Method for treating polluted river water by utilizing plant-sediment microbial fuel cell
A technology of fuel cells and microorganisms, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, electrochemical water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., which can solve the problems of inability to remove pollutants from the root, short chemical restoration period, and environmental condition requirements Relatively high-level problems, to achieve the effect of improving oxidation-reduction potential, increasing aesthetics, and improving repair performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
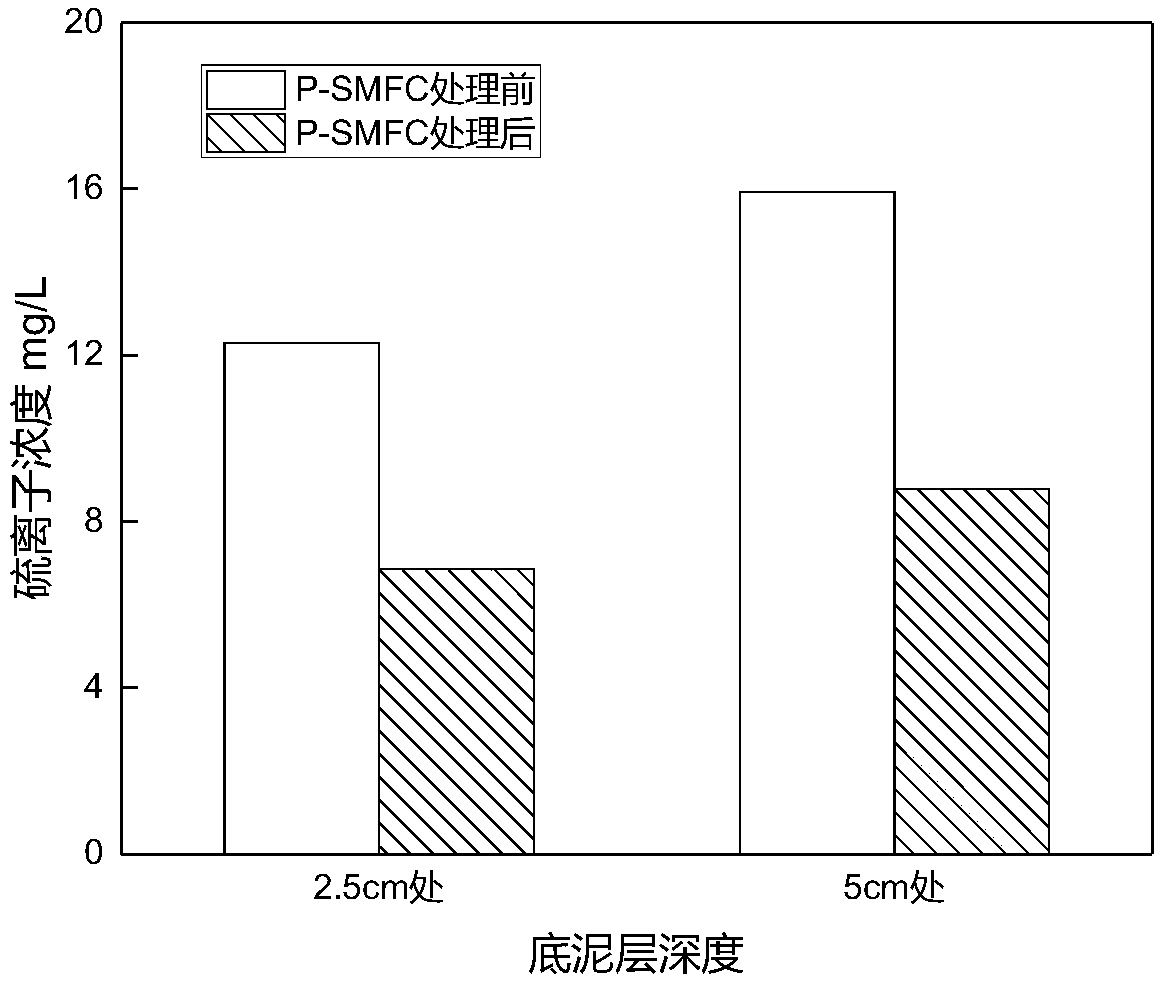
[0041] Put 12cm thick bottom mud into the bottom of a transparent plastic cuboid container (length 60, width 30, height 40cm) with a total volume of 45L, and add 18cm deep artificial simulated sewage above the bottom mud to simulate polluted river water. Drill a small hole with a diameter of 0.2 cm at a distance of 5 cm from the bottom of the container to pass through the wire connected to the anode. Place a high-density polyethylene floating bed on the surface of the overlying water, and equip a planting basket. The planting basket is filled with a sediment matrix mixed with quartz sand with a particle size of 2-3mm in a ratio of 1:1, and plant emergent plants in the planting basket. An anode is set at 5cm of the bottom mud of the polluted water body, so that the concentration of sulfur ions in the upper and middle bottom mud where most of the pollutants are concentrated is improved, and it is also beneficial for plants to take root in the bottom mud. The anode structure is a...
Embodiment 2
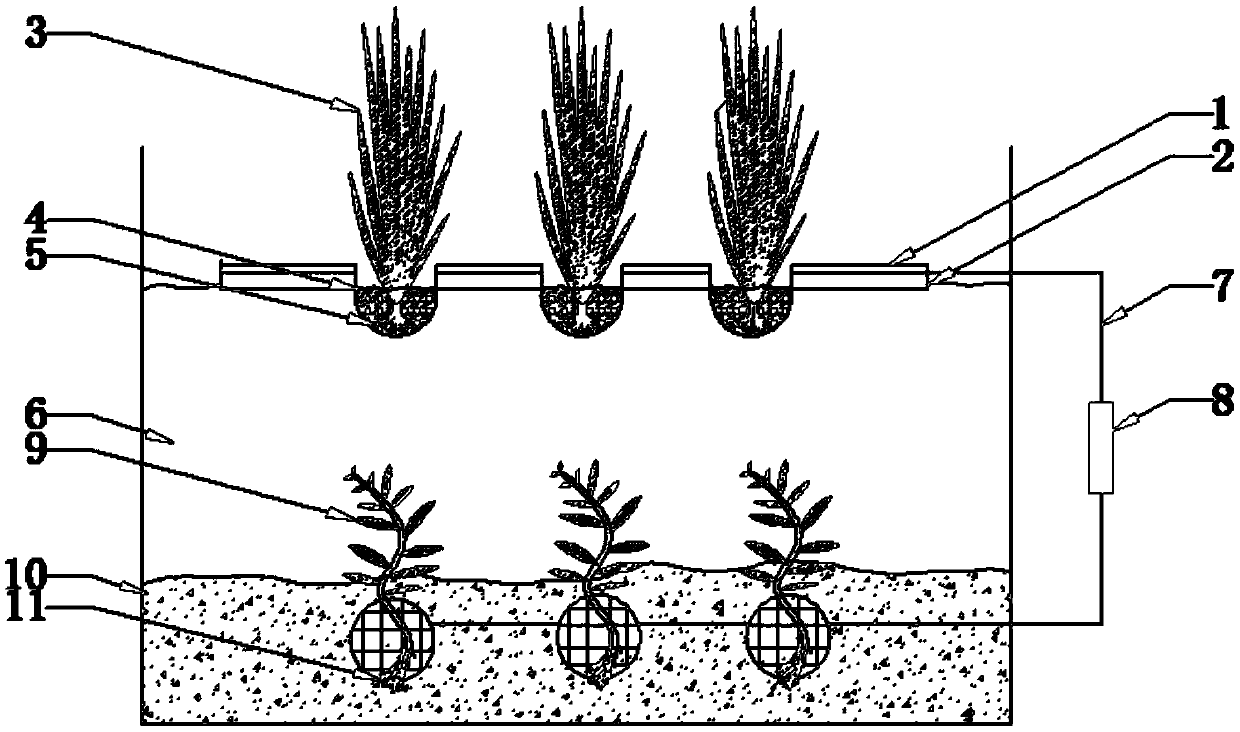
[0051] A device for in-situ restoration of polluted river water by using plant-sediment microbial fuel cells, the device is from top to bottom: cathode plate 1, floating bed floating plate 2, emergent plants 3, planting basket 4, matrix 5, polluted water Layer 6, wire 7, resistor 8, submerged plant 9, sediment layer 10, anode 11. The cathode plate 1 is covered on the floating plate 2 of the floating bed, and the planting basket 4 and the substrate 5 are arranged on the floating plate of the floating bed, and the emergent plants 3 are planted on the floating bed 2 of the floating plate through the substrate 5 . The anode 11 is a three-dimensional spherical network structure, located 5-8cm below the bottom mud layer 9, the roots of the submerged plants 9 are rooted in the bottom mud layer 10 through the anode 11, one end of the external wire 7 is connected to the cathode plate 1, and the other end is connected to the external wire 7. Resistor 8 is connected to anode 11, forming ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Run the P-SMFC device in embodiment 2, connect DC probe and data collector on the two poles of P-SMFC and carry out real-time collection with the frequency of 3min / time, automatically record in the computer by USB interface, generate to system with this The voltage is automatically collected. At the same time, set the SMFC system without adding aquatic plants, and connect the data collector with the P-SMFC system to automatically collect the output voltage at a frequency of 3min / time.
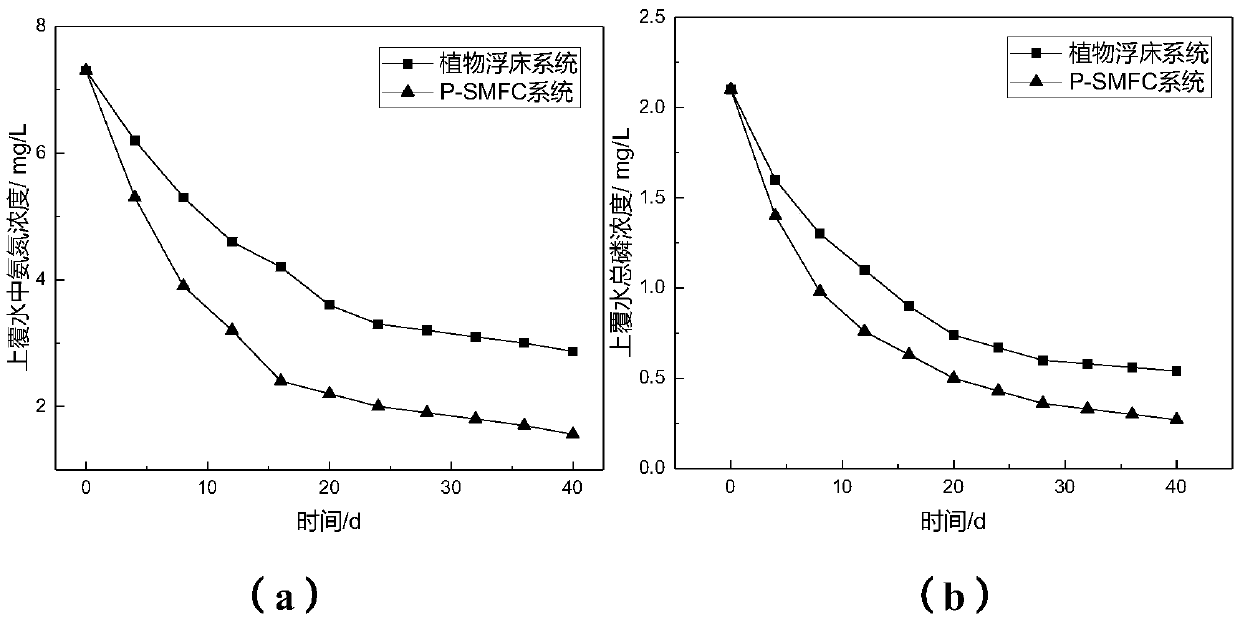
[0063] Figure 4 , Figure 5 It reflects the change of output voltage of P-SMFC and MFC system after 40 days of operation. The output voltage of the two systems is relatively stable in the early stage of operation. With the extension of operation time, the range of output voltage change becomes larger.
[0064] During the operation of the system, the output voltage of P-SMFC fluctuates in the range of 0.34-0.47V in the whole operation stage, the output voltage of SMFC fluctuates in the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com