Printing and dyeing wastewater biochar filter saturated filler functional reutilization method
A printing and dyeing wastewater and biological aerated filter technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, sustainable biological treatment, textile industry wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems of the lack of research on the treatment and disposal of waste fillers, the acceleration of mass transfer process, and the waste of resources and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving the biological treatment effect, reducing investment and operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
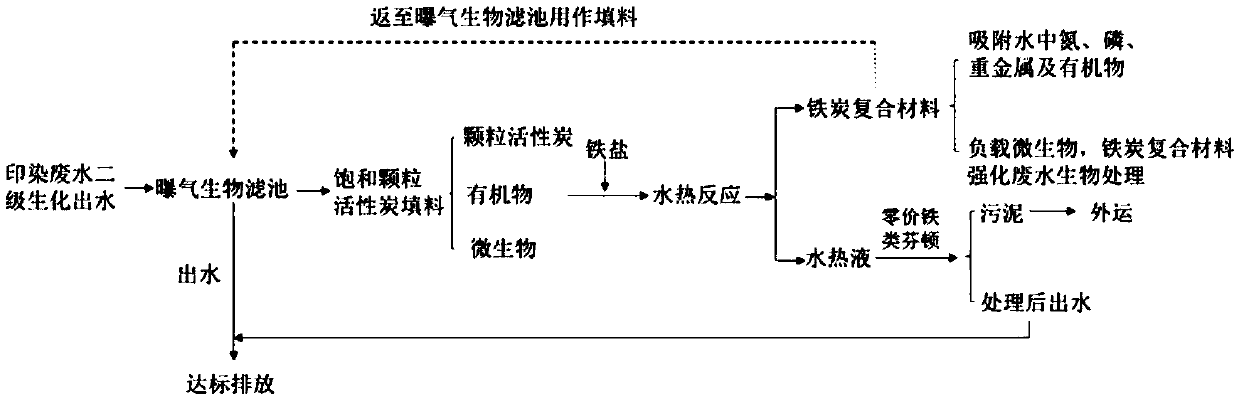
[0025] A printing and dyeing wastewater biochar filter saturated filler functional reuse method, comprising the following steps:
[0026] Step 1): Add iron powder and saturated granular activated carbon with a mass ratio of 1:6 into a hydrothermal closed reaction tank, the volume of which is 50% of the volume of the reaction tank, and add water to the reaction tank to raise the liquid level to the effective height 70%, use steam heating method, airtightly heat to the sludge temperature in the kettle is 180 ℃, keep for 160min;
[0027] Step 2): After the hydrothermal reaction is finished, wait for the reaction kettle to drop to normal temperature, discharge and separate the mixed material in the kettle to obtain the iron-carbon composite material;
[0028] Step 3): re-dosing the obtained iron-carbon composite filler into the biological aerated filter as filler, the composite filler accounts for 35% of the total filler volume, the removal rate of COD is 30% higher than that of t...
Embodiment 2
[0031] A printing and dyeing wastewater biochar filter saturated filler functional reuse method, comprising the following steps:
[0032] Step 1): Feed iron powder and saturated granular activated carbon with a mass ratio of 1:5 into a hydrothermal closed reaction tank, the volume of which is 60% of the volume of the reaction tank, and add water to the reaction tank to raise the liquid level to the effective height 75%, using heat conduction oil heating method, airtightly heated to the sludge temperature in the kettle is 180 ℃, keep for 4h;
[0033] Step 2): After the hydrothermal reaction is finished, wait until the reaction kettle is lowered to normal temperature, unload to a filter device, and process through filtration to separate and obtain the iron-carbon composite material;
[0034] Step 3): Add the obtained iron-carbon composite material into the biological aerated filter as filler again, the composite filler accounts for 45% of the total filler volume, the removal rat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com