Method for determining water-soluble protein content of soybean by near-infrared spectroscopy
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and water-soluble protein, which is applied in the field of near-infrared spectroscopy detection and can solve problems such as inaccurate content determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1 Establishment of soybean water-soluble protein near-infrared spectrum model
[0070] 1. Collection and analysis of spectral data of soybean samples
[0071] The instrument used in the test is a DA7200 near-infrared spectrum analyzer from Perten, Switzerland.
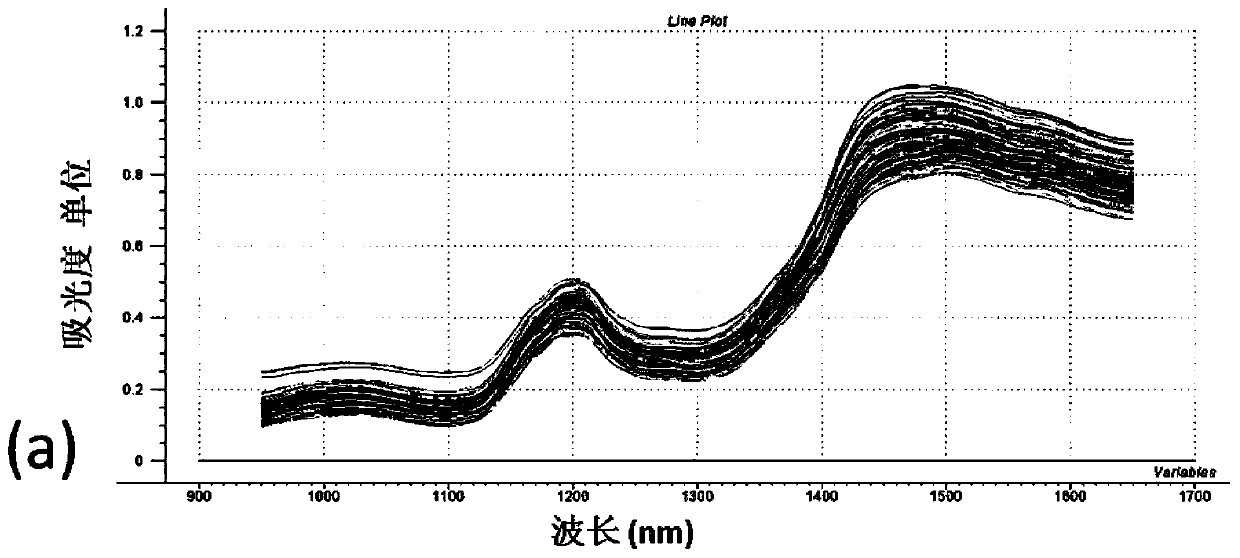
[0072] In this experiment, 186 soybean samples were selected, the seed coats of the soybean samples were removed, and they were placed in a sample rotating pool with a diameter of 75mm. Each sample was loaded and scanned 3 times to eliminate the influence of sample particle size, uniformity and inconsistency on the spectrum. , the instrument program automatically converts the reflectance spectrum information into absorbance values for storage, and uses the Unscrambler9.8 software of Perten Company to preprocess the spectrum and calculate the average spectrum.
[0073] 2. Extraction of soybean water-soluble protein
[0074] Crush the peeled soybeans, pass through a 60-mesh sieve, accurately weigh and ...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Comparison of different water-soluble protein extraction methods of embodiment 2
[0093] 1. Test steps:
[0094] The peeled soybeans were crushed to 60 mesh to obtain peeled soybean powder. Part of the peeled soybean powder is added to an aqueous solution to obtain a raw soybean milk solution. Divide the peeled soybean powder into five parts on average, each with 5g of soybean powder (0.0001g), and three of them are mixed with 50ml of water respectively, and the soybean powder solution after centrifugation is respectively separated by fast filter paper, medium speed filter paper and slow speed filter paper. Filter; Get a portion of peeled soybean powder and add 50ml of ether to dissolve the fat particles in the soybean powder, shake and dissolve and then centrifuge to pour off the ether; the remaining portion does not filter, as a control group ( figure 2 B).
[0095] Water-soluble protein is extracted with water at room temperature. Add defatted soybean samples to ...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3 Evaluation of Soybean Water-Soluble Protein Near Infrared Spectrum Model
[0105] 1. Experimental steps
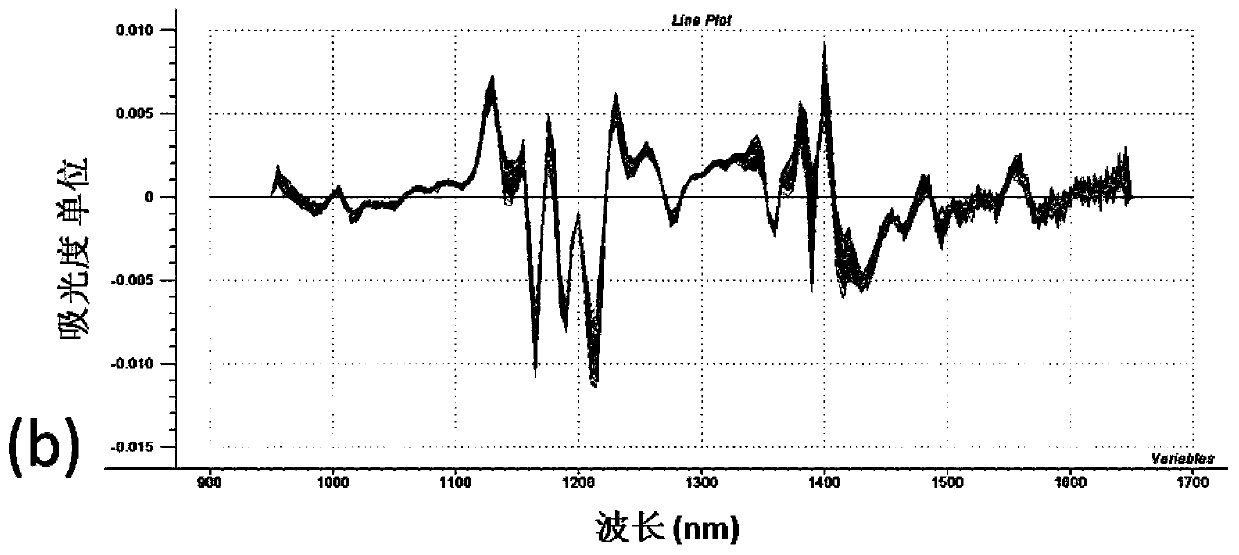
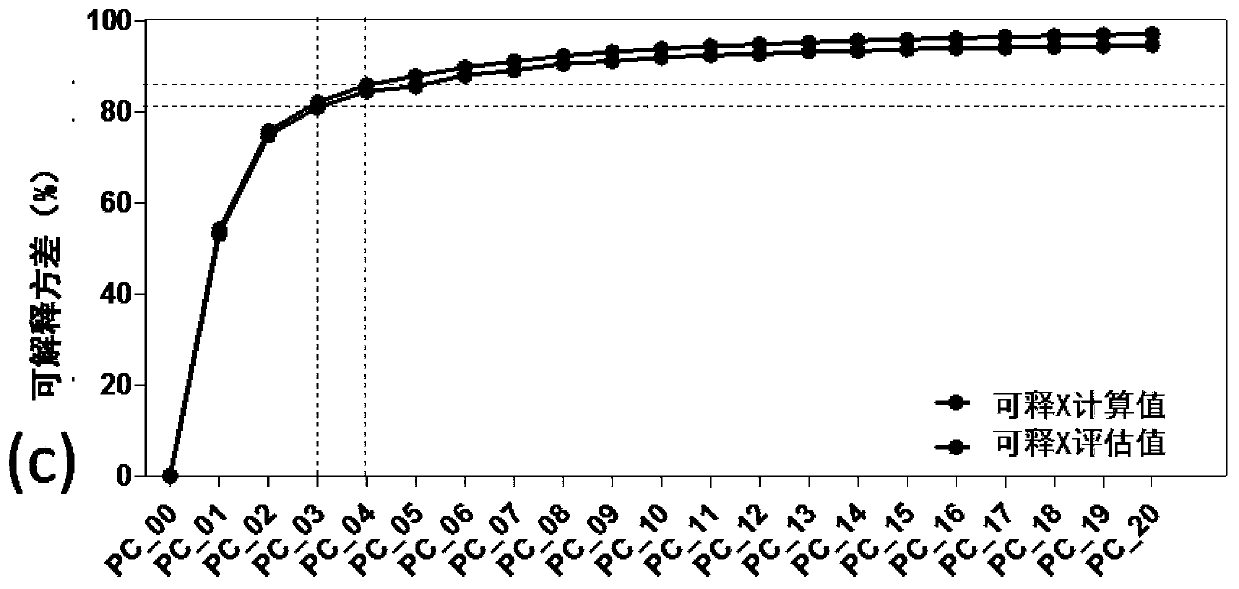
[0106] The outliers in the near-infrared spectrum were deleted, and the MSC+SG (second derivative) pretreatment method was used to obtain the WSPC (water-soluble protein content) PLS regression model. We selected 48 soybean varieties with different seed coat colors but yellow grain colors to construct the Soybean water-soluble protein was evaluated by near-infrared spectroscopy.
[0107] First, 48 soybean varieties were peeled and scanned by near-infrared spectroscopy to obtain predicted values. Then crush the peeled grains, pass through a 60-mesh sieve, accurately weigh and weigh 5g of soybean powder (0.0001g), mix with 50ml of ether, and shake continuously at 220r / min for 30min to fully dissolve the fat. Then centrifuge at 2000r / min for 10min, discard the supernatant, and place it in a fume hood for 30 minutes until the ether evaporates completely. Wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com