Gradient scattering structure spectrum analysis device and spectrum restoration method
A technology of scattering structure and spectral analysis, applied in the directions of Raman/scattering spectroscopy, spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, measuring device, etc., can solve problems such as inability to solve spectral analysis contradictions, and achieve fast real-time spectroscopy Restore, remove distortion, resolve effects of wide spectral analysis range and high spectral resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1, a kind of gradient scattering structure spectroscopic analysis device.
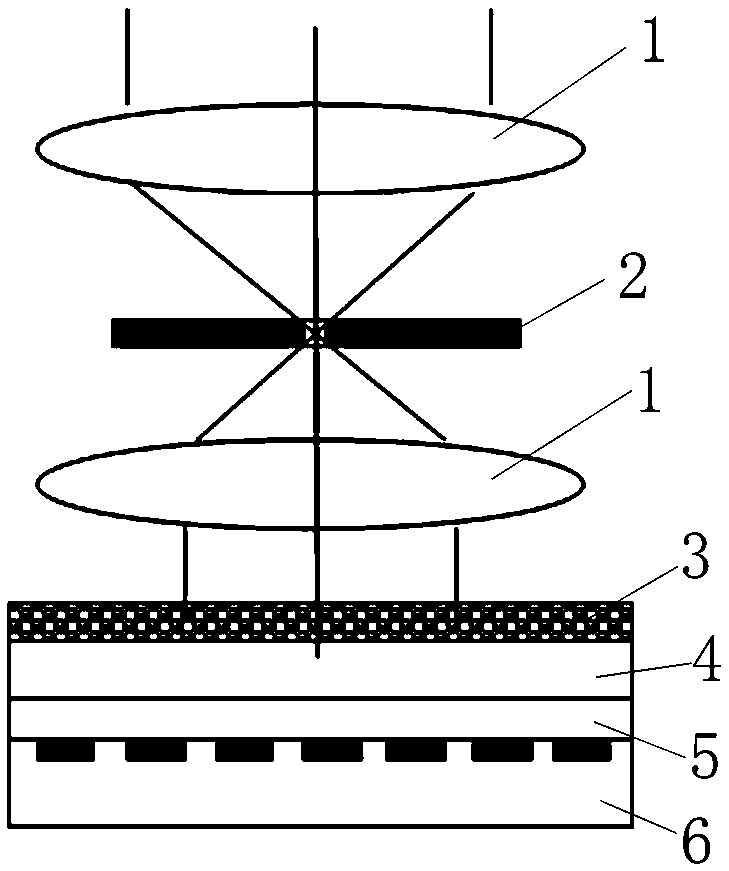
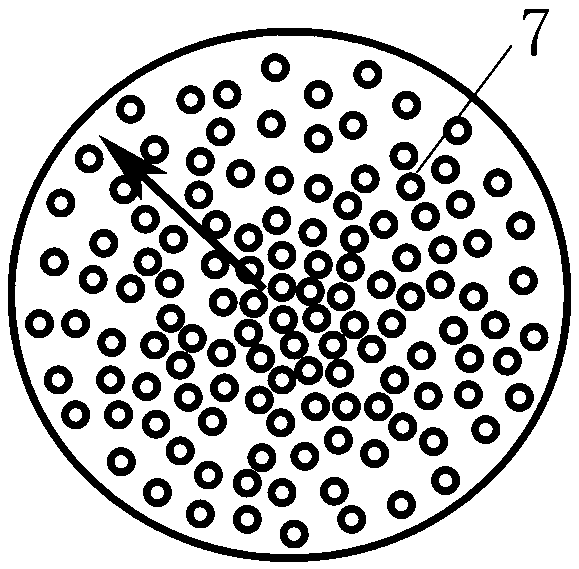
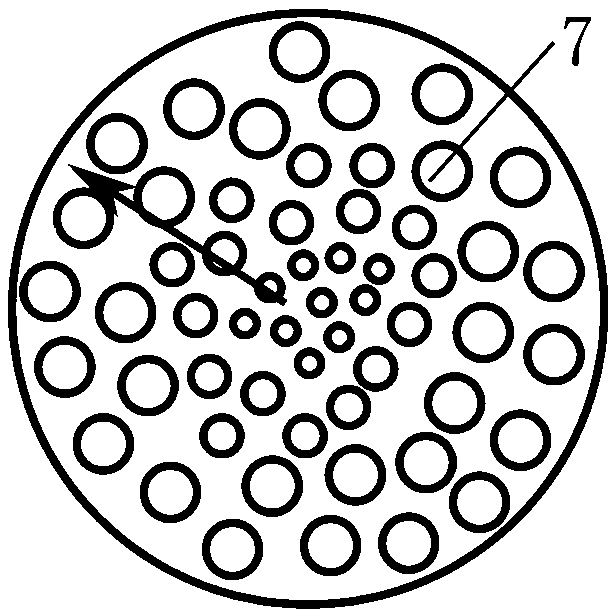
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the gradient scattering structure spectroscopic analysis device provided by the present invention includes a substrate 4 made of a transparent material, and a layer of scattering particles with a gradient structure feature is provided on the surface of the substrate 4 (either the upper surface or the lower surface) 3. The scattering particle layer 3 is composed of a group of scattering particles in nanometer to micrometer scale. The gradual structural feature of the scattering particle layer 3 is that the size, density and / or refractive index of the scattering particles have a gradual distribution law, and the gradual change distribution law includes a gradual change from the center to the outside, a gradual change from the outside to the inside, and a single direction. Scattering gradients and more. The gradual structural feature of the scattering ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2, a spectrum restoration method.
[0036] The spectral restoration method provided in this embodiment is performed based on the gradient scattering structure spectral analysis device described in Embodiment 1.
[0037] When measuring the spectrum, the light to be measured passes through the two confocal lenses 1 , then irradiates the scattering particle layer 3 , then passes through the distance matching layer 5 , and finally irradiates each pixel of the photodetector array 6 . Scattering occurs when light waves of different wavelengths pass through the scattering particle layer 3 with gradient structural features, and finally the light spots generated on the photodetector array 6 have light field pattern distributions with different characteristics.
[0038] According to Lorenz-Mie theory and multiple scattering theory, particle light scattering characteristics are closely related to particle shape, composition, density, refractive index, size and incident ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com