A dual-path combined hydrogen production method driven by low-grade thermal energy
A low-grade, thermal energy technology, applied to cells, electrolytic components, electrolytic processes, etc., can solve the problems of high energy conversion loss, large energy consumption, and high electrode potential
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
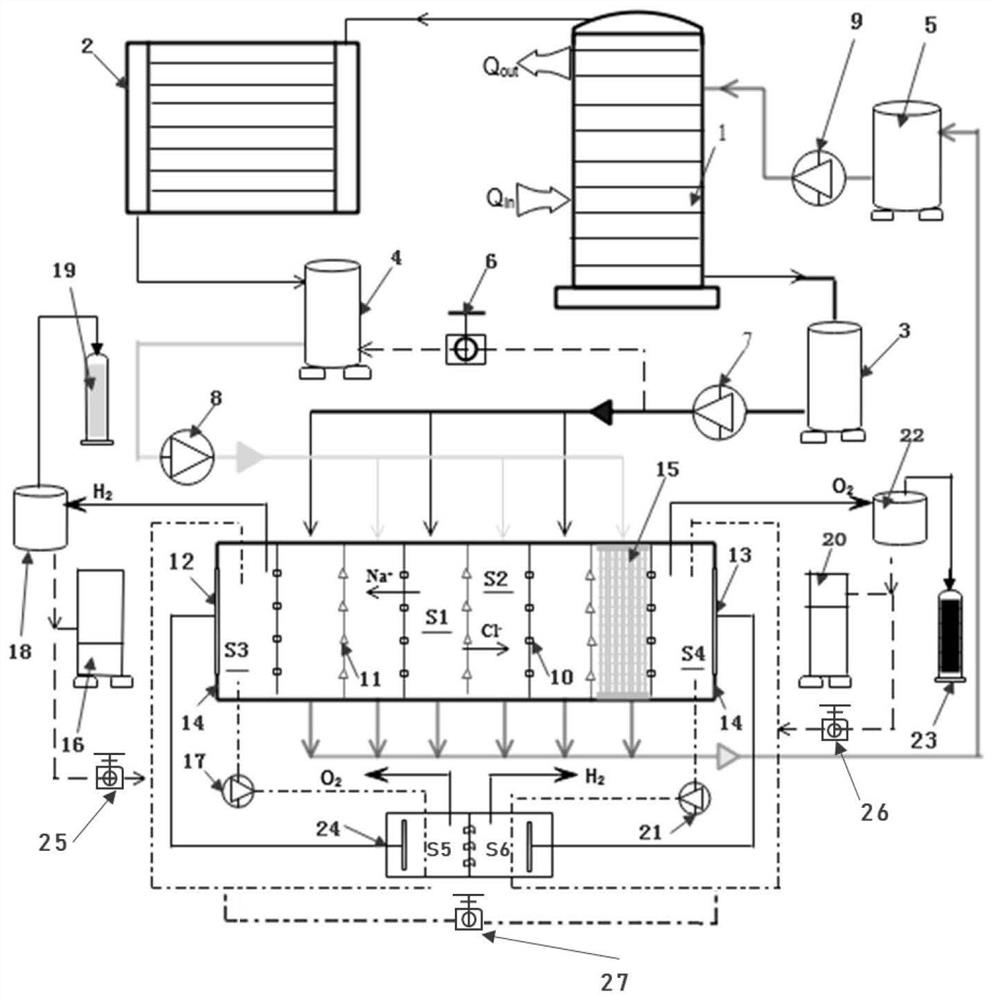
[0031] Embodiment 1: It is a low-grade thermal energy-driven dual-path combined hydrogen production method based on the principle of reverse electrodialysis, and its working principle is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0032] In the first step, the low-grade thermal energy stream (such as low-temperature heat transfer oil with a temperature of 120-130°C) enters the generator 1 from the inlet of the driving heat source at the bottom left of the generator 1, and the working solution (such as chlorination) is heated in the generator 1. Sodium aqueous solution, etc.), release heat and cool down to about 60°C, then leave the generator 1 from the outlet of the driving heat source on the upper left of the generator 1. After the waste liquid in the generator 1 is heated by the low-grade thermal energy stream, part of the solvent and a very small amount of solute will evaporate, and escape from the top of the generator in gaseous form and enter the condenser 2. After condensation, phase ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com