Method used for improving traditional fermentation food quality through co-culturing of saccharomyces cerevisiae and ester producing yeast
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, which is applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, can solve the problems of reducing the application effect and low ethyl acetate content, and achieve the effects of increasing production, high ethanol production, and optimizing culture conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 Saccharomyces cerevisiae ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) isolation of YF1914
[0040] After crushing Daqu and mixing it evenly, weigh 25 g, add 225 mL of sterile water, oscillate fully and soak for 15 min to make a suspension. Under aseptic conditions, take 0.1 mL of the suspension and dilute it step by step with sterile water to 10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 . Take 0.1 mL of each gradient suspension on a YPD plate, make three parallels for each dilution gradient, and spread sequentially from low concentration to high concentration. Place the medium plate at 30 o C cultured in a constant temperature incubator for 2 days to observe the growth of colonies. Pick up a single colony that is spherical, protruding on the surface, milky white, and opaque on the plate, and inoculate it on the YPD plate for multiple times until the bacteria are in the same shape under the microscope. Inoculate a single colony in 50 mL ethanol fermentation medium, 30 o C. Static cultu...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 Saccharomyces cerevisiae ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) for the preservation of YF1914
[0042] The saccharomyces cerevisiae obtained above ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) YF1914 is saved by the following methods:
[0043] (1) Preservation on slant: Inoculate the purified strains on the YPD slant, place it in the incubator for 48-72 h, and then store it at 4 o C stored in the refrigerator.
[0044] (2) Storage in glycerol tubes: Take 6 mL of 20% glycerol on the purified strain plate, scrape off the colony and mix it with 20% glycerol, divide the mixture into 1.5 mL sterile PE tubes, store at -80 o Save under C.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Saccharomyces cerevisiae ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) Identification of YF1914
[0046] The Saccharomyces cerevisiae ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae ) The identification of YF1914 included the following steps:
[0047] Step 1: Morphological Characterization
[0048] In order to identify the yeast strains involved, the following morphological characteristics were observed:
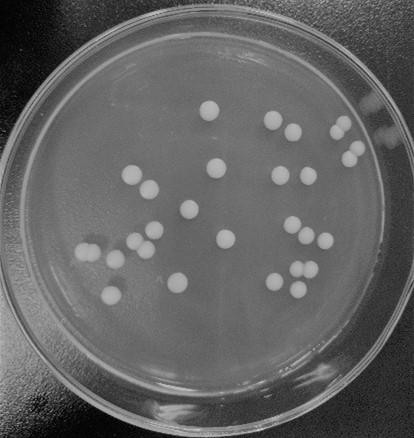
[0049] (1) Colony morphology and cell morphology: Inoculate the pure culture of the strain obtained in Example 1 on WL medium, and observe its morphological characteristics after 3 days. The result is as figure 1 , the colony is milky white, the surface is smooth and moist, the edges are regular, and the center is slightly raised. After magnifying it 1000 times under the optical microscope, the result is as follows: figure 2 , the cells are mostly oval or spindle-shaped, and reproduce by budding.
[0050] Step 2: Molecular Biological Identification
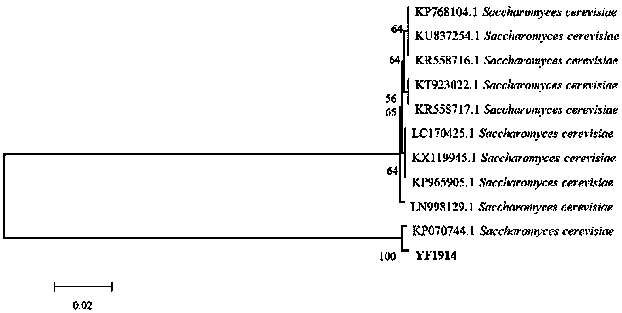
[0051] In order to identify the abo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com