Method for purifying nano-antibody drug by employing Protein A affinity chromatography
A nanobody and chromatographic purification technology, which is applied in peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve high purity, unsatisfactory, poor specificity of nickel affinity chromatography, etc., to achieve Shortened purification time, simple operation, and high protein loading capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0045] Example 1. Selection of Protein A Column
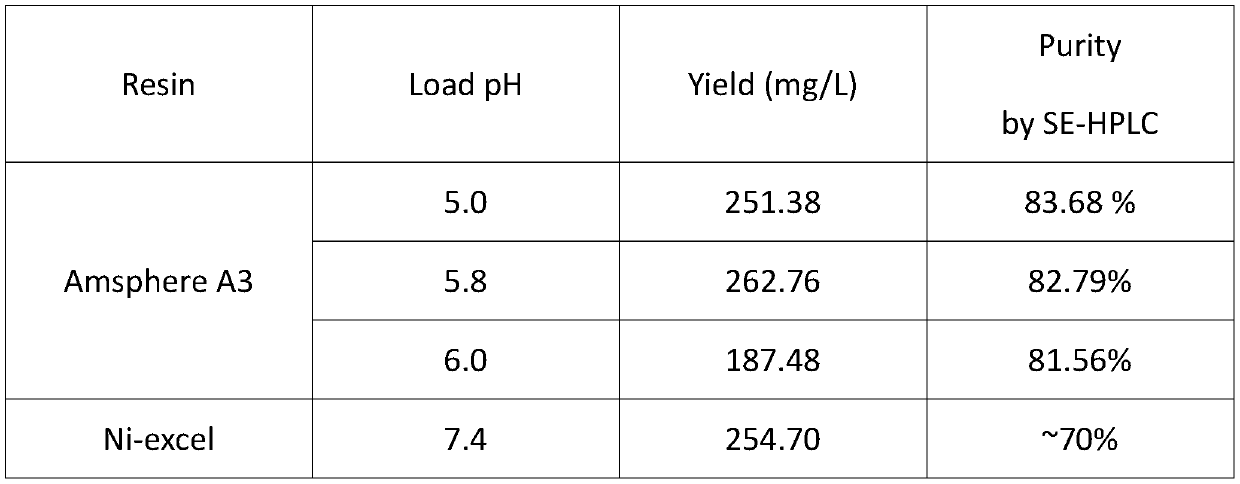
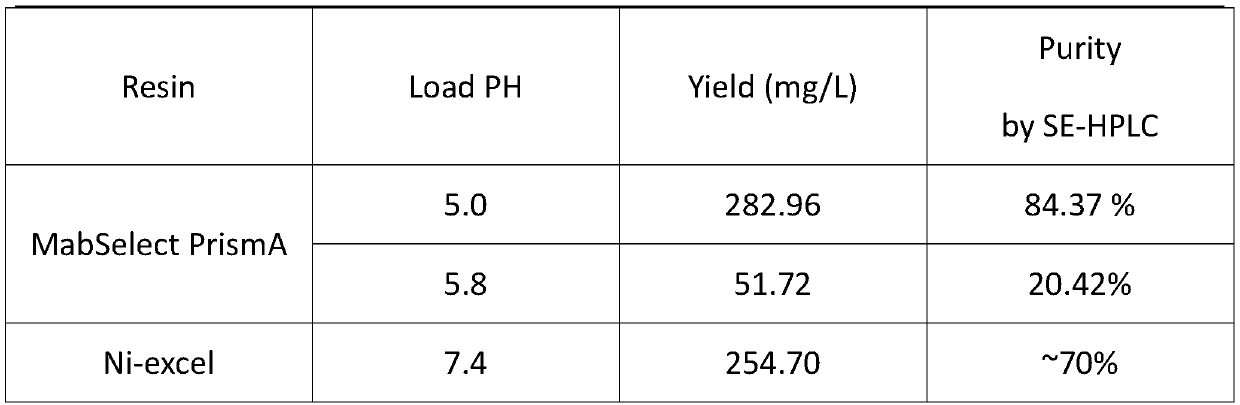
[0046] At present, there are many brands and types of Protein A on the market. Common ones include GE's MabSelect series, Bio-rad, Thermo Fisher, Toyopearl and Sigma. Among them, the MabSelect series are the most widely used, including sub-series such as SuRe, PrismA and Xtra. These Protein A fillers are all modified and recombinantly expressed on the basis of Staphylococcus aureus protein A. The dynamic load, affinity, specificity or purity, repeatability, alkali resistance and other stability of the purification, endotoxin And host protein control has been improved to varying degrees. In the process of protein A filler restructuring, Protein A of different brand series will also show conformational differences, which will generate specific affinity for several relatively constant polar or charged amino acid residues in the framework of the Nanobody. This application screened and selected JSR LifeSciences Amsphere TM A3, GE Ma...
example 2
[0056] Example 2. Adjust the sample to realize the affinity of Nanobody and Protein A
[0057] Several constant residues in the framework region of Nanobody achieve affinity with Protein A based on charge interactions, but the culture conditions of antibody-expressing cells are usually neutral pH, and the pI values of these polar or charged residues are mostly around 6.5. Some are lower and negatively charged at neutral pH. The experimental results show that when the sample pH is not adjusted and the sample is loaded under neutral conditions, a large amount of protein is present in the flow-through fluid and cannot be effectively combined with the filler. When the pH of the sample is adjusted to 5.0-5.8, the charged properties or the amount of charge of the constant residues in the framework region will be changed, which will enhance the affinity of the Nanobody and Protein A, and the protein will be completely bound to the filler. Through verification, when the pH of the samp...
example 3
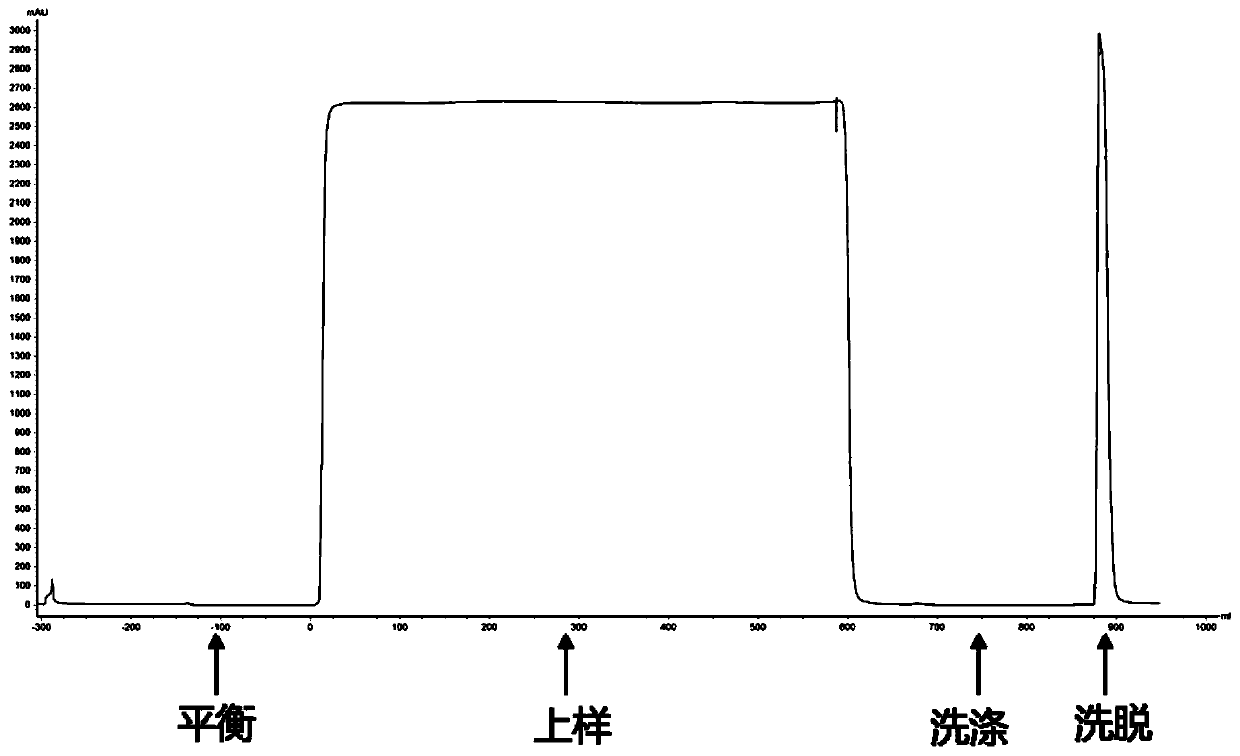
[0058] Example 3. Example of JSR Amsphere Protein A purified Nanobody
[0059] Equilibrate buffer: 0.1M Sodium Acetate, pH 5.0-6.0;
[0060] Wash buffer: 0.1M Sodium Acetate, pH 5.0-6.0;
[0061] Elution buffer: 0.1M Glycine, pH 3.5;
[0062] Regeneration buffer: 0.1M NaOH;
[0063] Storage buffer: 20% Ethanol;
[0064] (1) First adjust the pH of the Nanobody supernatant to 5.0-6.0;
[0065] (2) Equilibrate the chromatography column with an equilibration buffer of 10 times the column volume;
[0066] (3) Sample loaded and adjusted;
[0067] (4) Wash with 10 times the column volume of washing buffer;
[0068] (5) Elution with 15 times column volume of elution buffer;
[0069] (6) After complete elution, use 5 times the column volume of regeneration solution to regenerate and clean the residual protein;
[0070] (7) After equilibrating the column with 5 column volumes of equilibration buffer, store the column with 2 column volumes of storage solution.
[0071]
[0072] According to the results, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com