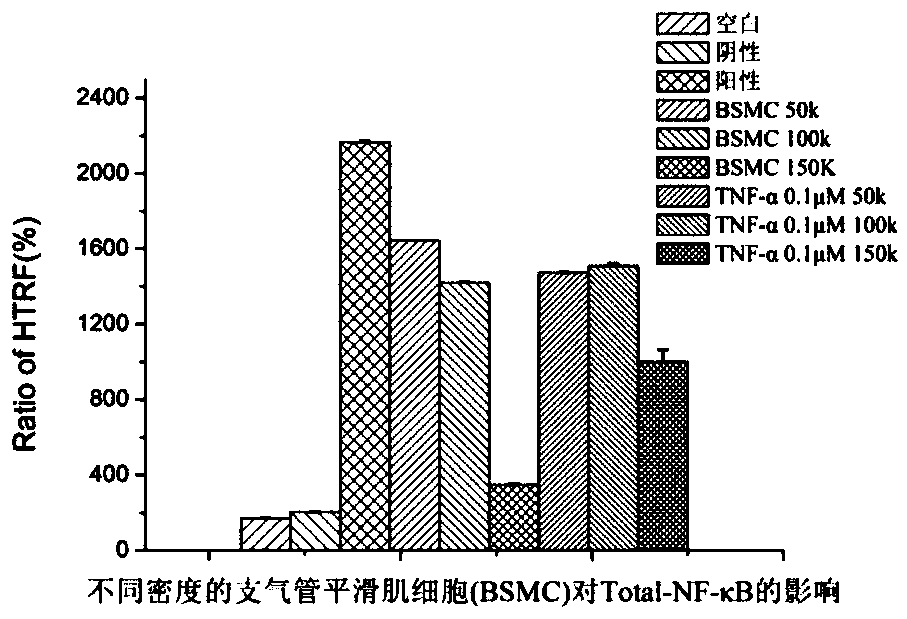
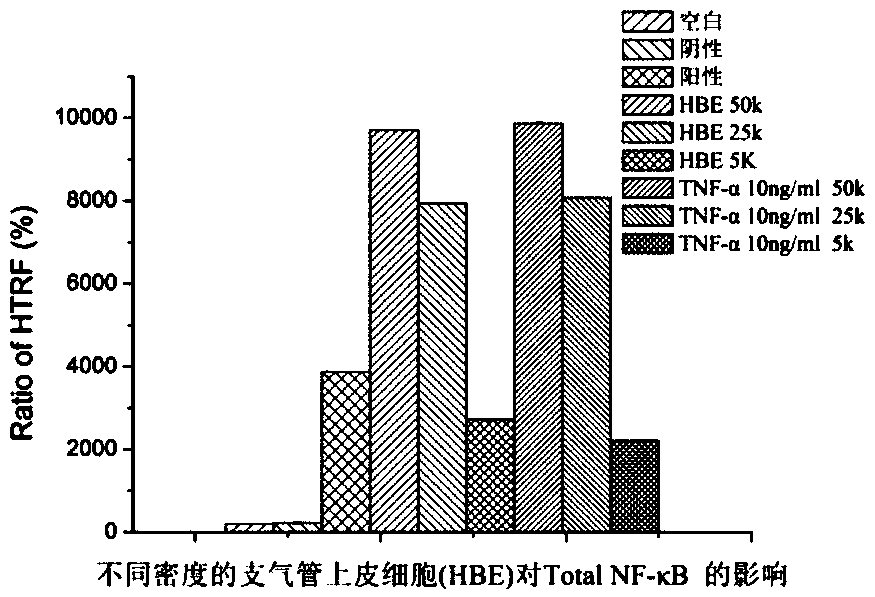
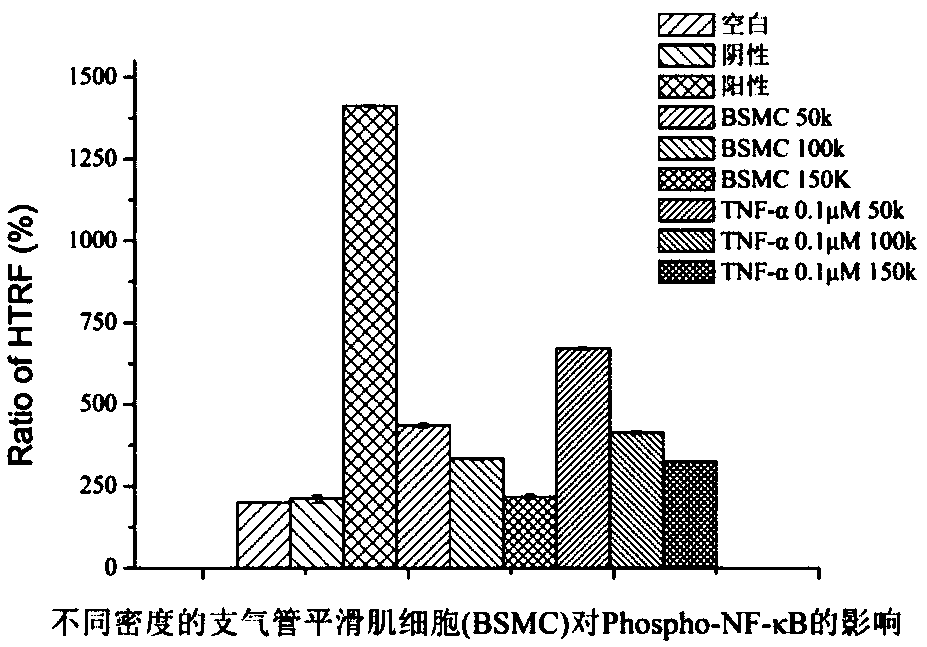
[0041] 1. Materials, reagent preparation, cell culture and HTRF assay method
[0042] 1.1 Reagents: NF-κB detection kit (Cisbio company, batch number 10-009-13); TNF-α (Peprotech company, batch number 101373); LPS (sigma company, batch number: 017M4112V); DMEM / F12 complete medium (containing FBS, bFGF, Insulin, Hydrocortisone, Penicillin, Streptomycin, produced by Qishi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number 20150920); 0.25% Trypsin (containing 0.02% EDTA, Gino Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd., batch number 17052901); fetal bovine serum (Zhejiang Tianhang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number 20171011); PBS (Jinuo Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd., batch number 17092406); dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was of analytical grade, provided by Hewlett-Packard Chemical Instrument Co., Ltd.
[0043] 1.2 Cell lines: human bronchial epithelial cells (Human bronchial epithelial cells, HBE), rat primary bronchial smooth muscle cells (Bronchial smooth muscle cells, BSMC), purchased from Qishi Biot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com