Biological-enzyme pretreatment method for regenerated cellulose fibers
A technology of regenerated cellulose and biological enzymes, which is applied in fiber treatment, ultrasonic/sonic fiber treatment, physical treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of washing, large damage to fabric fibers, and high COD emissions, and is conducive to environmental protection, resistant to Good abrasiveness and other indicators, and the effect of reducing pollution emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
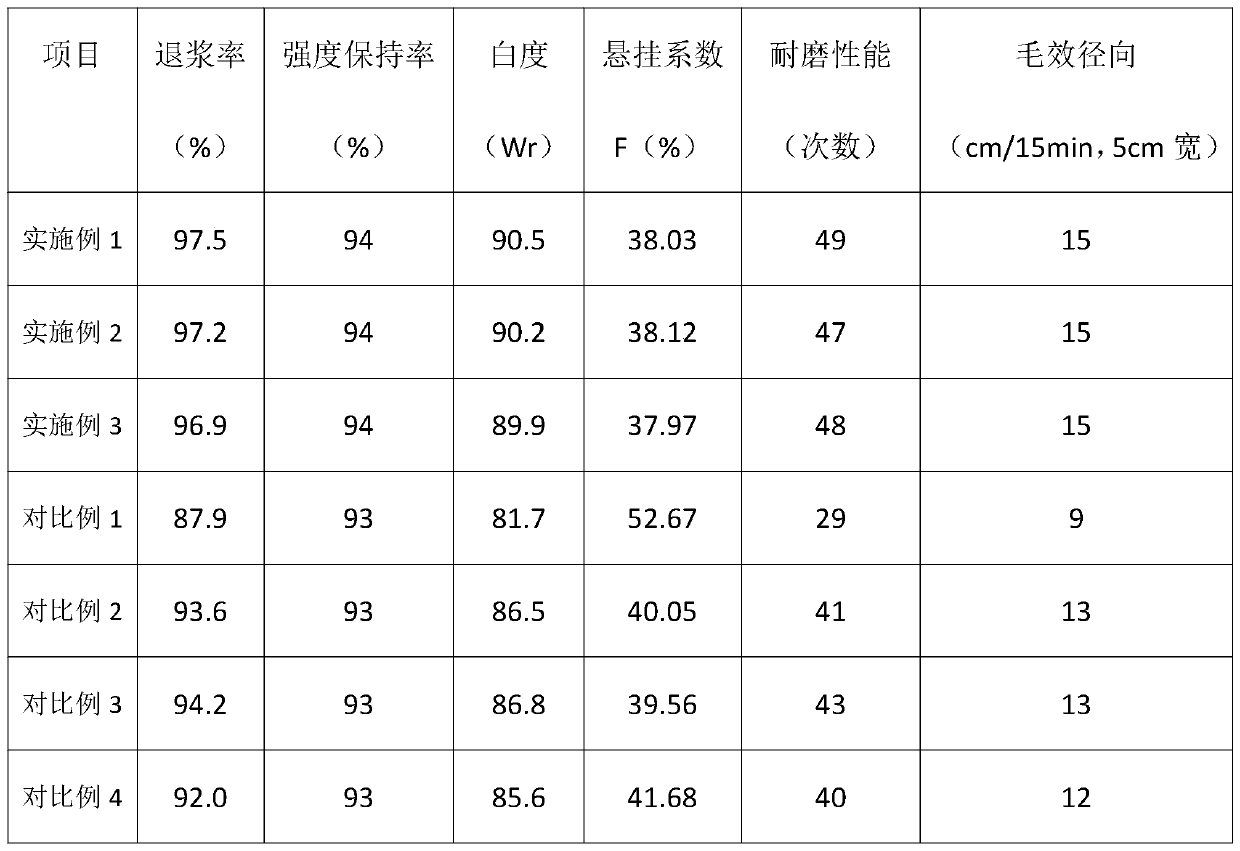
Embodiment 1
[0026] The invention provides a kind of viscose fiber biological enzyme pretreatment method, comprises the following steps:
[0027] Step 1, pretreatment: put the viscose fiber to be treated into the deionized aqueous solution at room temperature, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the deionized aqueous solution to 7.0, turn on the stirring device to stir, so that the deionized aqueous solution and the viscose fiber are mixed evenly, Then raise the temperature to 55°C and keep it warm for 30 minutes; then raise the temperature of the solution in the device to 65°C, keep the viscose fiber below the liquid level, continue to keep warm for 30 minutes, and then drain the solution; wash the viscose fiber with gradient cooling;
[0028] Step 2, biological treatment: control the temperature at 30°C, mix alkaline pectinase and amylase and add sodium lauryl sulfate to obtain an enzyme solution, put the enzyme solution in the device; turn on the stirring device to stir, and heat...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The invention provides a kind of viscose fiber biological enzyme pretreatment method, comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, pretreatment: put the viscose fiber to be treated into the deionized aqueous solution at room temperature, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the deionized aqueous solution to 8.0, turn on the stirring device to stir, so that the deionized aqueous solution and the viscose fiber are mixed evenly, Then raise the temperature to 65°C and keep it warm for 45 minutes; then raise the temperature of the solution in the device to 90°C, keep the viscose fiber below the liquid level, continue to keep warm for 45 minutes, and then drain the solution; wash the viscose fiber with gradient cooling;
[0037]Step 2, biological treatment: control the temperature at 40°C, mix alkaline pectinase and amylase and add sodium lauryl sulfate to obtain an enzyme solution, put the enzyme solution in the device; turn on the stirring device to stir, and heat ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The invention provides a kind of viscose fiber biological enzyme pretreatment method, comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, pretreatment: put the viscose fiber to be treated into the deionized aqueous solution at room temperature, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the deionized aqueous solution to 7.5, turn on the stirring device to stir, so that the deionized aqueous solution and the viscose fiber are mixed evenly, Then raise the temperature to 60°C and keep it warm for 35 minutes; then raise the temperature of the solution in the device to 70°C, keep the viscose fiber below the liquid level, continue to keep warm for 35 minutes, and then drain the solution; wash the viscose fiber with gradient cooling;
[0046] Step 2, biological treatment: control the temperature at 35°C, mix alkaline pectinase and amylase and add sodium lauryl sulfate to obtain an enzyme solution, put the enzyme solution in the device; turn on the stirring device to stir, and heat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| whiteness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com