Low-parameter heat recovery system
A heat recovery, low-parameter technology, applied in heat recovery systems, energy-saving heating/cooling, steam engine installations, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to realize thermal cycle, and achieve the effect of saving costs, improving work efficiency, and saving energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
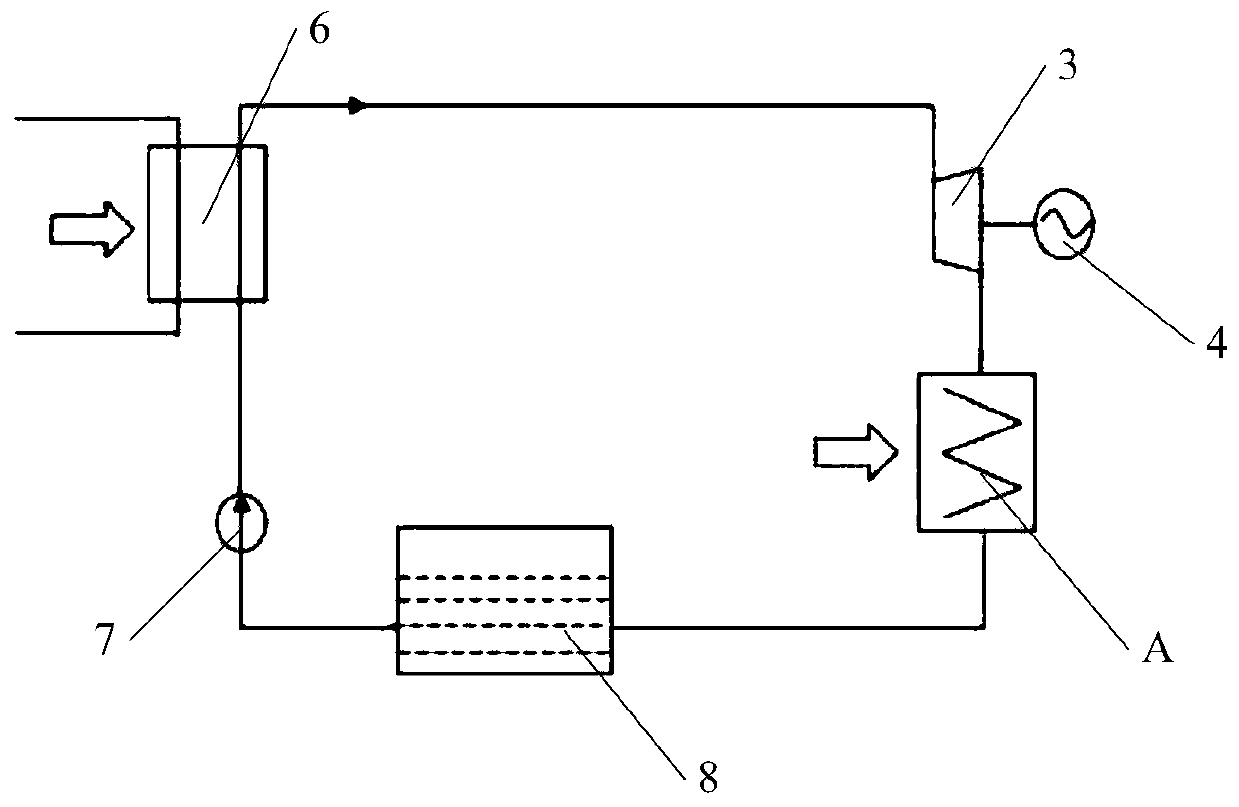
[0030] like figure 2 As shown, the low-parameter heat recovery system provided by this embodiment includes a first heat exchanger 1, a second heat exchanger 2, a steam turbine 3, a generator 4, a jet heat pump 5, a regenerator 6, a working medium pump 7 and a storage liquid tank8.
[0031] The liquid storage tank 8 is used to store the working medium liquid. Common working medium liquids include liquid nitrogen, liquid air, R410A refrigerant, liquid carbon dioxide, liquid hydrogen, liquid helium, etc. In this example, liquid nitrogen is preferably selected. The liquid nitrogen The temperature under normal pressure is -196°C, and 1 cubic meter of liquid nitrogen can be expanded to 696 cubic meters of pure gaseous nitrogen at 21°C. In the liquid state, a liquid discharge channel 81, a gas-liquid mixing channel 82, an exhaust channel 83, and a liquid inlet channel are arranged on it.
[0032] The working medium pump 7 adopts a cryogenic liquid pump, which is convenient for the...
Embodiment 2
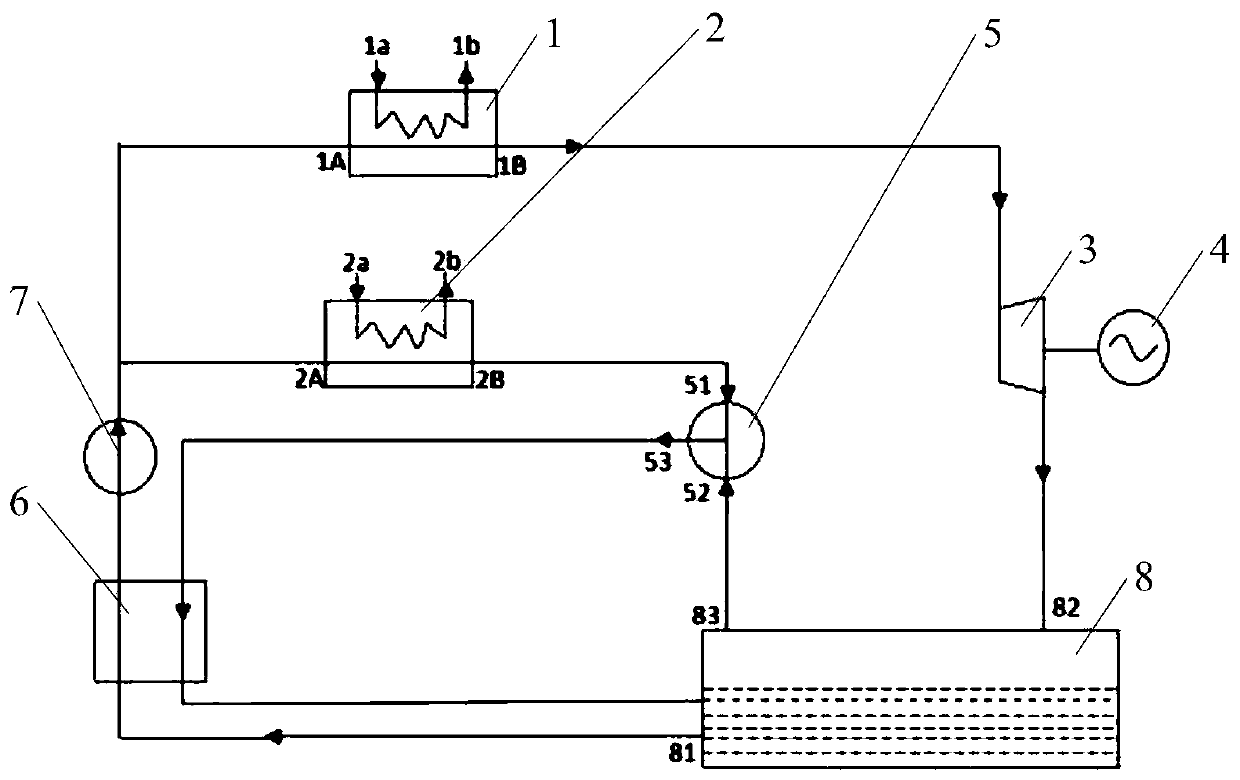
[0047] This embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the auxiliary circulation system is not changed, only one heat exchanger and two valves are added on the main circulation system, specifically, as image 3 As shown, the first heat exchanger 1 is connected with a third heat exchanger 9, and a first valve 10 is connected in parallel to the first heat exchanger 1, and a second valve 11 is connected in parallel to the third heat exchanger 9. .
[0048] The external recovery of waste heat in this embodiment adopts the ambient heat source, and the main circulation system of this embodiment uses a two-stage heat exchanger to exchange heat between the liquid nitrogen and the ambient heat source, so that the ambient heat source cools down, the liquid nitrogen is heated into nitrogen gas, and the steam turbine 3 can be operated Drive the engine to generate electricity, and then the ambient heat source cools down and then blows it into the air through the fan to cool ...
Embodiment 3
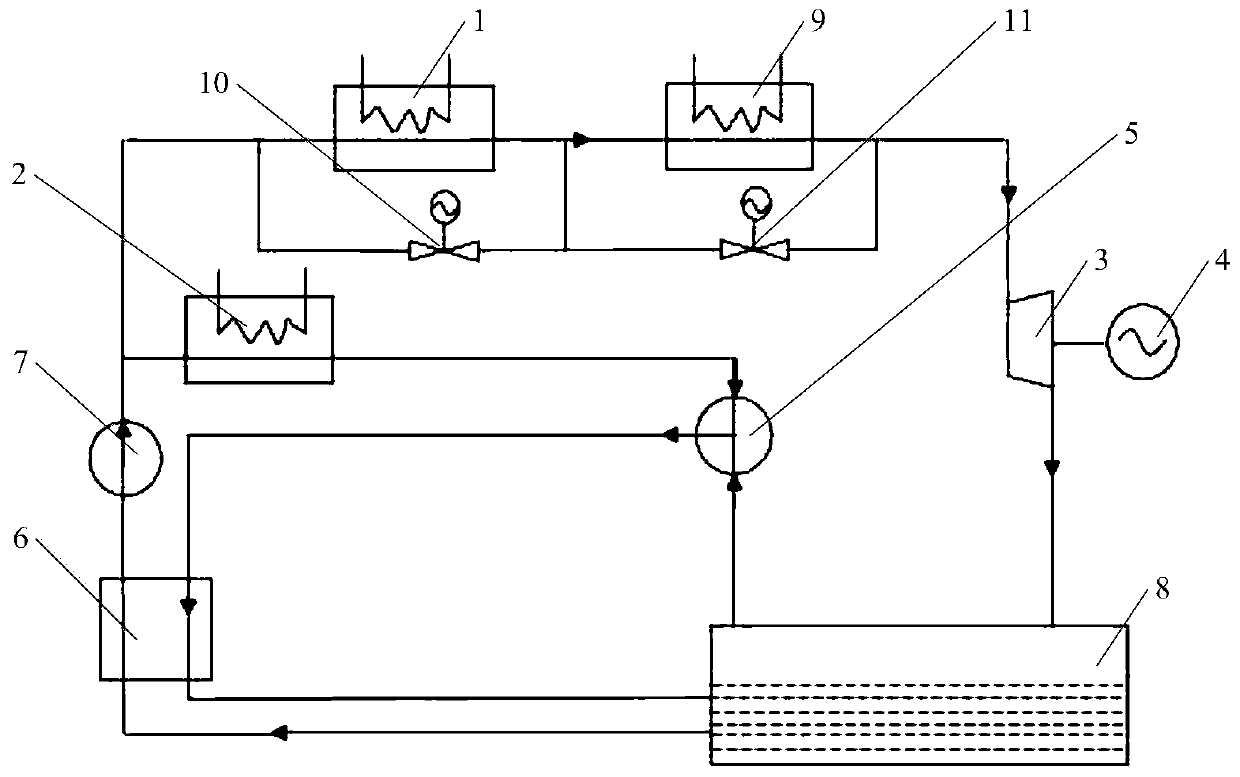
[0050] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 2, the auxiliary circulation system is not changed, only the same number of heat exchangers and valves are added to the main circulation system, and its connection structure is the same as that of the third heat exchanger 9 and the second valve 11, specifically like Figure 4 As shown, add N heat exchangers, N=1, 2, 3, ... n (n is an integer), the heat exchanger will take away the heat energy of the room, concentrate the heat energy and flow it into the steam turbine 3 to do work, and drive the generator 4 to generate electricity , Adjusting the opening of the valve, or the flow rate of the low-temperature working medium, can adjust the cooling capacity. The combined cooling and power generation system provided in this implementation case performs combined cooling and power generation for various buildings, residential areas, industrial areas, large enterprises, and urban complexes. Buildings, residential quarters, in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com