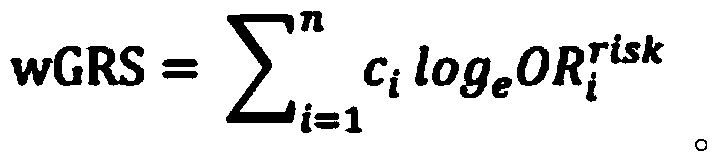Early-warning detection kit for acute and chronic mountain sickness susceptibility genes
A detection kit, a technology for altitude sickness, applied in genomics, microbial determination/inspection, chemical library, etc., can solve the problems of scattered gene research, low throughput, high cost, avoid incidence and mortality, detect Low cost and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Primer design and synthesis
[0040] For the 96 gene polymorphic sites in Table 3, corresponding PCR amplification primers and specific extension primers were designed, as shown in Table 4.
[0041] Among them, in order to prevent the PCR primers from entering the detection window of the mass spectrometer and interfering with the detection effect, a certain number of bases, such as ACGTTGGATG, are added to the 5' end of each PCR primer to increase the molecular weight of each PCR primer, thereby exceeding the detection efficiency of the mass spectrometer. window.
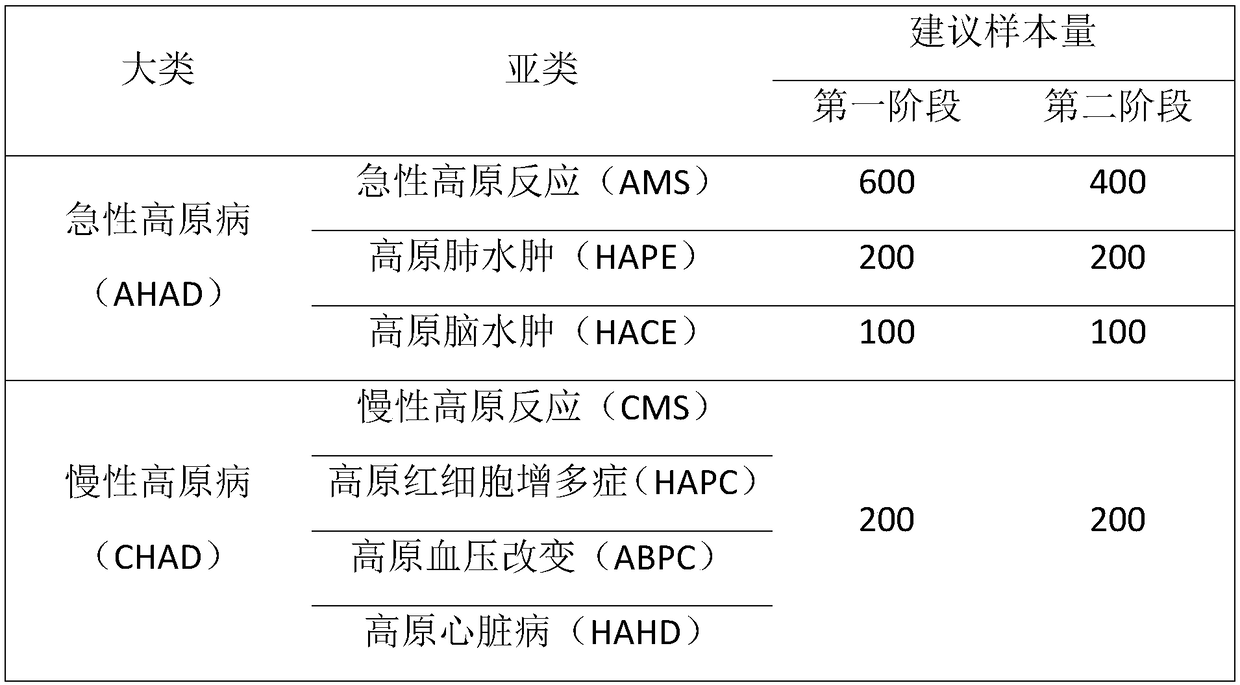
[0042] Table 3 Genes and loci related to altitude sickness
[0043]
[0044]
[0045] Table 4 Primer sequence list
[0046]
[0047]
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] (2) Divide the SNP sites in Table 4 into 4 groups according to the hole position numbers, mix the upstream and downstream primers of each SNP site contained in each group, and obtain the corresponding 4 groups of amplification p...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2: Risk assessment analysis method
[0073] (1) OR value (odds ratio), also known as odds ratio and odds ratio, mainly refers to the ratio of the exposed population to the non-exposed population in the case group divided by the ratio of the exposed population to the non-exposed population in the control group. A commonly used indicator in case-control studies. First use the OR value to evaluate the degree of association between the single nucleotide polymorphism and the disease: OR A =(n A *m a ) / (m A *n a ), wherein, a is the designated reference base, A is the base to be analyzed, n is the case group, and m is the control group; OR A The calculation table is shown in Table 8:
[0074] Table 8 Base distribution
[0075]
[0076] OR A The calculation of:
[0077] OR A =(n A / m A ) / (n a / m a )=(n A *m a ) / (m A *n a )
[0078] Explanation:
[0079] Risk type: OR A When >1, it means that the frequency of A in the case group is greater than t...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Select 24 samples, refer to the instructions of the nucleic acid extraction kit manufacturer, and extract DNA from the whole blood, saliva or other tissues of the patient (subject), the concentration and purity of the DNA meet the detection requirements; the rest follow the method of Example 1 , test the subjects, and make an overall assessment of the individual risk based on the test results at each site. The test results of 24 subjects using the kit of the present invention show that the accuracy of the kit of the present invention is 100%, and the sensitivity reaches 1ng / μl of genomic DNA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com