A method for producing 1,3-propanediol with methanol/formaldehyde and glucose as co-substrate
A technology of propanediol and propanediol dehydrogenase, which is applied in the field of producing 1,3-propanediol, can solve the problems of long synthetic pathway, low yield of 1,3-PDO, difficult regulation and strengthening, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
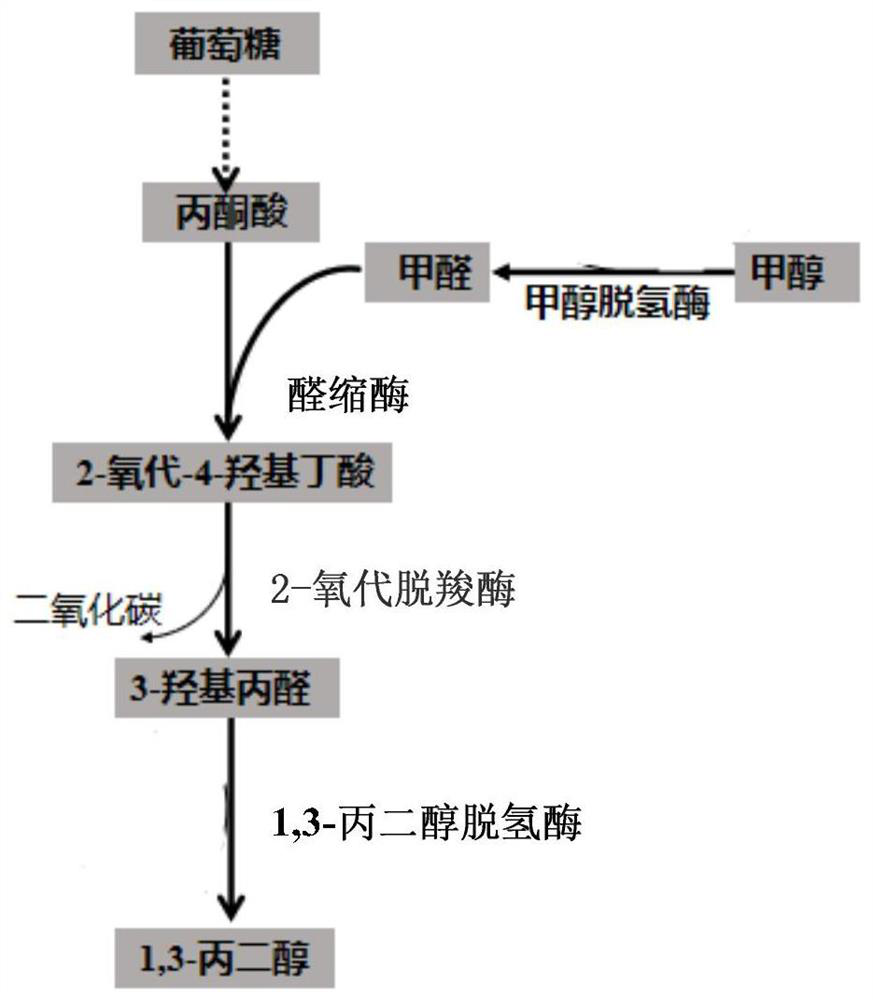
[0074] Example 1 Screening and characterization of suitable aldolases for novel 1,3-PDO production pathways
[0075] The aldolase genes from different sources are: 2-oxo-4-hydroxybutyrate aldolase KHB derived from Escherichia coli; 2-keto-3 derived from Escherichia coli - Deoxy-L-rhamnolate aldolase YfaU; 2-oxo-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase RnKHG from rat (Rattus norvegicus); 2-oxo from human (Homo sapiens) -4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase HsKHG; 2-oxo-4-hydroxyglutarate aldolase BtKHG derived from bovine (Bos taurus), constructed on the expression vector pET22b, respectively: pET22b-KHB; pET22b-YfaU; pET22b-RnKHG; pET22b-HsKHG; pET22b-BtKHG.
[0076] The above expression vectors were respectively transformed into E. coli expression host E.coli BL21(DE3), cultivated at 37°C until the OD reached 0.5-0.6, then added 0.2mM IPTG to induce gene expression, continued to cultivate at 30°C for 10h, and then collected the cells. After sonication, the supernatant was taken for use.
[0077...
Embodiment 2
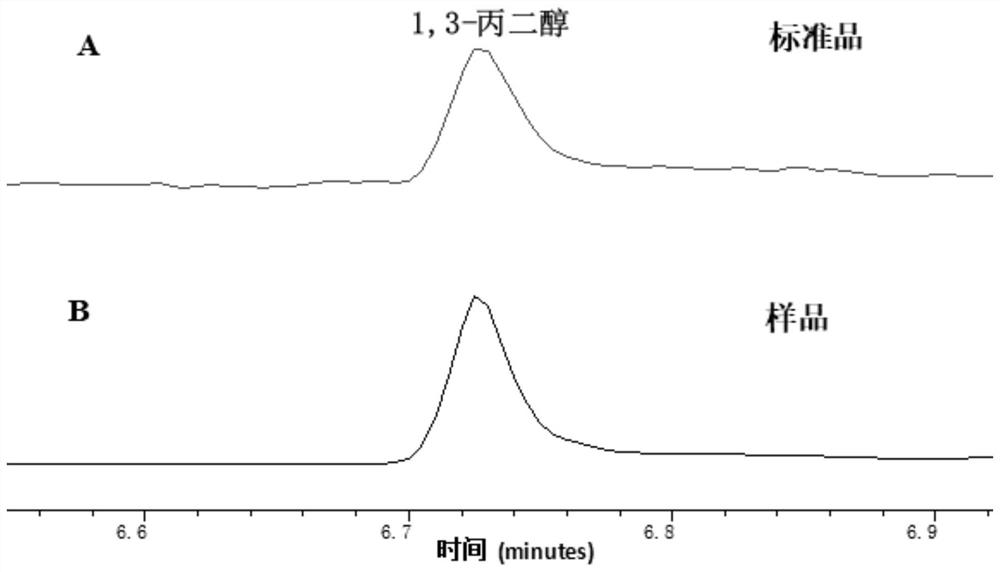
[0078] Example 2: In vitro verification of formaldehyde to 1,3-PDO new biosynthetic pathway
[0079] The KHB coding gene (SEQ ID NO.2) derived from Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) was constructed on the expression vector pET22b, and the KDC coding gene (SEQ ID NO.3) derived from Lactococcus lactis (Lactococcus lactis) was constructed to express On the vector pET22b, the DhaT gene (SEQ ID NO. 4) derived from Klebsiella pneumoniae was constructed on the expression vector pET22b. The above expression vectors were respectively transformed into E. coli expression host E.coli BL21(DE3), cultivated at 37°C until the OD reached 0.5-0.6, then added 0.2mM IPTG to induce gene expression, continued to cultivate at 30°C for 10h, and then collected the cells. After sonication, the supernatant was taken for use.
[0080] Add formaldehyde at a final concentration of 10 mM, 10 mM sodium pyruvate, 20 mM NADH, and 1 mM thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) to a total volume of 1 mL of PBS buffer wit...
Embodiment 3
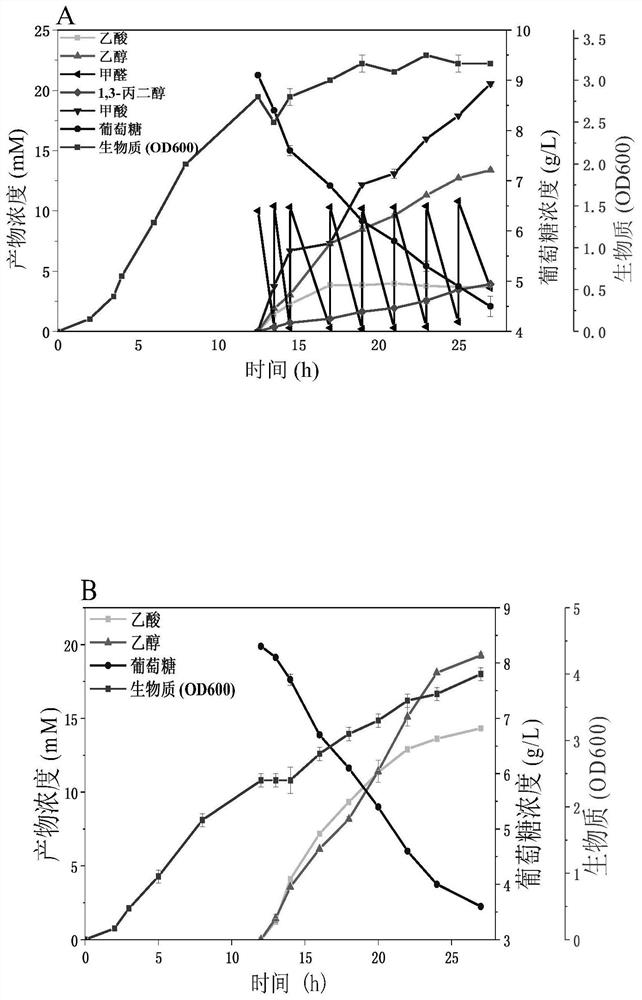
[0081] Example 3: Construction of formaldehyde to 1,3-PDO new biosynthetic pathway recombinant strain
[0082] Utilize kit In-fusion HD Cloning Kit (Clontech Laboratories, Inc, US) to construct plasmid pRSFduet-1-KHB-KDC-DhaT: first, plasmid vector pRSFduet-1 and KDC encoding gene (SEQ ID NO.3) were passed through NdeI, NcoI Restriction endonucleases were used for double digestion, and enzyme ligation was performed to obtain pRSFduet-1-KDC. Afterwards, the KHB coding gene (SEQ ID NO.2) was amplified by PCR using primers KHB-F and KHB-R, and the DhaT gene (SEQ ID NO.4) was amplified by PCR using primers DhaT-F and DhaT-R. The pRSFduet-1-KDC plasmid was amplified by PCR, and the primers were pRSFduet-1-KDC-F and pRSFduet-1-KDC-R, respectively. The fragments were connected with the In-fusion kit, and the newly synthesized plasmid was named pRSFduet-1- KHB-KDC-DhaT. (See Table 3 for primers)
[0083] Plasmid pRSFduet with 2-oxo-4-hydroxybutyrate aldolase (KHB), branched-chain-2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com