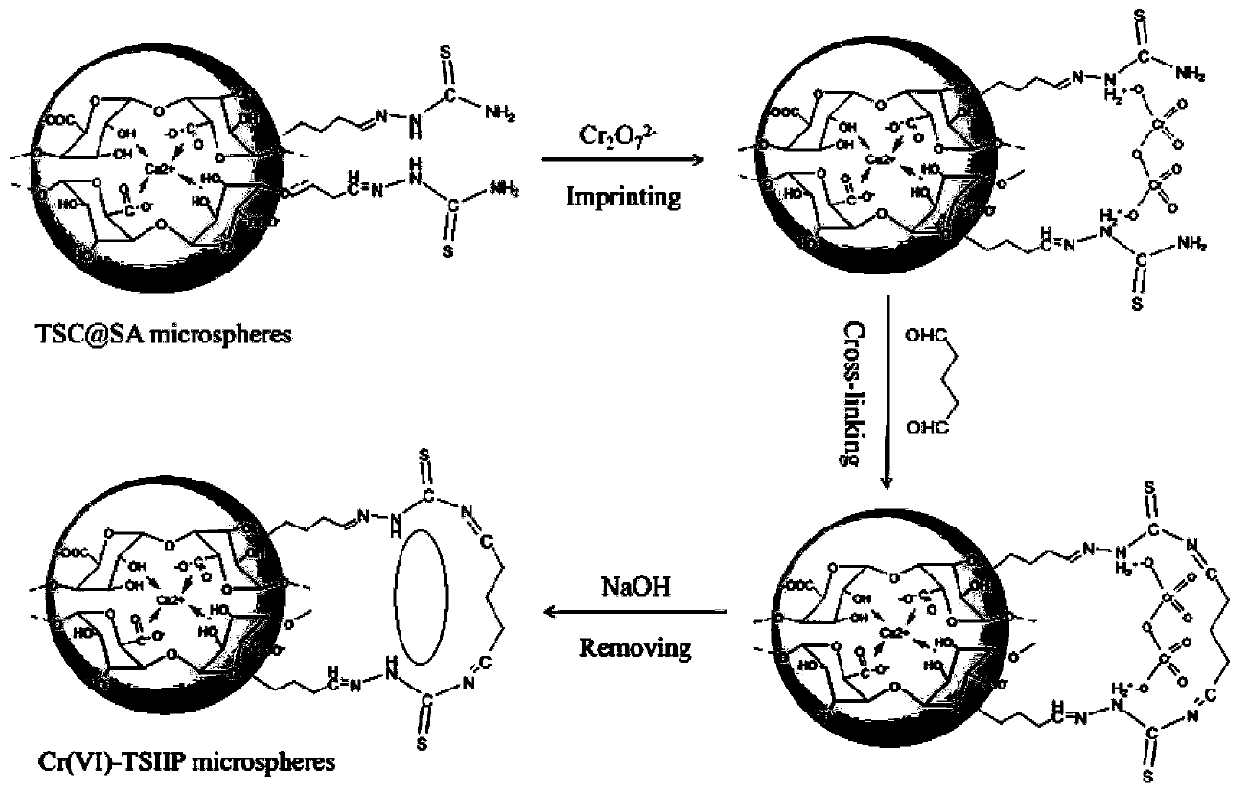
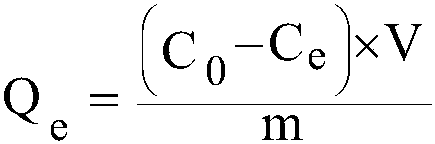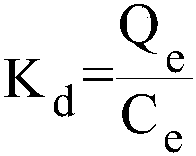Microsphere adsorbent for highly selective adsorption of Cr(VI) and preparation method and application thereof
A highly selective, microsphere adsorption technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of non-selective and poor adsorbents, and improve imprinting efficiency and adsorption. speed, high adsorption capacity, and the effect of avoiding difficult elution of template ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] (1) Dissolve 2g of sodium alginate powder in 100mL of deionized water to prepare a 2wt% sodium alginate solution, and then add it dropwise to 100mL of 1wt% CaCl 2 In the solution, stir while adding, drop completely within 2 hours, and the magnetic stirring speed is 300rpm; cross-link at room temperature for 7 hours, filter, and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres;
[0057] (2) Then drop the above-mentioned gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres into 50mL of thiosemicarbazide aqueous solution containing glutaraldehyde, wherein the mol ratio of sodium alginate repeating structural unit, glutaraldehyde, and thiosemicarbazide is 1: 1:1, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 4-5, keep the temperature at 65°C, and react with magnetic stirring for 6 hours at a magnetic stirring speed of 600rpm; filter and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain thiosemicarbazide-modified sodium alginate microspheres;...
Embodiment 2
[0066] (1) Dissolve 2g of sodium alginate powder in 100mL of deionized water to prepare a 2wt% sodium alginate solution, and then add it dropwise to 100mL of 1wt% CaCl 2 In the solution, stir while adding, drop completely within 1 hour, the magnetic stirring speed is 500rpm; cross-link at room temperature for 6 hours, filter, and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres;
[0067] (2) Then the above-mentioned gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres are dropped into 60mL of thiosemicarbazide aqueous solution containing glutaraldehyde, wherein the mol ratio of sodium alginate repeating structural unit, glutaraldehyde, and thiosemicarbazide is 2: 1:1, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 4-5, keep the temperature at 60°C, and react with magnetic stirring for 5 hours at a magnetic stirring speed of 500rpm; filter and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain thiosemicarbazide-modified sodium alginate microsphere...
Embodiment 3
[0076] (1) Dissolve 2g of sodium alginate powder in 100mL of deionized water to prepare a 2wt% sodium alginate solution, and then add it dropwise to 100mL of 1wt% CaCl 2 In the solution, stir while adding, drop completely within 2 hours, the magnetic stirring speed is 400rpm; cross-link at room temperature for 6 hours, filter, and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres;
[0077] (2) Then drop the above-mentioned gelatinous sodium alginate microspheres into 70mL of thiosemicarbazide aqueous solution containing glutaraldehyde, wherein the mol ratio of sodium alginate repeating structural unit, glutaraldehyde, and thiosemicarbazide is 1: 1:1, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 4-5, keep the temperature at 65°C, and react with magnetic stirring for 6 hours at a magnetic stirring speed of 600rpm; filter and wash repeatedly with deionized water to obtain thiosemicarbazide-modified sodium alginate microspheres;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com