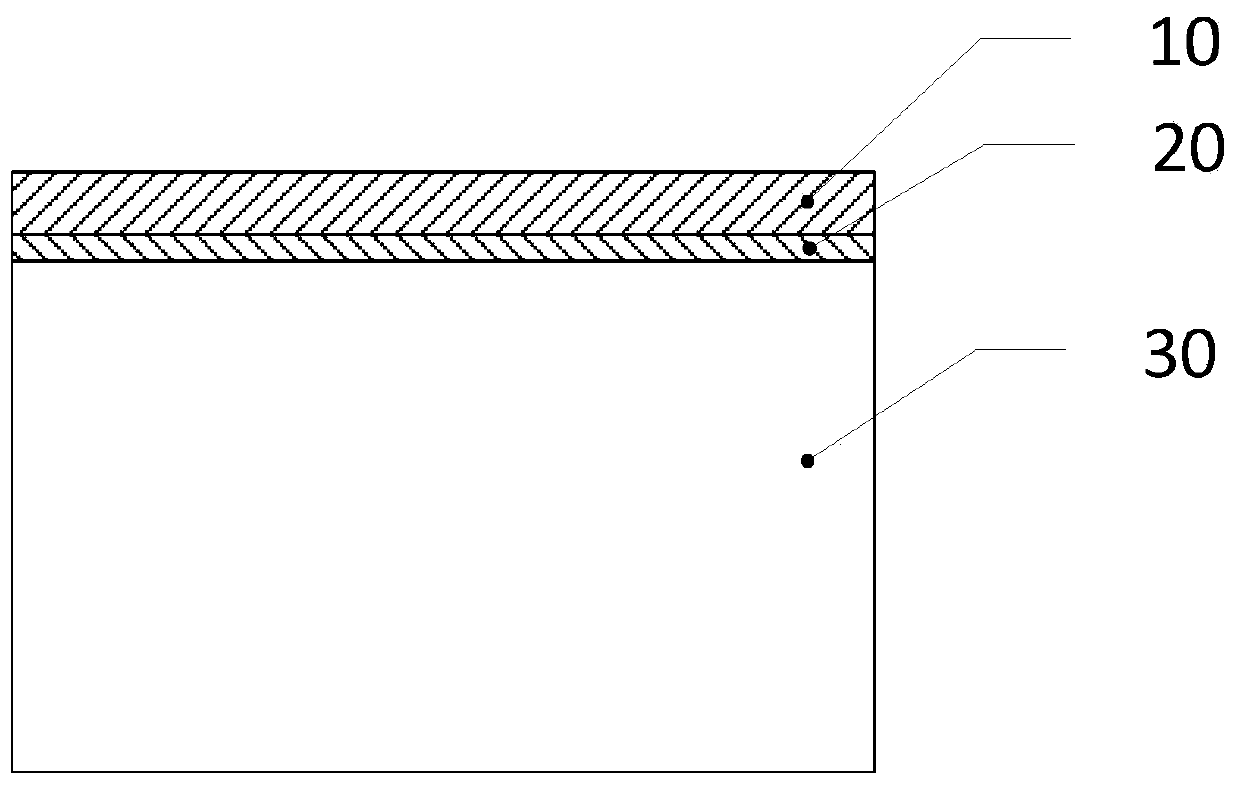
Method and application for preparing surface oxidized ceramic layers of zirconium and zirconium alloy
A technology of surface oxidation and oxidizing ceramics, which is applied in the field of medical implant materials, can solve the problems of adverse effects on the performance of the surface oxide ceramic layer, loss of thickness, and difficulty in meeting the use requirements of the surface oxide ceramic layer, so as to maintain integrity and uniformity. , to ensure the effect of protective performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
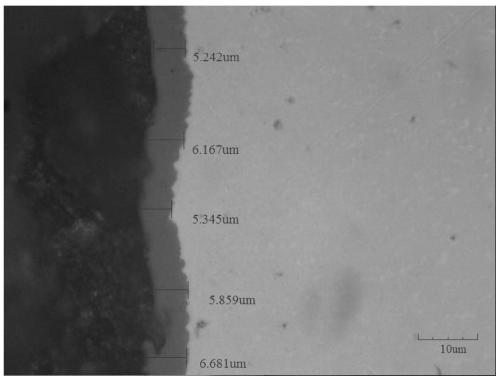
[0050] The Zr-2.5Nb alloy (zirconium alloy containing 2.5wt% Nb) is ground and polished to change the surface roughness. The surface roughness of sample 1 is reduced to Ra=0.3792 μm, and the surface roughness of sample 2 is reduced to Ra=0.0038 μm . Put sample 1 and sample 2 together in a tube furnace, heat to 550°C in the air environment, keep warm for 6 hours, exhaust the air and feed argon into the furnace, and slowly cool to 100°C at a cooling rate of 5°C / min. Take it out after it is below ℃, and measure it with a roughness meter. The roughness of sample 1 after oxidation treatment increases to Ra=0.6852 μm, and the roughness of sample 2 increases to Ra=0.0158 μm. The cross-sectional photo of sample 1 under the metallographic microscope after oxidation is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the oxide ceramic layer, the oxygen-rich diffusion layer and the metal substrate are arranged from left to right. Through grinding and polishing, the surface roughness of sample 1 is gradu...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The commercially pure zirconium was ground and polished to change the surface roughness. The surface roughness of sample 3 was reduced to Ra=0.3886 μm, and the surface roughness of sample 4 was reduced to Ra=0.0042 μm. Put sample 3 and sample 4 together in a tube furnace, heat to 600°C in the air environment, keep warm for 4 hours, exhaust the air and feed argon into the furnace, and slowly cool to 100°C at a cooling rate of 5°C / min. It was taken out after it was below ℃, and measured by a roughness meter. The roughness of sample 3 after oxidation increased to 0.7705 μm, and the roughness of sample 4 increased to 0.0158 μm. The cross-sectional photo of sample 3 under the metallographic microscope after oxidation is as follows: Figure 5 As shown, the surface roughness is gradually reduced to Ra=0.0177μm after grinding and polishing. Figure 6 shown. The surface roughness of sample 4 after oxidation has met Ra Figure 7 shown.
[0055] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The Zr-2.5Nb alloy was ground and polished to change the surface roughness. The surface roughness of sample 5 was reduced to Ra=0.0056 μm, and the surface roughness of sample 6 was reduced to Ra=0.0055 μm. Put sample 5 and sample 6 into the tube furnace respectively, heat to 600°C in the air environment, keep warm for 4 hours, after sample 5 exhausts the air and injects argon into the furnace, slowly cool at a rate of 5°C / min Take it out after cooling to below 100°C, and sample 6 is directly cooled to below 100°C in the original oxidation atmosphere at a cooling rate of 5°C / min and then taken out. Measured by the roughness meter, the roughness of the oxidized sample 5 increased to 0.0162 μm, and the roughness of the sample 6 increased to 0.0426 μm.
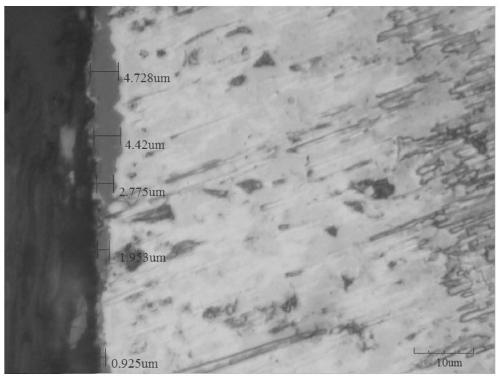
[0059] The cross-sectional photo of sample 5 under the metallographic microscope is as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the average thickness of the generated oxide ceramic layer is about 9.54 μm, the oxide ceramic layer has a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com