Method for efficiently removing heavy metal pollutants on basis of fluorinated zero-valent iron
A technology of zero-valent iron and heavy metals, which is applied in the application field of preparation and removal of pollutants, can solve the problems of inability to improve the electronic selectivity of zero-valent iron, complex operation, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation and low requirements for equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
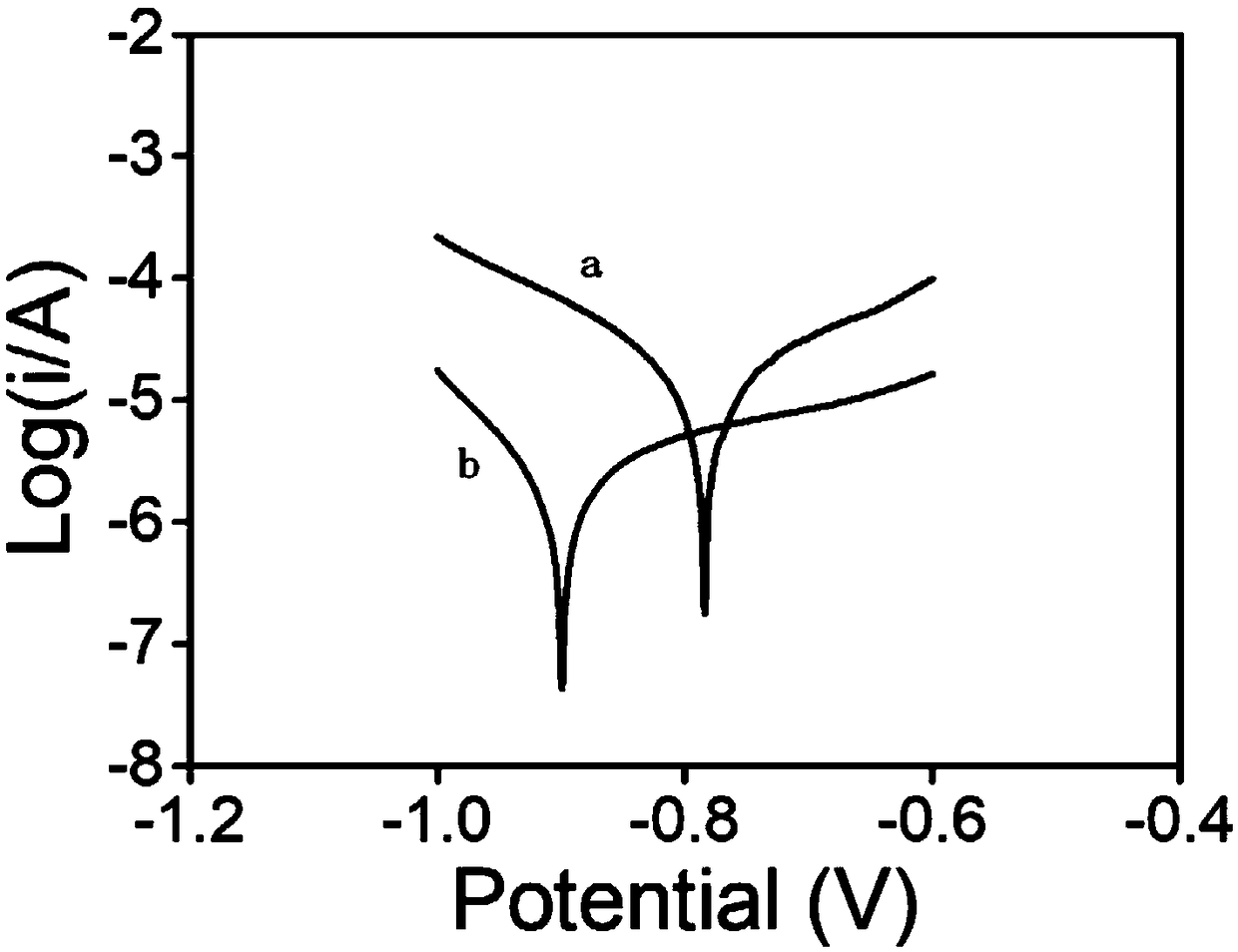
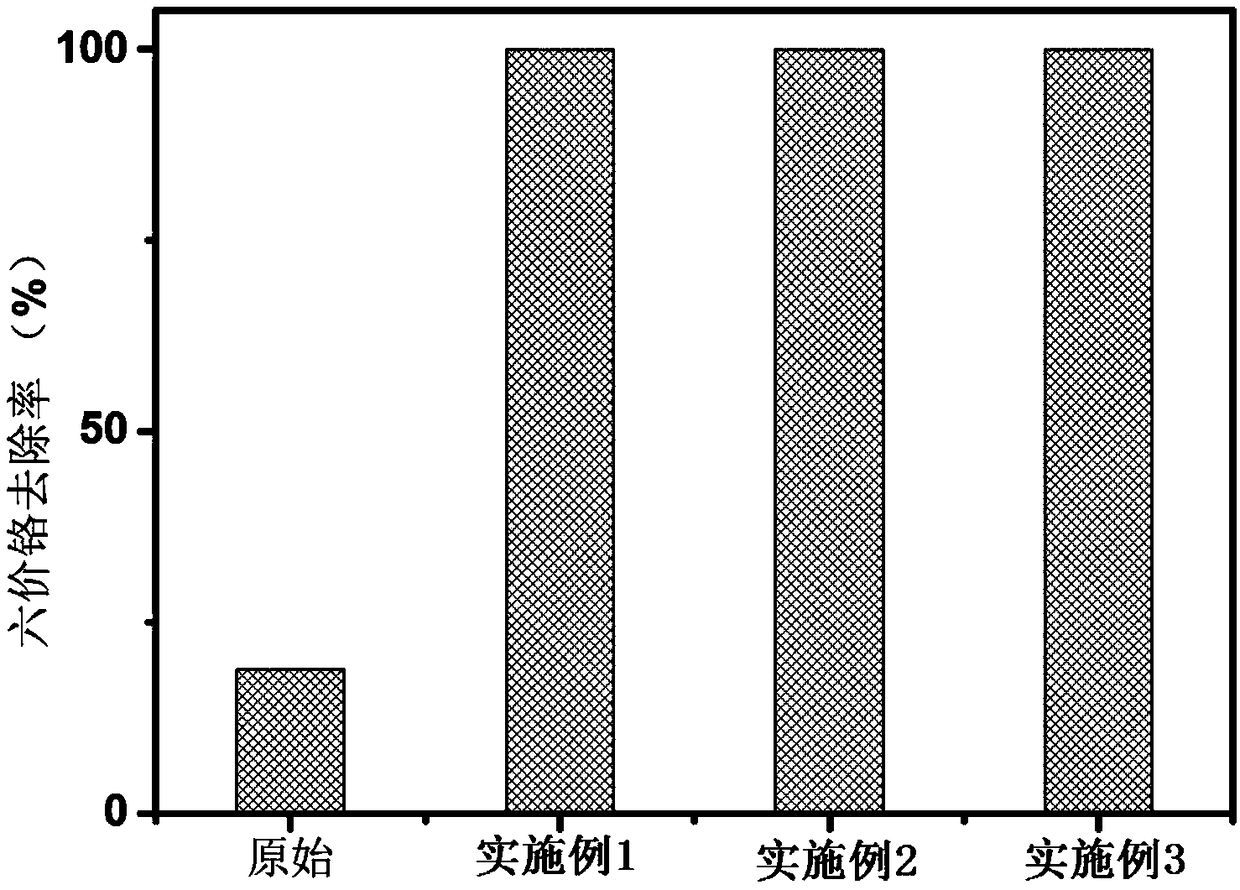
[0020] Example 1. First prepare 50mL of 0.01M sodium fluoride solution in a 100mL beaker, add 0.005M sodium petroleum sulfonate solution, and add 0.56g of zero-valent iron. React at 25°C for 60min, then wash with deionized water and ethanol three times respectively, filter the sample, and dry it in a vacuum oven at 25°C for 18h; L, the dosage of zero-valent iron fluoride is 2g / L, after 90 minutes of reaction, the removal rate of chromium reaches 99%, the electron selectivity of the original zero-valent iron is about 2.3%, and the electron selectivity after modification is as high as 23%. , the removal rate of chromium is still as high as 95% after 5 cycles.
example 2
[0021] Example 2. First prepare 50mL of 1M hydrofluoric acid solution in a 100mL beaker, add 0.001M sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution, and add 3g of zero-valent iron. React at 25°C for 90min, then wash with deionized water and ethanol three times respectively, the sample is filtered and dried in a vacuum drying oven at 25°C for 12h; L, the dosage of zero-valent iron fluoride is 2g / L, after 30 minutes of reaction, the removal rate of chromium reaches 99%, the electron selectivity of the original zero-valent iron is about 2.3%, and the electron selectivity after modification is as high as 25%. , the removal rate of chromium is still as high as 93% after 5 cycles.
example 3
[0022] Example 3. First prepare 50mL of 0.05M trifluoroacetic acid solution in a 100mL beaker, add 0.0001M sodium tridecylsulfonate solution, and add 5.6g of zero-valent iron. React at 25°C for 120min, then wash with deionized water and ethanol three times respectively, the sample is filtered and dried in a vacuum oven at 25°C for 16h; under aerobic conditions, the rotation speed is 200 rpm, and the initial concentration of hexavalent chromium is 5mg / min. L, the dosage of zero-valent iron fluoride is 2g / L, after 30 minutes of reaction, the removal rate of chromium reaches 99%, the electron selectivity of the original zero-valent iron is about 2.3%, and the electron selectivity after modification is as high as 32%. , the removal rate of chromium is still as high as 96% after 5 cycles.
[0023] The zero-valent iron in the above-mentioned Examples 1-3 is micron-sized zero-valent iron.
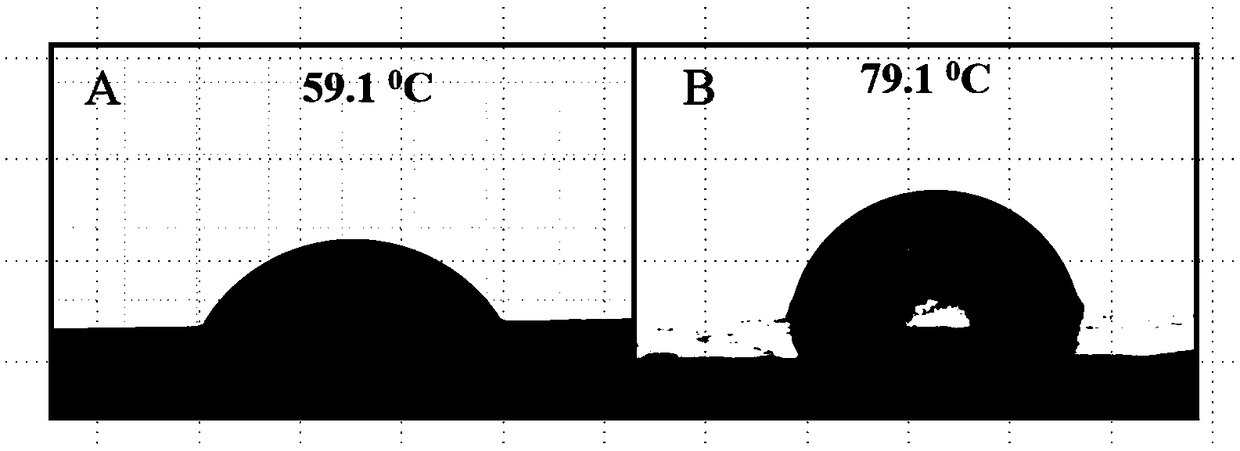
[0024] The contact angle results of original zero-valent iron and modified zero-valent iron (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com