Method for low-pressure sintering hybrid power module by nano-silver solder paste
A mixed-power, low-pressure sintering technology, which is applied to semiconductor/solid-state device components, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as unsuitable pressure, large area difference, and easy damage of SiC diode chips.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
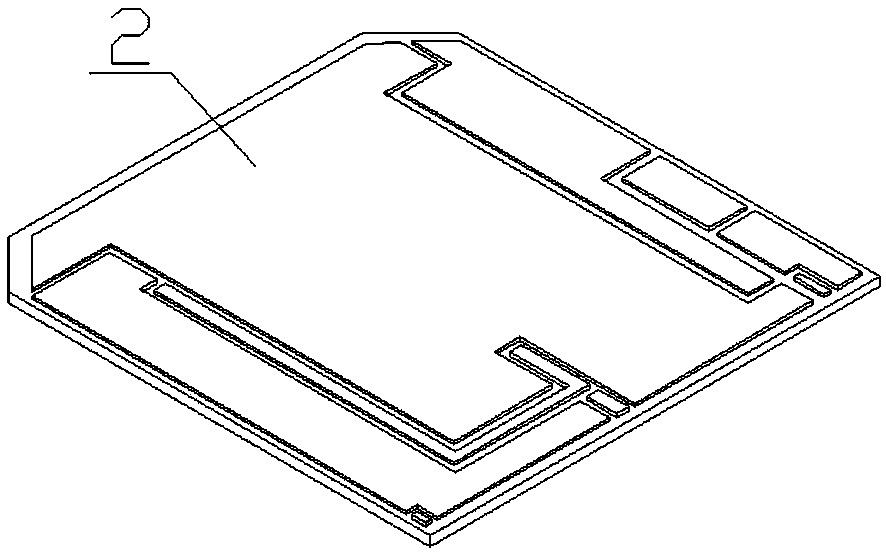
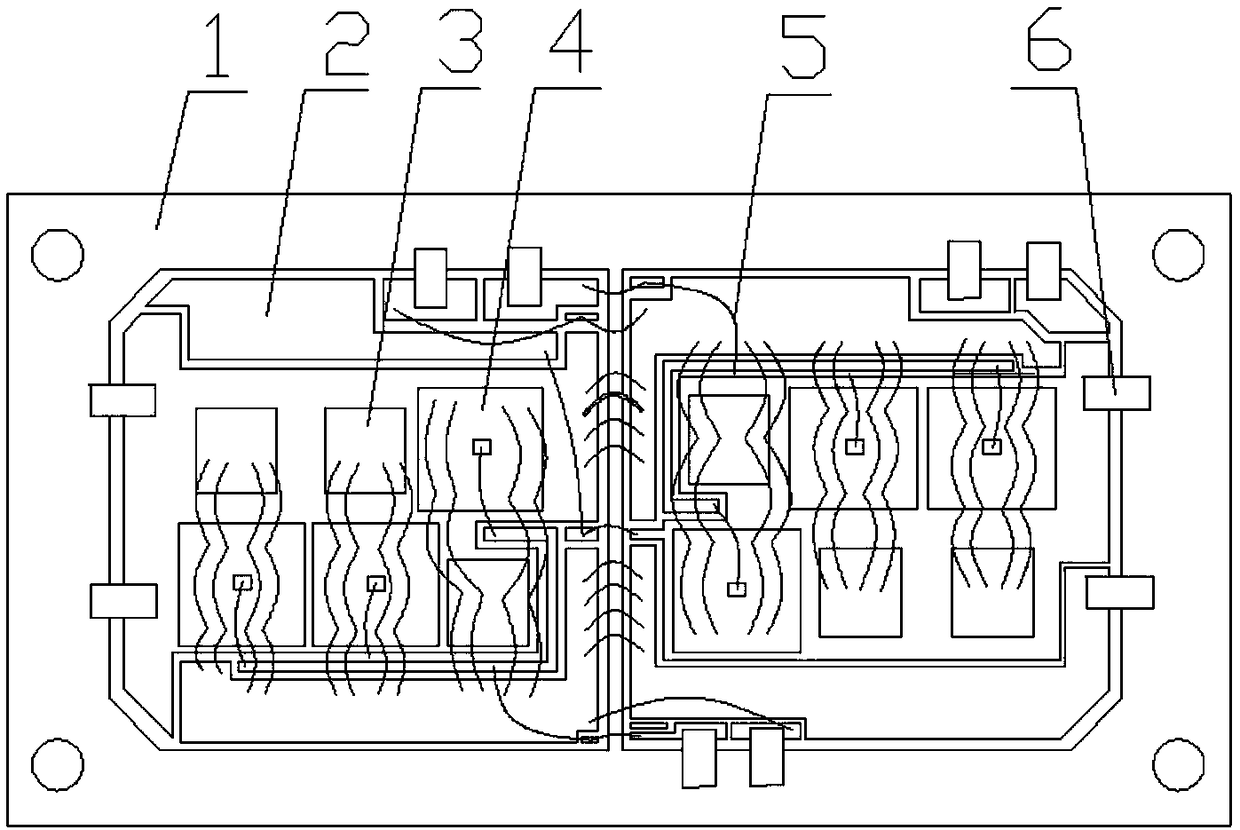
[0035] Example 1: Ultrasonic cleaning of copper-clad substrate (2) and copper base plate (1), then printing nano-silver solder paste on the substrate (2) and patch wetting; pre-drying: first put the sample on the heating table to heat Pre-drying at 90°C and holding for 10 minutes; pressurization: apply a pressure of 2 MPa to the large-area Si-based IGBT chip (4), and no pressure on the small-area SiC diode chip (3); sintering: then increase the temperature at a rate of 5°C / min Heating at a rate of 270°C and keeping it warm for 20 minutes in a mixed atmosphere of 50% air + 50% nitrogen; reduction: followed by vacuuming and nitrogen formic acid mixture for 10 minutes. After sintering and molding, the shear strengths of the chips in both areas reach above 30MPa. After sintering, follow-up processes such as wire bonding, secondary welding, housing installation, glue coating and sealing, and sealing agent filling are carried out.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: Ultrasonic cleaning of the copper-clad substrate (2) and the copper base plate (1), and then printing nano-silver solder paste on the substrate (2) and patch wetting. Pre-drying: first heat the sample on a heating table to 100°C and keep it warm for 12 minutes to complete the pre-drying; pressurization: apply a pressure of 2 MPa to the large-area Si-based IGBT chip (4), and apply a pressure of 2 MPa to the small-area SiC diode chip (3) Pressurized; sintering: then heated to 270°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min and kept in a 50% air + 50% nitrogen mixed atmosphere for 20 minutes; reduction: followed by vacuuming and nitrogen formic acid mixture for 10 minutes. After sintering and molding, the shear strengths of the chips in both areas reach above 30MPa. After sintering, follow-up processes such as wire bonding, secondary welding, housing installation, glue coating and sealing, and sealing agent filling are carried out.
Embodiment 3
[0037]Embodiment 3: Ultrasonic cleaning of the copper-clad substrate (2) and the copper base plate (1), and then printing nano-silver solder paste on the substrate (2) and patch wetting. Pre-drying: first heat the sample on a heating table to 90°C and keep it warm for 10 minutes to complete the pre-drying; pressurization: apply a pressure of 2 MPa to the large-area Si-based IGBT chip (4), and apply a pressure of 2 MPa to the small-area SiC diode chip (3). Pressurization; sintering: then heated to 280°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min and kept in a 50% air + 50% nitrogen mixed atmosphere for 30 minutes; reduction: followed by vacuuming and nitrogen formic acid mixture for 12.5 minutes. After sintering and molding, the shear strengths of the chips in both areas reach above 30MPa. After sintering, follow-up processes such as wire bonding, secondary welding, housing installation, glue coating and sealing, and sealing agent filling are carried out.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com