Xanthomonadins synthesis related gene and application thereof in constructing colorless xanthan gum genetically engineered bacteria
A technology of genetic engineering and xanthan gum, which is applied in the construction of colorless xanthan gum-producing engineering bacteria, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, large solvent consumption, and high production cost, so as to save production cost and improve product quality , The effect of simplifying the production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: Cloning of XC_4092 gene
[0037] This embodiment discloses the cloning method of XC_4092 gene, comprising the following steps:
[0038] S1. According to the DNA sequence of the XC_4092 gene, design a pair of amplification primers: Up primer and Down primer, the sequence of the Up primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, and the sequence of the Down primer is shown in SEQ ID NO.10;
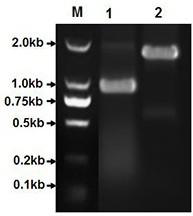
[0039] S2, to Xcc The total DNA of 8004 was used as a template, PCR amplification was carried out with Up primer and Down primer, and the XC_4092 gene fragment of about 740 bp was obtained;
[0040] S3. Ligate the XC_4092 gene fragment obtained in step S2 into the pMD19-T vector, and ligate at 16°C for 2 hours to obtain plasmid pYYH-1;
[0041]S4. Sequencing the plasmid pYYH-1 in step S3 to prove that the inserted gene fragment is correct.
[0042] What needs to be explained about the above steps is that the PCR amplification program in step S2 is: ①pre-denaturation at 95°C for 10 m...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: Construction of Gene Knockout Recombinant Plasmid
[0049] This example discloses a method for constructing a gene knockout recombinant plasmid, aiming to use two homologous recombination gene knockout methods to delete Xcc Gene XC_4092 in the 8004 genome, thereby achieving the purpose of constructing the engineering bacteria producing colorless xanthan gum. The construction method of the XC_4092 gene knockout recombinant plasmid is as follows:
[0050] S1. Design PCR primer pairs P1-F and P2-R for the upstream fragment of the XC_4092 gene (about 520bp), and PCR primer pairs P3-F and P4-R for the downstream fragment of the XC_4092 gene (about 570bp);
[0051] S2, to Xcc The total DNA of 8004 was used as a template, and the upstream fragment of the XC_4092 gene and the downstream fragment of the XC_4092 gene were respectively amplified by PCR;
[0052] S3. Using the fusion PCR method, using the upstream and downstream fragments of the XC_4092 gene obtaine...
Embodiment 3
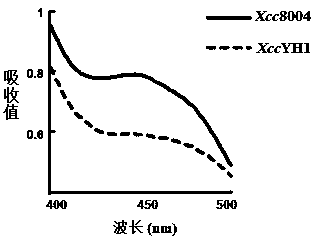
[0065] Embodiment 3: produce the construction of colorless xanthan gum engineering bacteria
[0066] This embodiment discloses a method for constructing a colorless xanthan gum-producing engineering bacterium, that is, constructing a colorless xanthan gum-producing engineering bacterium through two homologous recombination gene knockout methods, including the following steps:
[0067] S1, using CaCl 2 Prepare competent Escherichia coli S17-1 by induction method, introduce the recombinant plasmid pYYH-2 in Example 2 into competent Escherichia coli S17-1, and obtain transformants E. coli S17-1 / pYYH-2;
[0068] S2, the transformant obtained in step S1 E. coli S17-1 / pYYH-2 was introduced by conjugation transfer Xcc 8004, and then cultured on resistant plates, so that the XC_4092 gene deletion fragment on pYYH-2 was compatible with Xcc The XC_4092 gene fragment on the 8004 genome undergoes homologous recombination exchange, and the single colony grown on the resistance plat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com