Method for purifying p-phenylenediamine by using zone melting of microwave device
A technology of p-phenylenediamine and regional smelting, which is applied in the purification/separation of amino compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high precision requirements for multi-stage sweating crystallization temperature, low product output, and affecting product quality, etc., to achieve Thorough enrichment, high product yield and high degree of automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] After hydrogenation of p-nitroaniline, solvent removal, decoking, delightening and rectification obtain p-phenylenediamine crude product, the main content is 99.5% (mass percentage), and the main impurity is o-phenylenediamine, the content is 0.48 % (mass percentage content), other impurity content is 0.02% (mass percentage content), since the rectification process is after decoking, most of the heavy components have been extracted with tar, other impurities in the crude product are relative to p-benzene Diamine is a light component with a slightly lower boiling point and is difficult to remove by rectification;
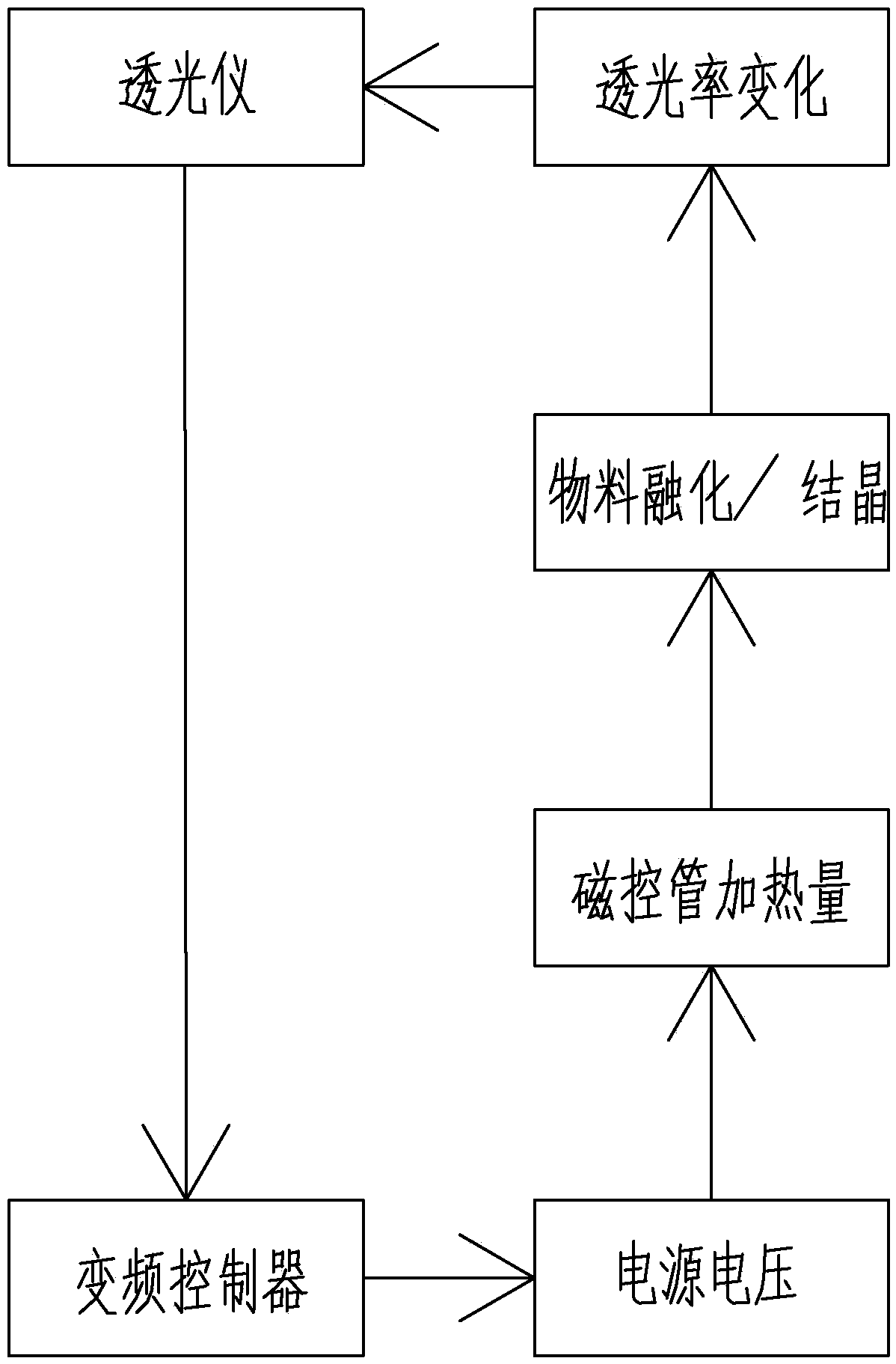
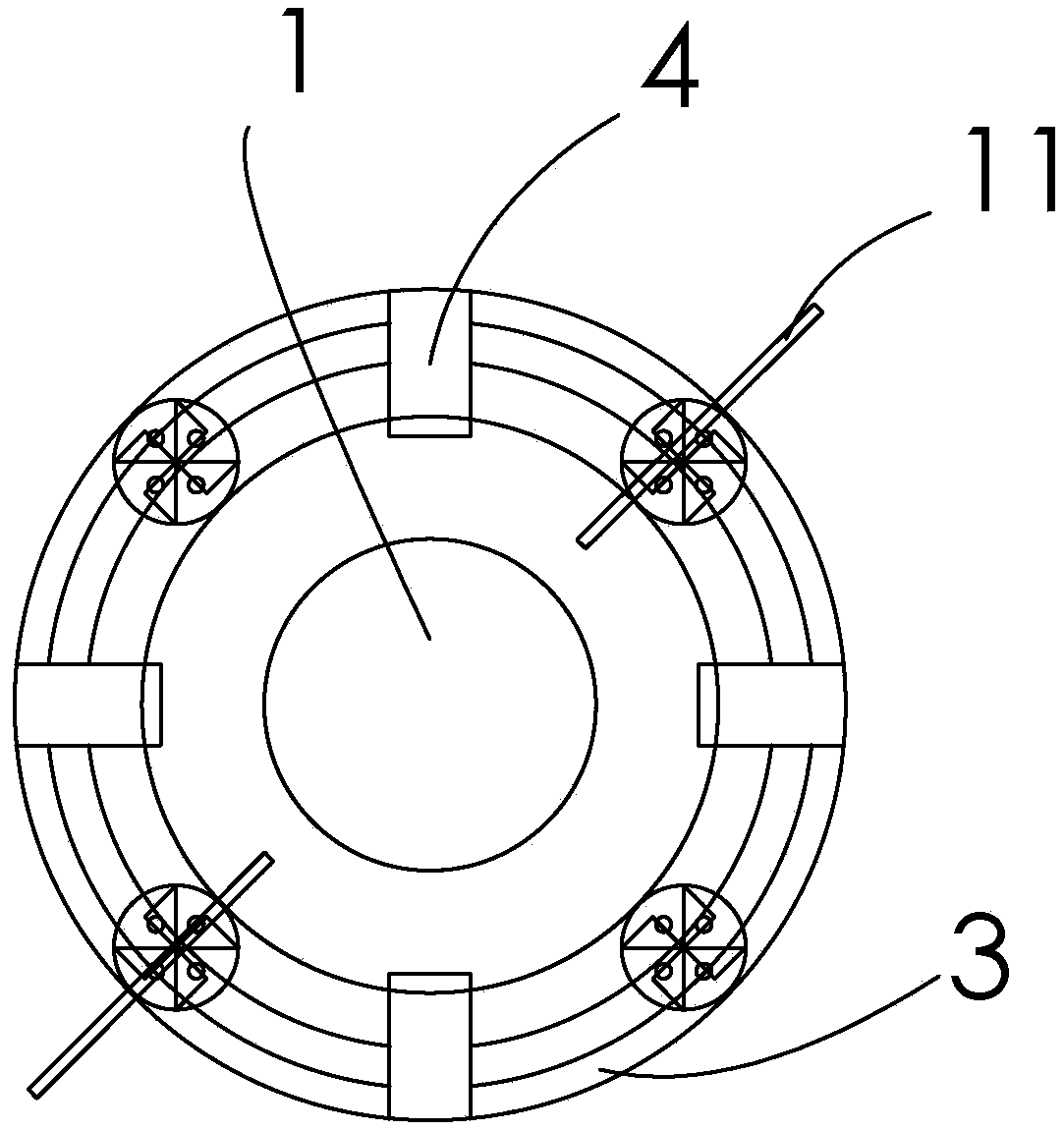
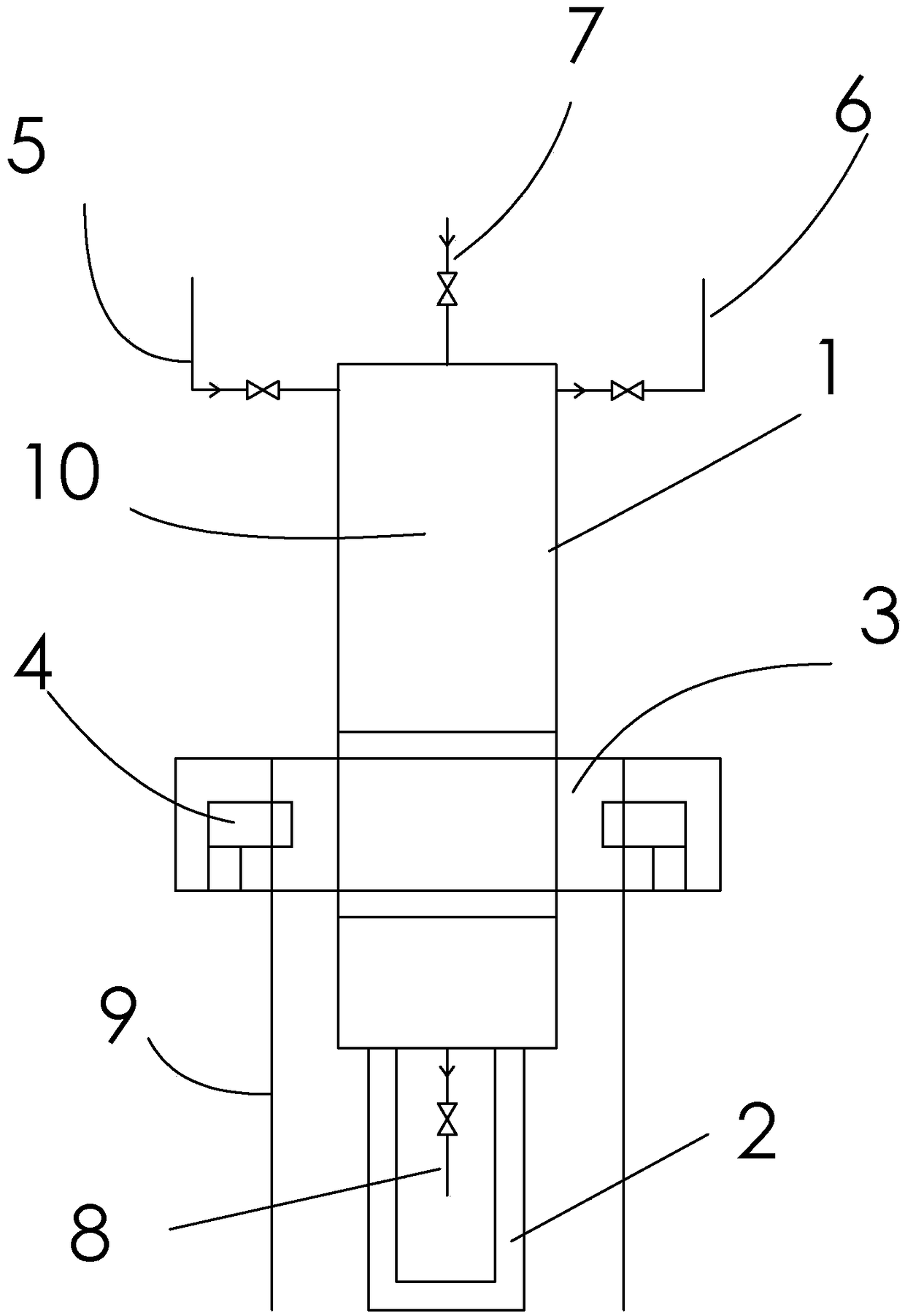
[0026] Crystallization: Replace the quartz glass column 1 with nitrogen until the oxygen content is lower than 100ppm, put the molten solution of p-phenylenediamine crude product 10 into the quartz glass column 1 while it is hot, and cool down under the protection of nitrogen to crystallize. The inner diameter of the quartz glass column 1 is 2cm, the thickness...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The difference from Example 1 is that the regional melting and regional crystallization steps are repeated 3 times to further enrich the impurities to the bottom of the quartz glass column 1, and the final step of crystallization is to melt the p-phenylenediamine in the quartz glass column 1 from the bottom , melt the material at a height of 15cm from the bottom, and discharge 10% p-phenylenediamine raffinate by total weight. The p-phenylenediamine content in the raffinate is 95.1%. The distilled product can be used as feed material in the crystallization step, and the remaining p-phenylenediamine is melted and discharged, cooled and crystallized into slices to obtain the finished p-phenylenediamine, which has a p-phenylenediamine content of 99.99% to 99.992%;
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: The difference from Example 2 is in the final step of crystallization section: melting the p-phenylenediamine in the quartz glass column 1 from the bottom, melting the material at a height of 30 cm from the bottom, and discharging 20% p-phenylenediamine by total weight The raffinate, the content of p-phenylenediamine in the raffinate is 97.5%. This p-phenylenediamine raffinate is applied mechanically in the rectification operation, and the product after rectification can be used for the feed of the crystallization step, and the remaining p-phenylenediamine Discharge after melting, cool and crystallize into slices to obtain the finished product of p-phenylenediamine, the content of which is 99.995% to 99.999%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com