Method of efficiently synthesizing solvents and organic acids by butanol fermentation
A butanol fermentation and organic acid technology, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of low butyric acid/butanol, low butyric acid concentration, inability to obtain high value-added products of in-situ synthesis of butyl butyrate, and achieve efficient synthesis , increase production and reduce the cost of fermentation raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 2
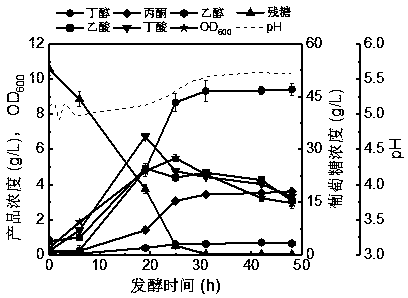
[0039] Embodiment 2: Butanol fermentation process with 0.2 g / L vanillin added
[0040] The preparation process of the activation solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0041] The preparation process of the Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0042] The Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution was transferred to a 5 L anaerobic fermentation tank with an inoculum of 10% (v / v), and the anaerobic fermentation tank was filled with 3 L Clostridium fermentation medium (where the glucose concentration was 60 g / L, the vanillin concentration is 0.2 g / L), the fermentation temperature is 37°C, and the pH control strategy during the fermentation process is expressed as follows: During the acid production period (~0-15 h), the pH is automatically controlled to 5.0 by the control cabinet , using 14% (w / v) ammonia water; during the solventogenic phase (~15-48 h)...
Embodiment approach 3
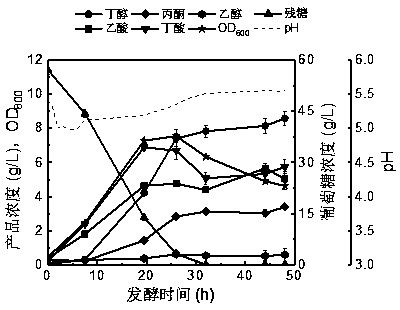
[0046] Embodiment 3: Butanol fermentation process with 0.2 g / L vanillic acid added
[0047] The preparation process of the activation solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0048] The preparation process of the Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0049] The Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution was transferred to a 5 L anaerobic fermentation tank with an inoculum of 10% (v / v), and the anaerobic fermentation tank was filled with 3 L Clostridium fermentation medium (where the glucose concentration was 60 g / L, the concentration of vanillic acid is 0.2 g / L), the fermentation temperature is 37°C, and the pH control strategy during the fermentation process is expressed as follows: During the acid production period (~0-15 h), the pH is automatically controlled to 5.0 by the control cabinet, 14% (w / v) ammonia was utilized; during the solventogenic pha...
Embodiment approach 4
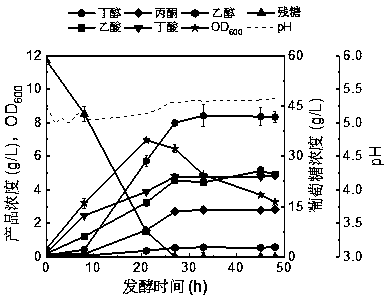
[0053] Embodiment 4: Butanol fermentation process with addition of 0.1 g / L vanillin and 0.1 g / L vanillic acid
[0054] The preparation process of the activation solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0055] The preparation process of the Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0056]The Clostridium acetobutylicum seed solution was transferred to a 5 L anaerobic fermentation tank with an inoculum of 10% (v / v), and the anaerobic fermentation tank was filled with 3 L Clostridium fermentation medium (where the glucose concentration was 60 g / L, the concentration of vanillin is 0.1 g / L, the concentration of vanillic acid is 0.1 g / L), the fermentation temperature is 37°C, and the pH control strategy during the fermentation process is expressed as follows: During the acid production period (~0-15 h) , the pH is automatically controlled to 5.0 through the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com