Satellite-borne laser radar foot point accurate positioning method based on surface model
A surface model and lidar technology, applied in the field of remote sensing, can solve the problems of deviation of elevation measurement results, difficulties in high-precision terrain data, and the use of flat surface areas as elevation control points, etc., to achieve high universality and high plane positioning accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
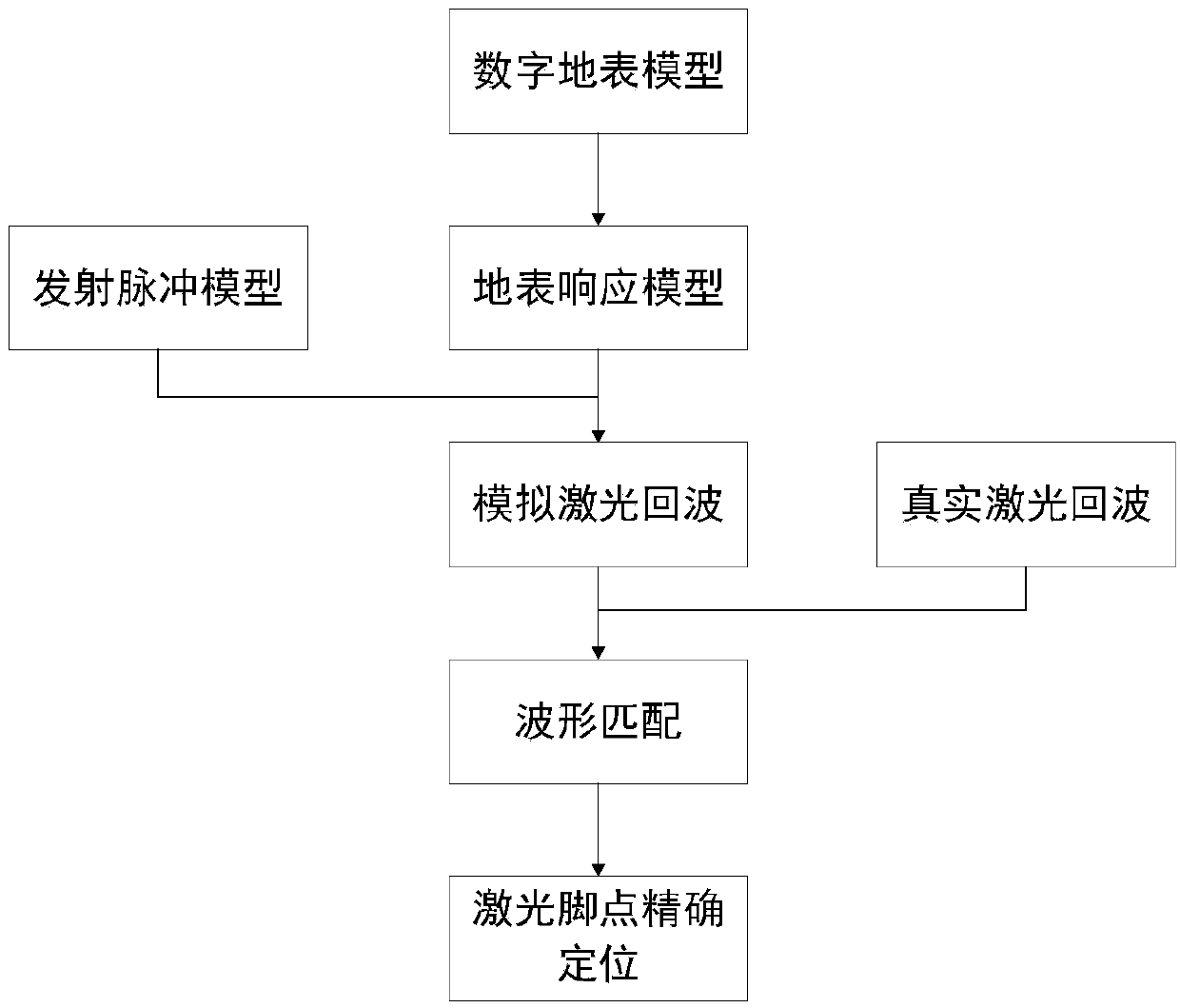
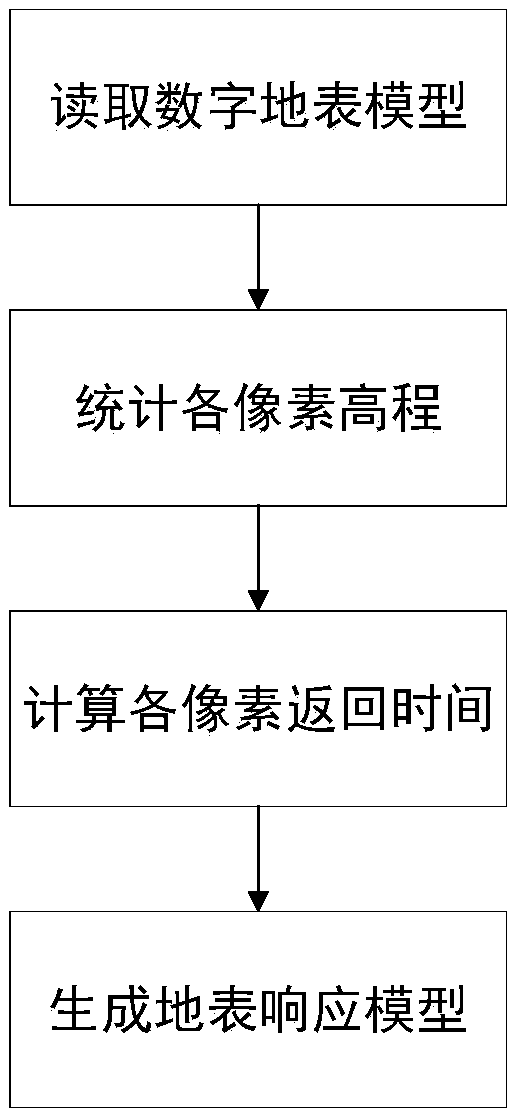
[0032] figure 1 For the overall flow diagram of the present invention, refer to figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment discloses a method for precise positioning of spaceborne laser radar feet based on terrain features, including the following steps:
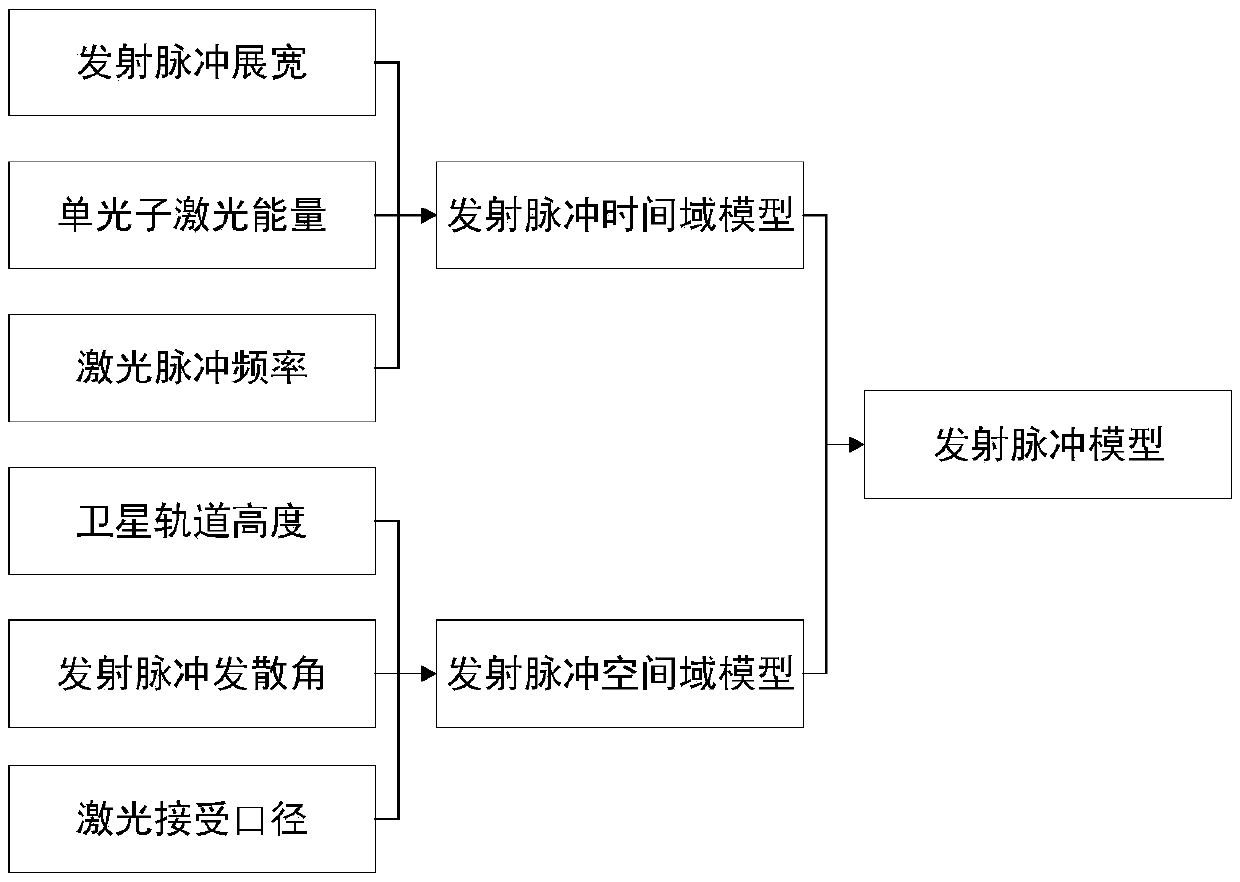
[0033] S1. Based on the satellite orbit parameters and launch pulse parameters, establish a simulated laser radar launch pulse model:
[0034] figure 2 For the schematic flow chart of generating the emission pulse model of the present invention, refer to figure 2 As shown, the implementation process of step S1 is:
[0035] S11. Establish a laser pulse time-domain model by setting parameters such as laser emission pulse width, laser energy, laser pulse frequency, and emission pulse duration, and its time-domain energy distribution is a one-dimensional Gaussian distribution;
[0036] Among them, the time domain model of the transmitted pulse is expressed as:
[0037]
[0038] In formula (1), E(t) is the laser emission...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com