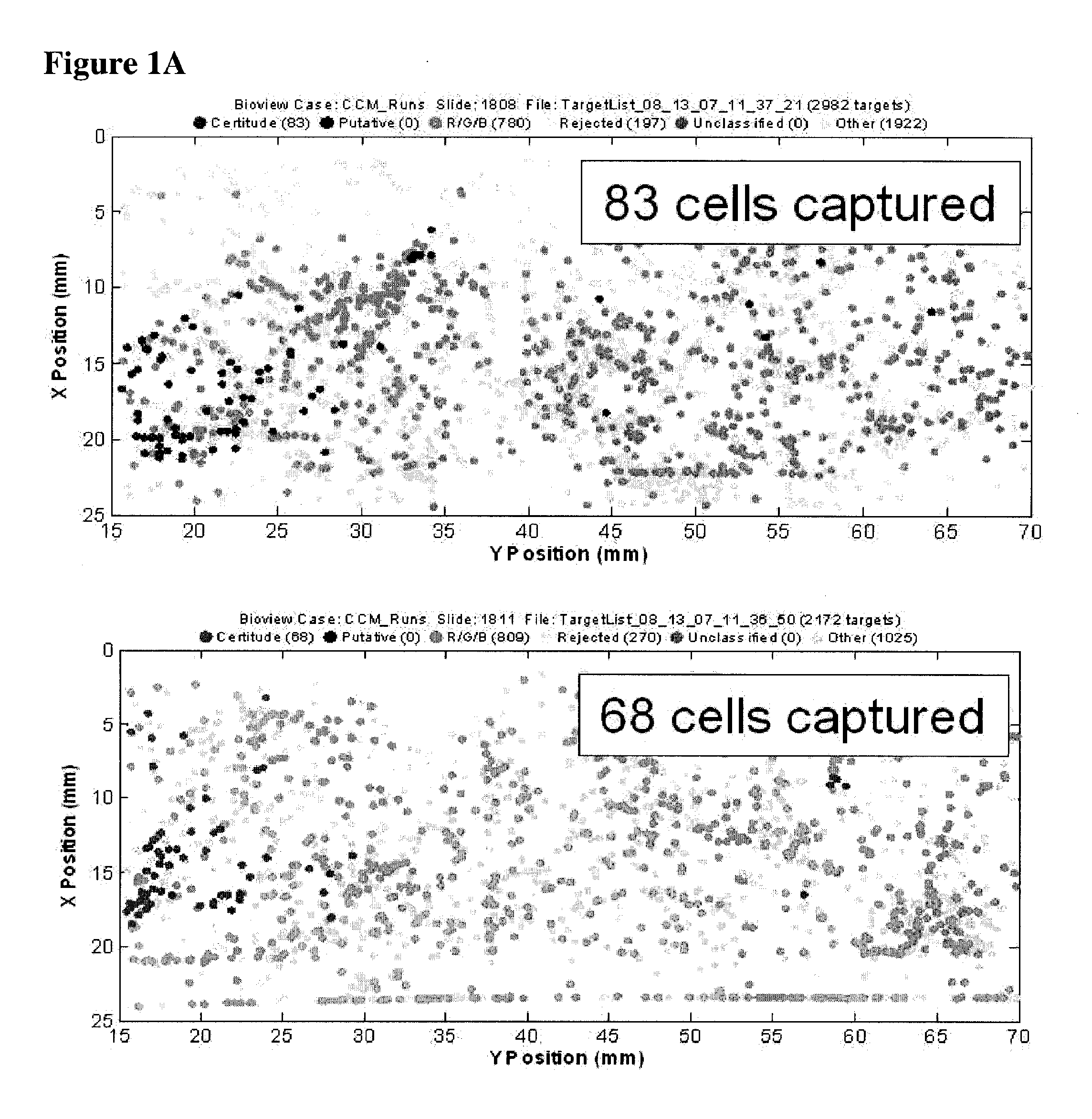
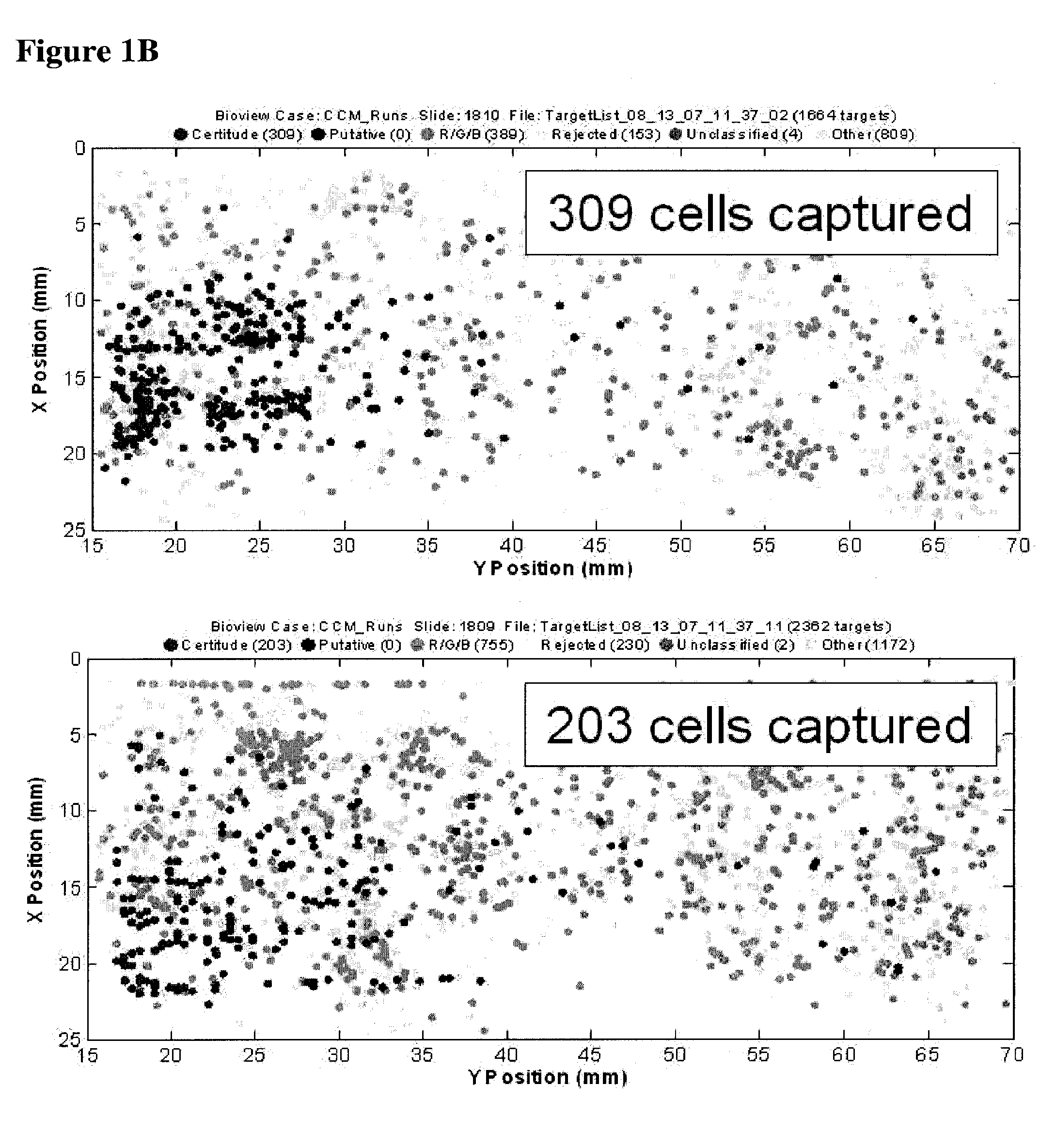
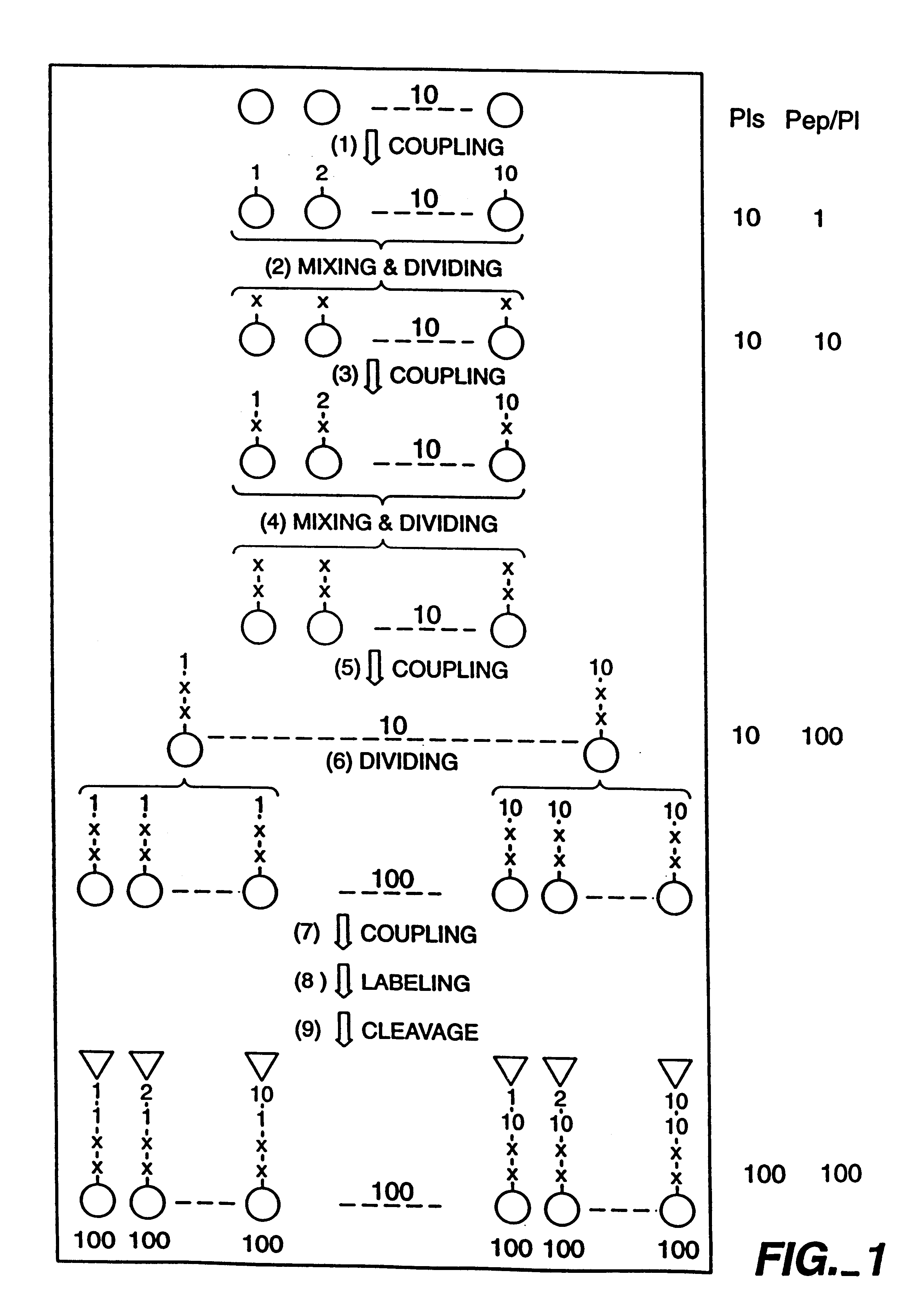
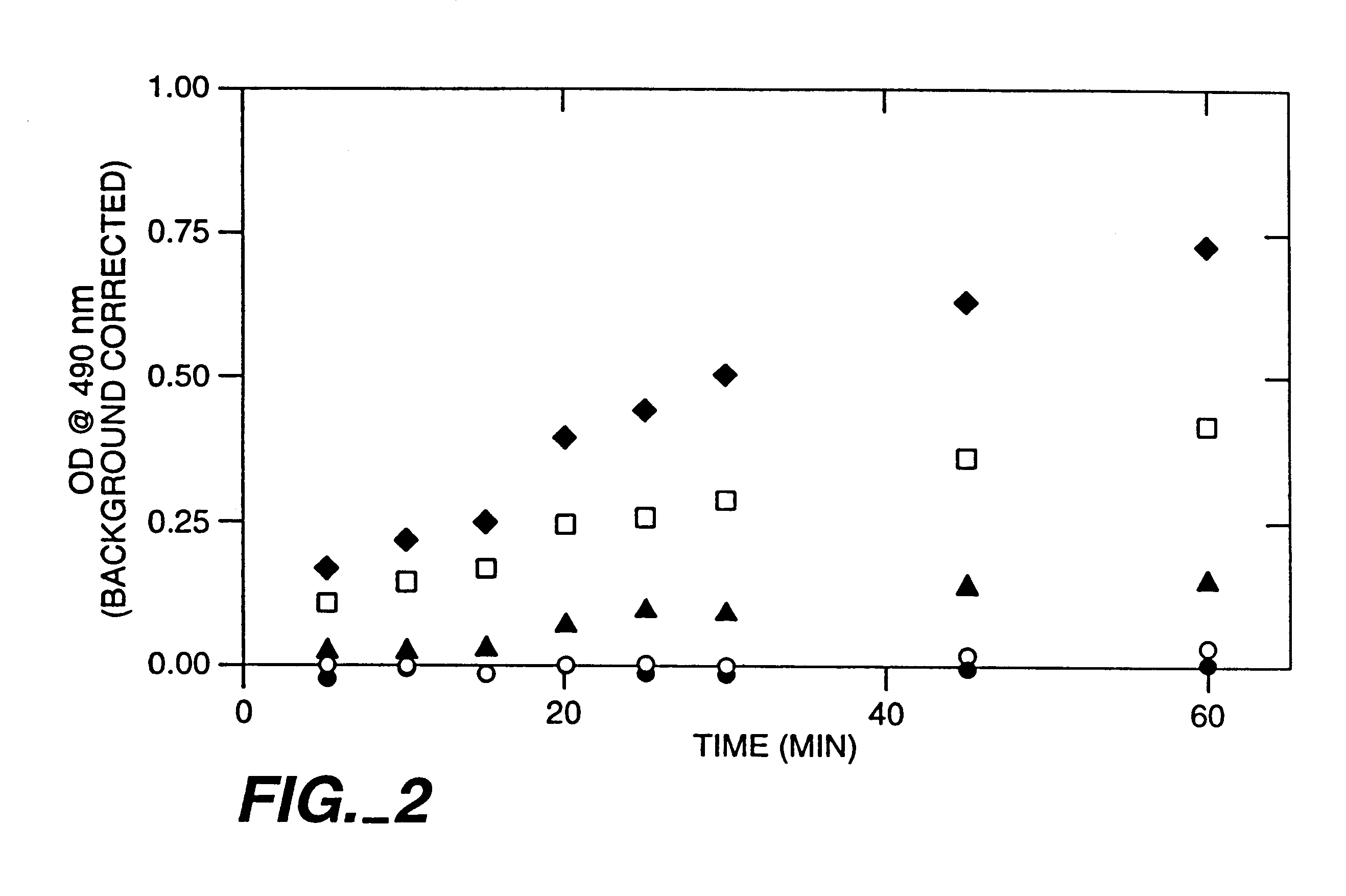
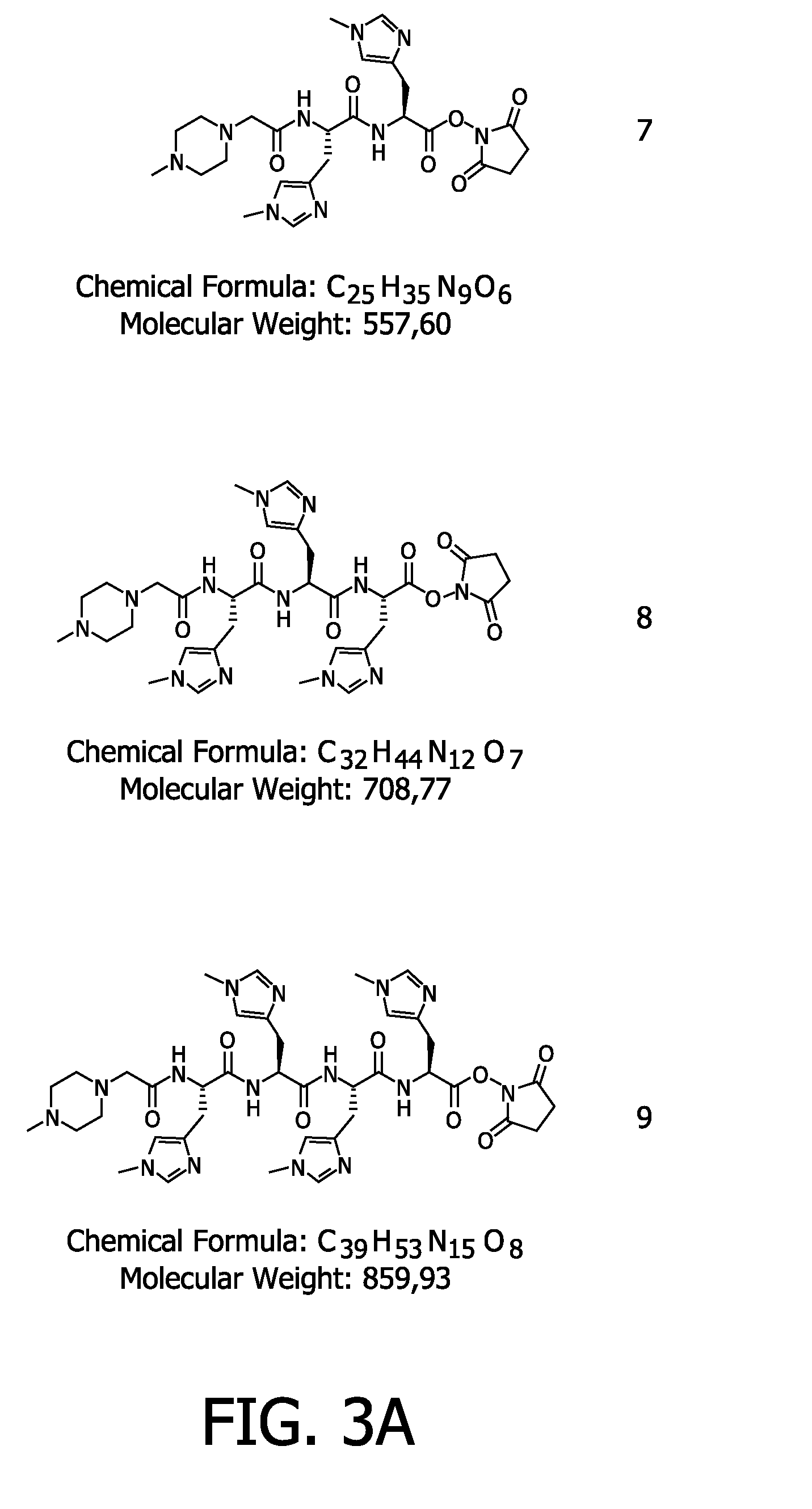
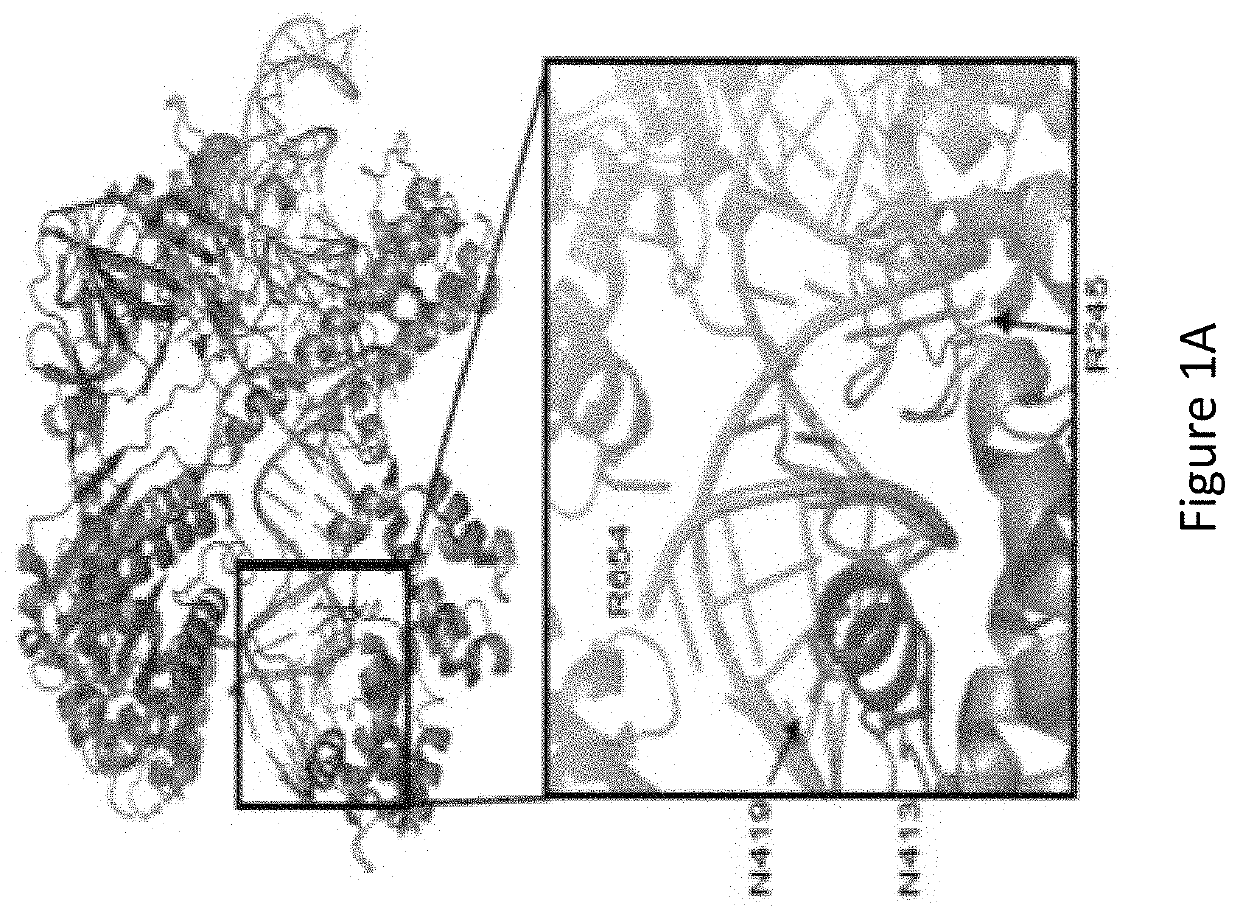
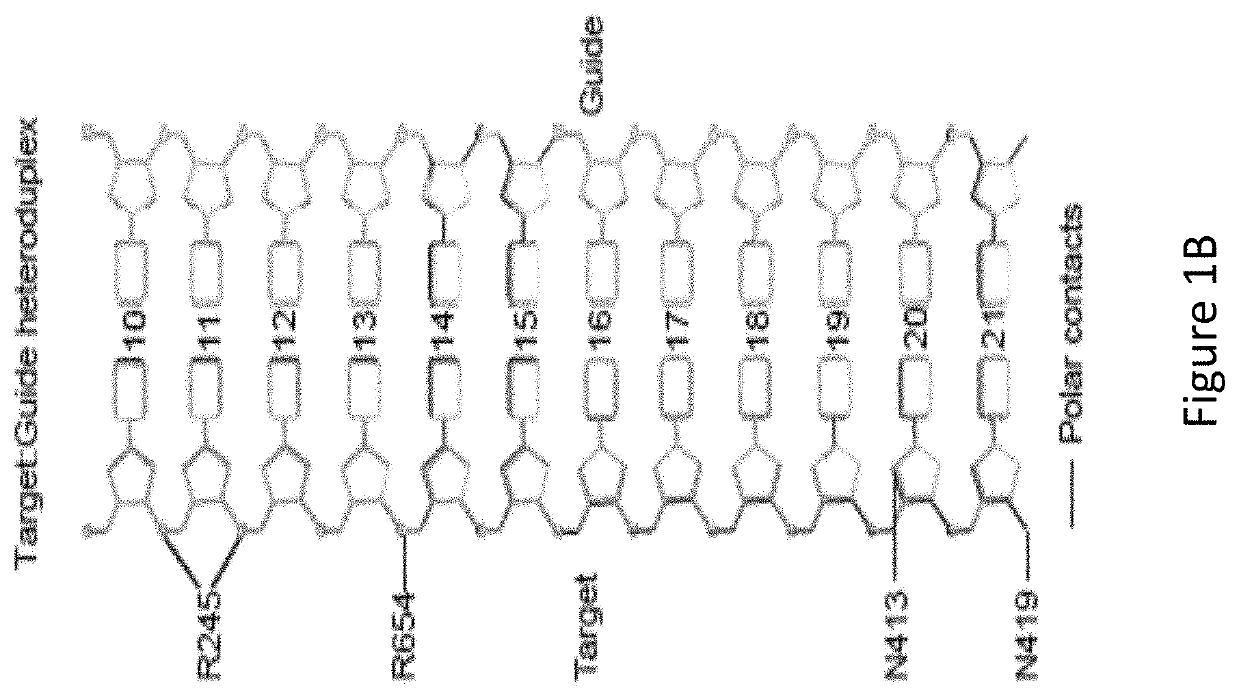
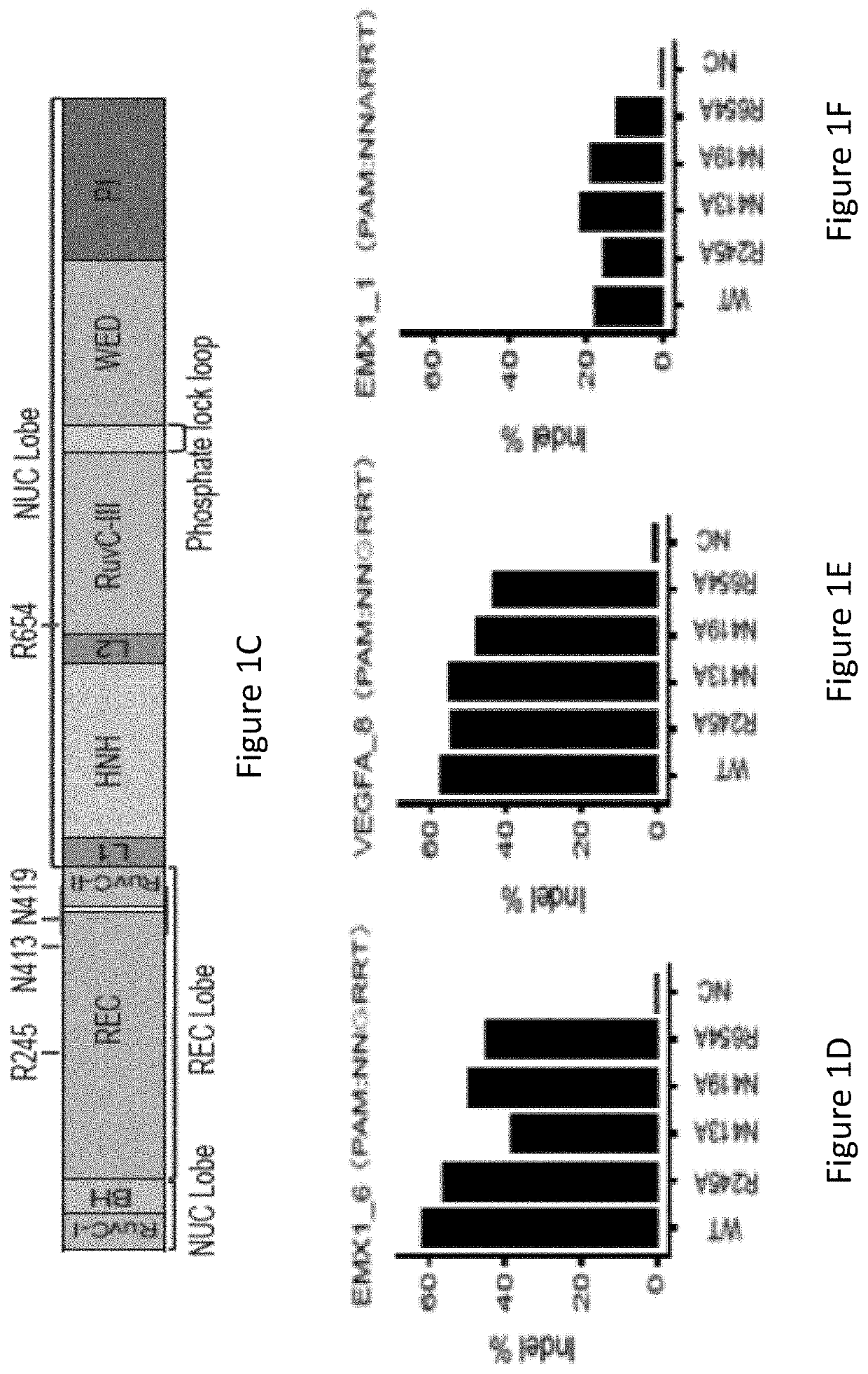
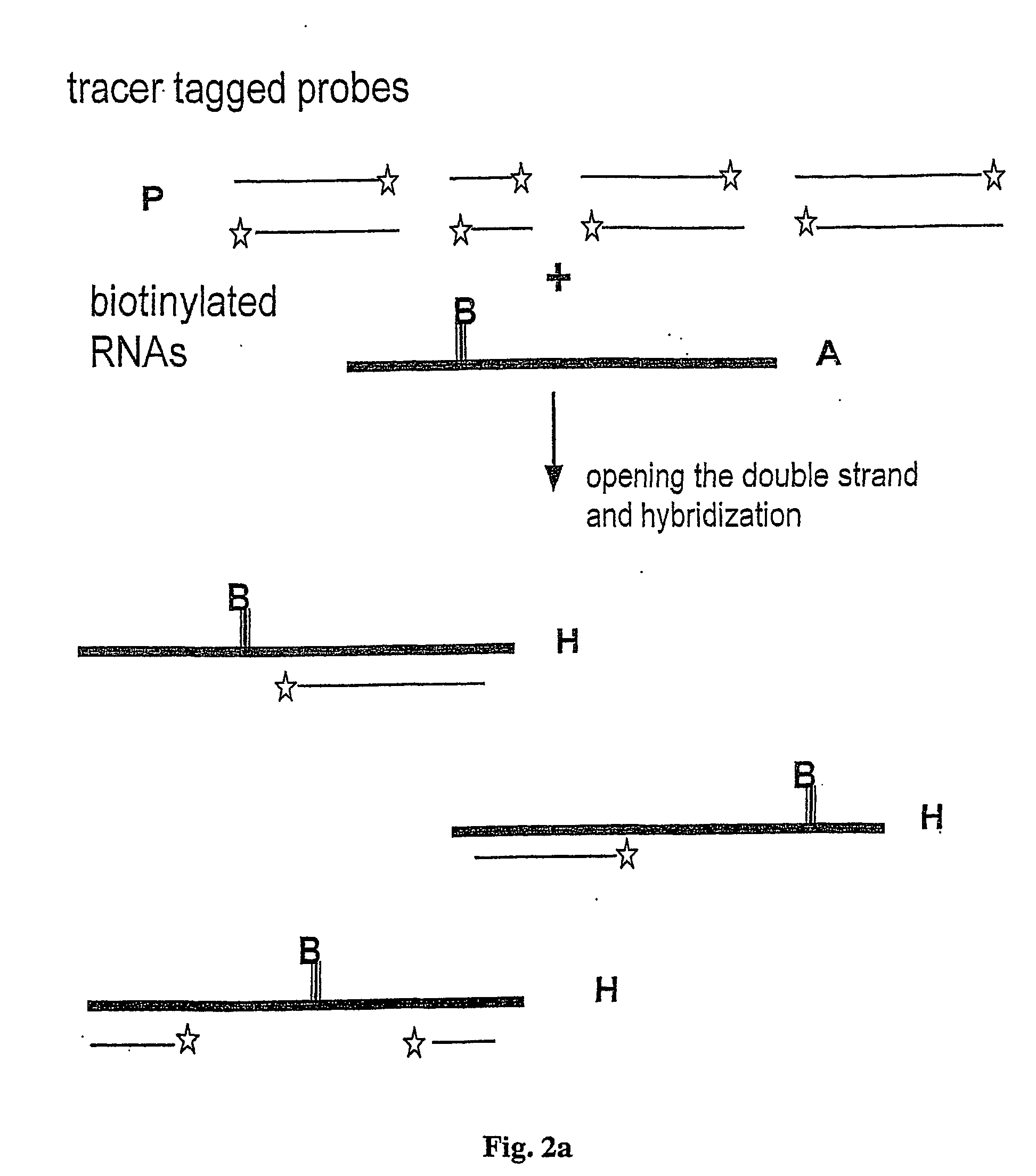Patents
Literature
33 results about "Affinity labeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of preferential labeling of specific binding molecules or sites in a mixture by coupling the label to the corresponding ligand; e.g., enzyme labeling by reactive dyes coupled to substrate.
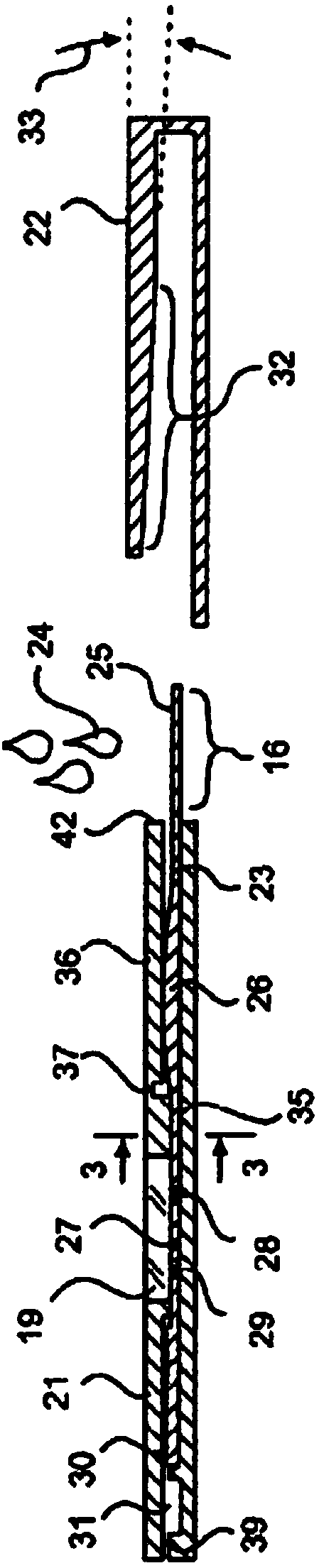
Tagged ligands for enrichment of rare analytes from a mixed sample
InactiveUS8008032B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellAnalyte
Method of enriching specific cells from cellular samples are disclosed, comprising contacting in solution a cellular sample with affinity-tagged ligands (ATLs) each comprising a first ligand linked to an affinity tag, wherein the ligand selectively binds a cellular marker of the rare cells and the affinity tag can be selectively captured by a capture moiety, wherein the affinity tags do not comprise a magnetic particle; and flowing the sample through a microfluidic device comprising the capture moiety to selectively retain ATL-bound cells. Methods for enriching circulating tumor cells, and devices for enriching specific cells from cellular samples are also disclosed.
Owner:GPB SCI
Tagged Ligands For Enrichment of Rare Analytes From A Mixed Sample
ActiveUS20090215088A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellAnalyte
Method of enriching specific cells from cellular samples are disclosed, comprising contacting in solution a cellular sample with affinity-tagged ligands (ATLs) each comprising a first ligand linked to an affinity tag, wherein the ligand selectively binds a cellular marker of the rare cells and the affinity tag can be selectively captured by a capture moiety, wherein the affinity tags do not comprise a magnetic particle; and flowing the sample through a microfluidic device comprising the capture moiety to selectively retain ATL-bound cells. Methods for enriching circulating tumor cells, and devices for enriching specific cells from cellular samples are also disclosed.
Owner:GPB SCI
Affinity labeling libraries and applications thereof
InactiveUS6277583B1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsCombinatorial chemistryAffinity labeling
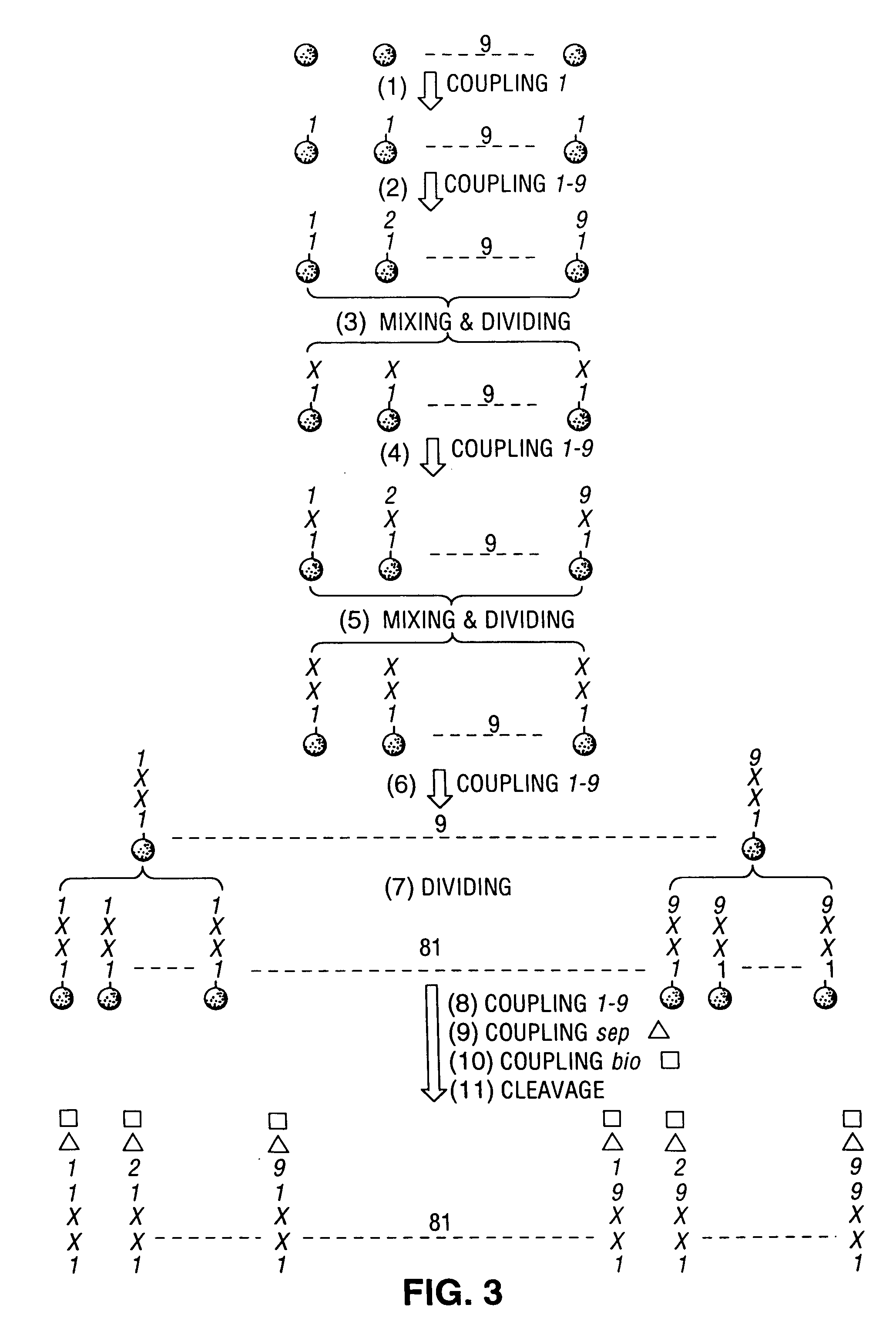
Novel methods and compositions are provided for preferentially bonding an oligomeric molecule to a macromolecular target where the target is a member of a complex mixture and / or there is preferential bonding at one of a plurality of available bonding sites of the macromolecular target. The methods represent a complete system for both producing and identifying affinity label molecules from a combinatorial library which preferentially bind to a marcomolecular target or target site and preferentially binding those affinity labels to a macromolecule of interest either ex vivo or in vivo. Macromolecular targets include a variety of cellular- and non-cellular-associated proteins.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Affinity markers for human serum albumin
InactiveUS7166695B2Eliminate side effectsProlong lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAffinity labelingIn vivo
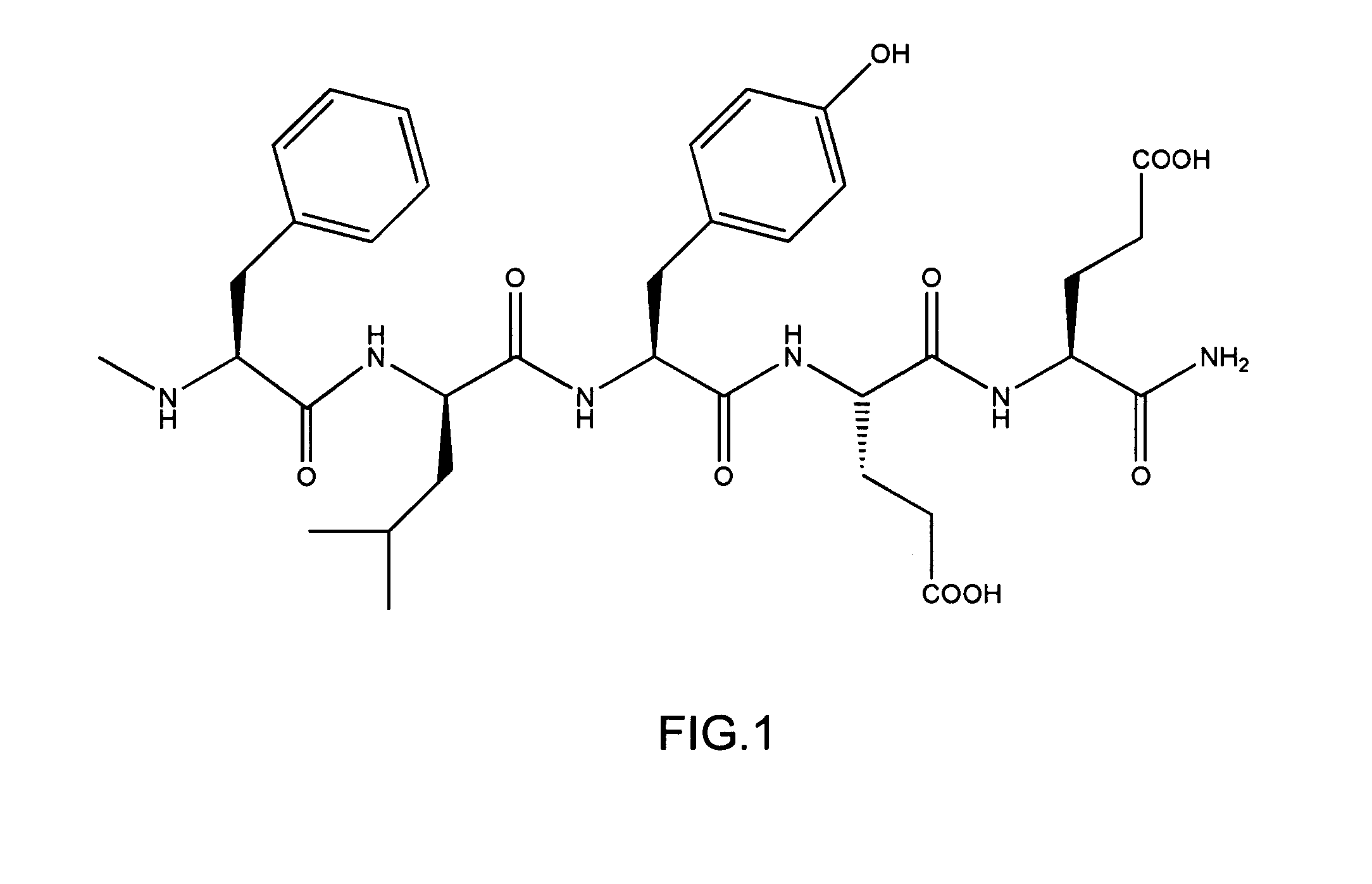
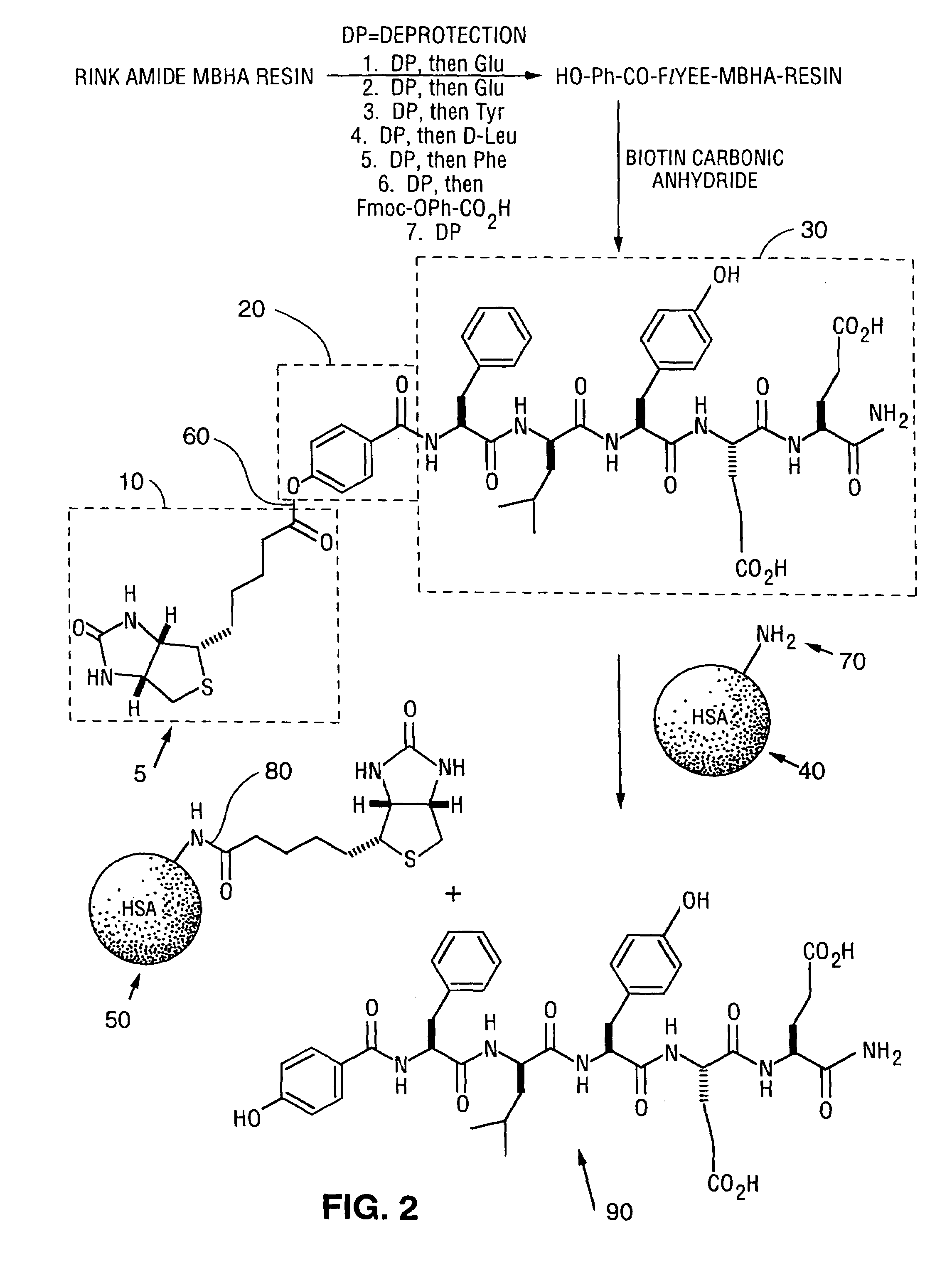
Methods and compositions are provided for identifying compounds having affinity or complementarity to a target molecule. Compounds according to the invention may be described by the formula E-Ca—R—Cb-A, wherein E is a therapeutic or diagnostic agent, R is a reactive group, Ca and Cb are connector groups between E and R and between R and A, respectively, and A is an affinity group comprising the sequence F-1-Y-E-E. Compounds according to the invention may be used for labeling the target molecule, particularly where the target molecule is naturally found in a complex mixture, such as a physiological fluid, like blood. By affinity labeling in vivo, the lifetime of physiologically active entities can be greatly enhanced by becoming bound to long-lived blood components. The covalently bound entity may also serve as an antagonist or agonist of a particular binding protein or as an enzyme inhibitor.
Owner:CONJUCHEM
Compositions and methods for purification and detection of hdl and apoa1
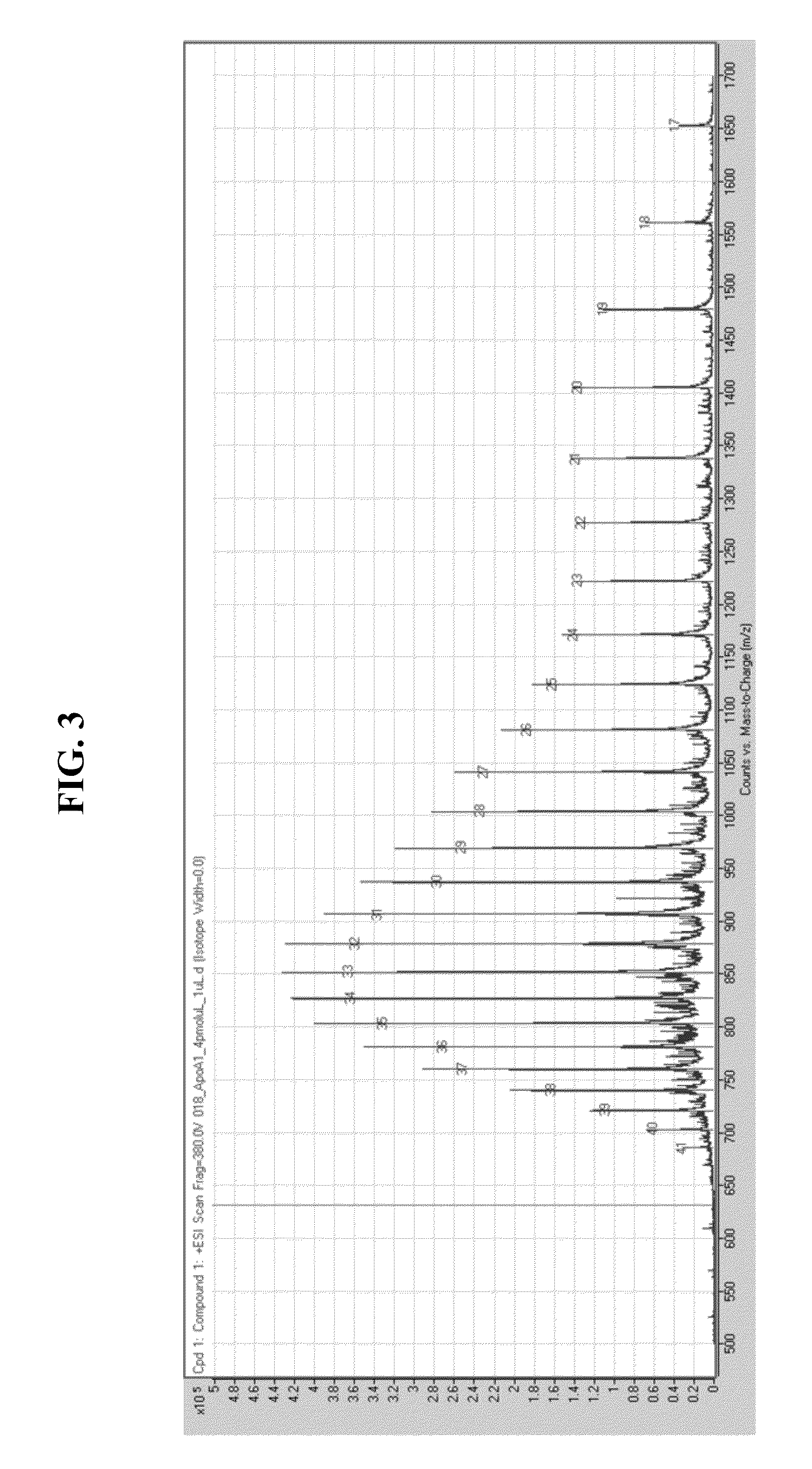
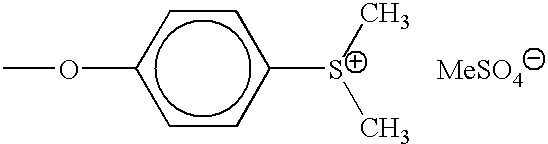
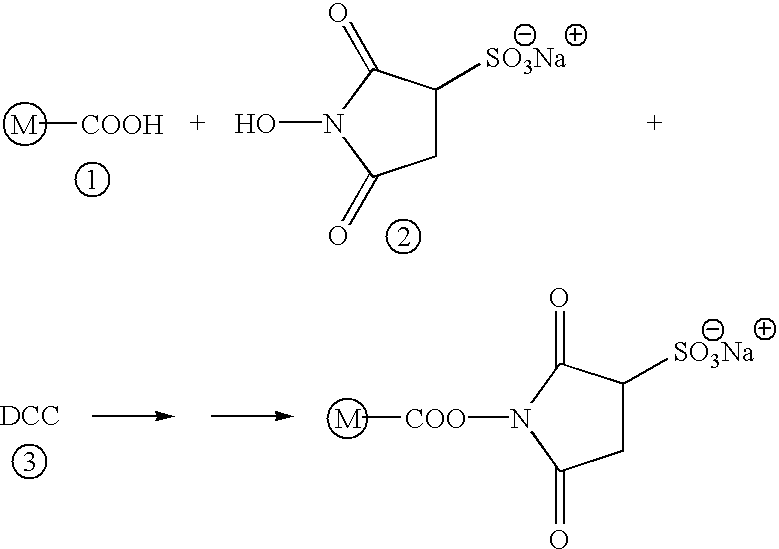
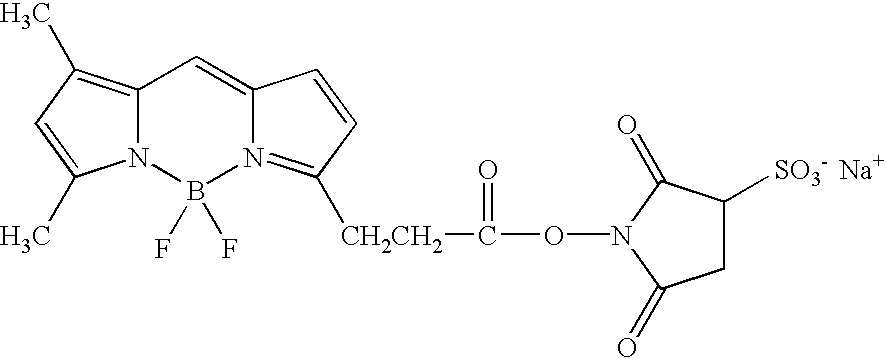
ActiveUS20150331000A1Quick purificationPeptide librariesApolipeptidesBinding peptideMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
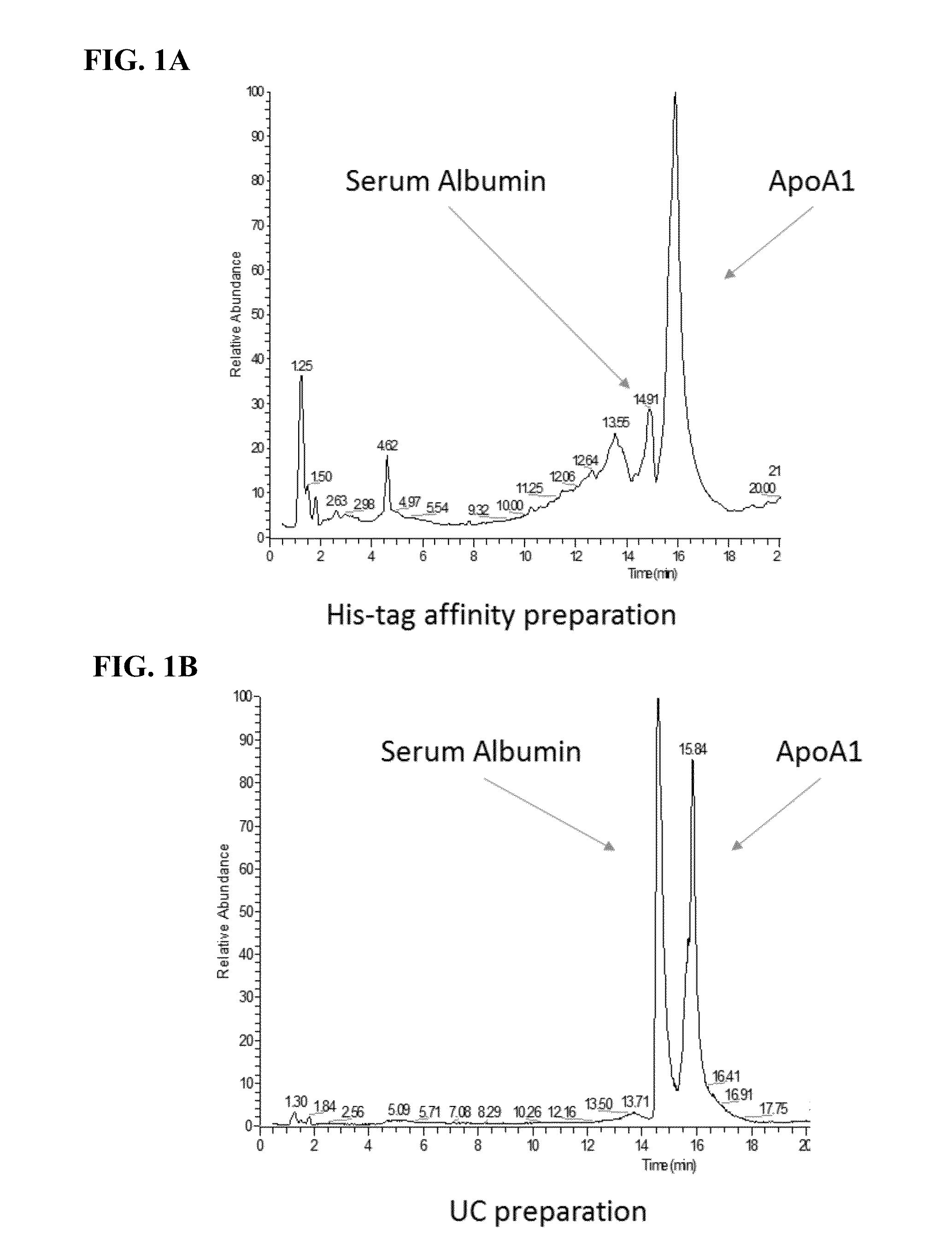
The present invention provides methods, kits, and compositions for purifying HDL molecules from a sample (e.g., blood sample) using HDL tagging molecules comprising an HDL lipophilic core binding peptide (e.g., portion of ApoA1) and an affinity tag. The present invention also provides methods, kits, and compositions for detecting non-fragmented ApoA1 with mass spectrometry. The present invention further provides methods, kits, and compositions for tagging HDL molecules in a sample with detectably labeled ApoA1 molecules such that the ratio of detectably labeled ApoA1 molecules to native ApoA1 proteins may be determined.
Owner:CLEVELAND HEARTLAB
N-terminal and C-terminal markers in nascent proteins
This invention relates to non-radioactive markers that facilitate the detection and analysis of nascent proteins translated within cellular or cell-free translation systems. Nascent proteins containing these markers can be rapidly and efficiently detected, isolated and analyzed without the handling and disposal problems associated with radioactive reagents. Methods are described for incorporating N-terminal, C-terminal and (optionally) affinity markers into a nascent protein
Owner:AMBERGEN INC
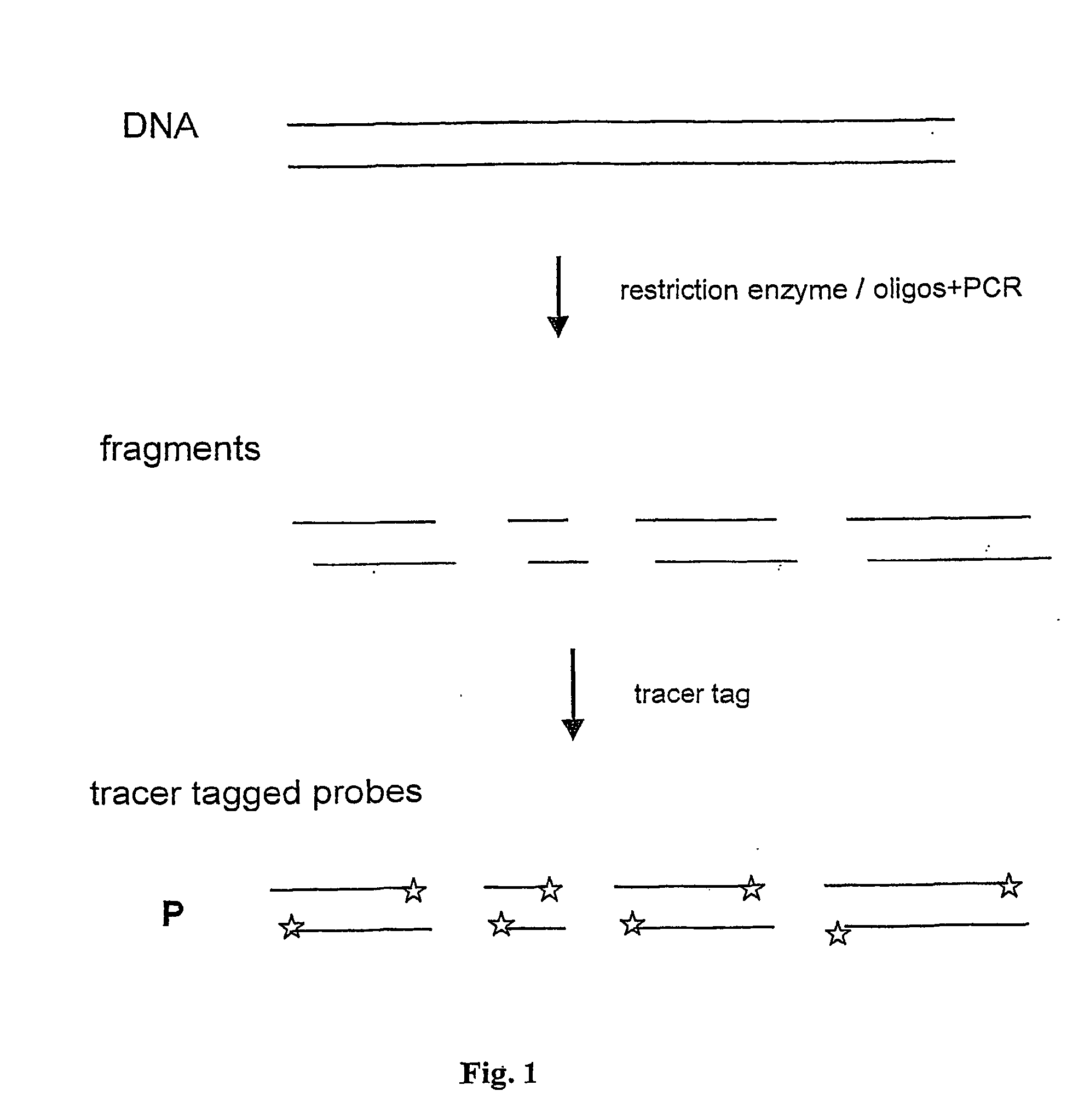
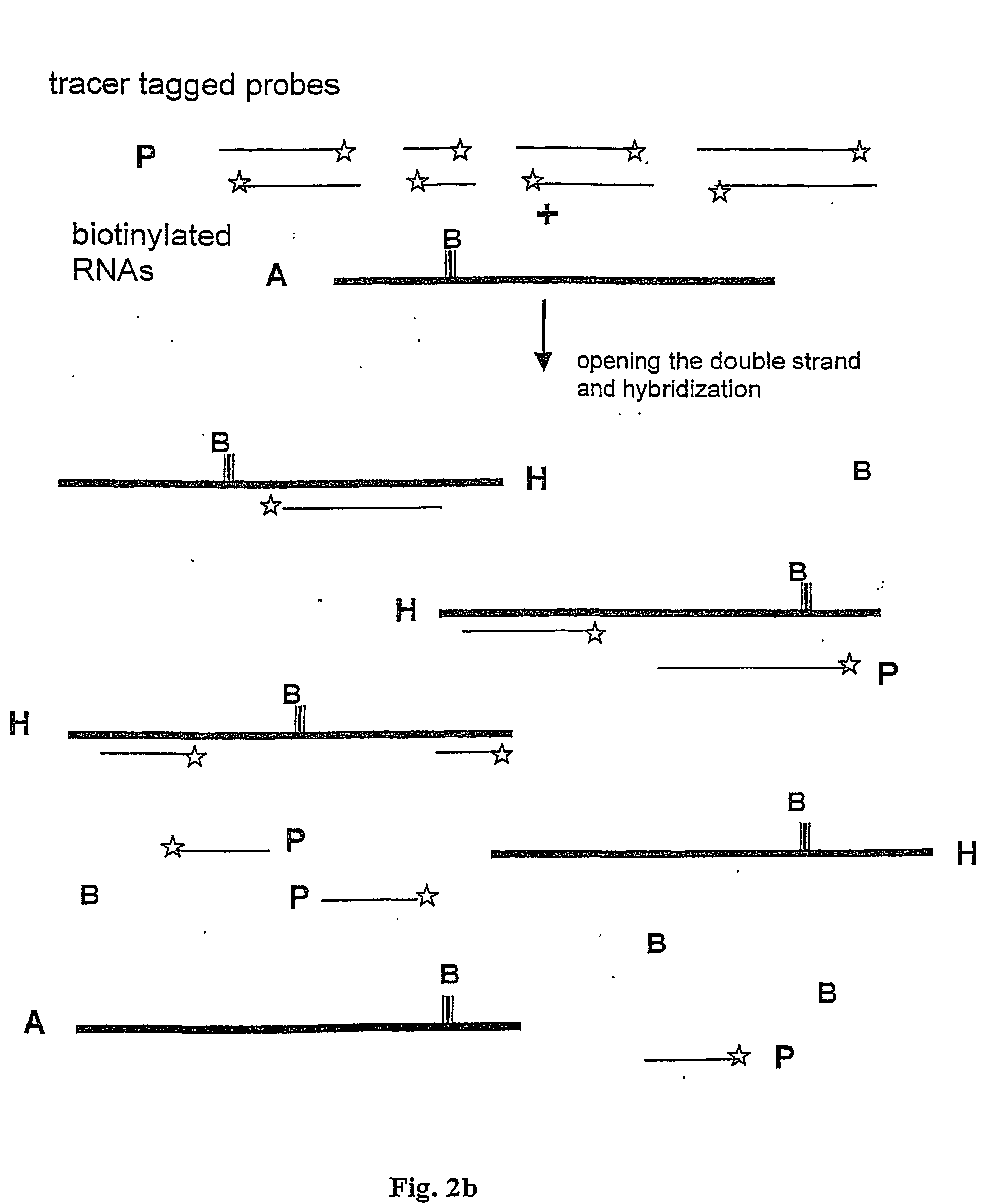
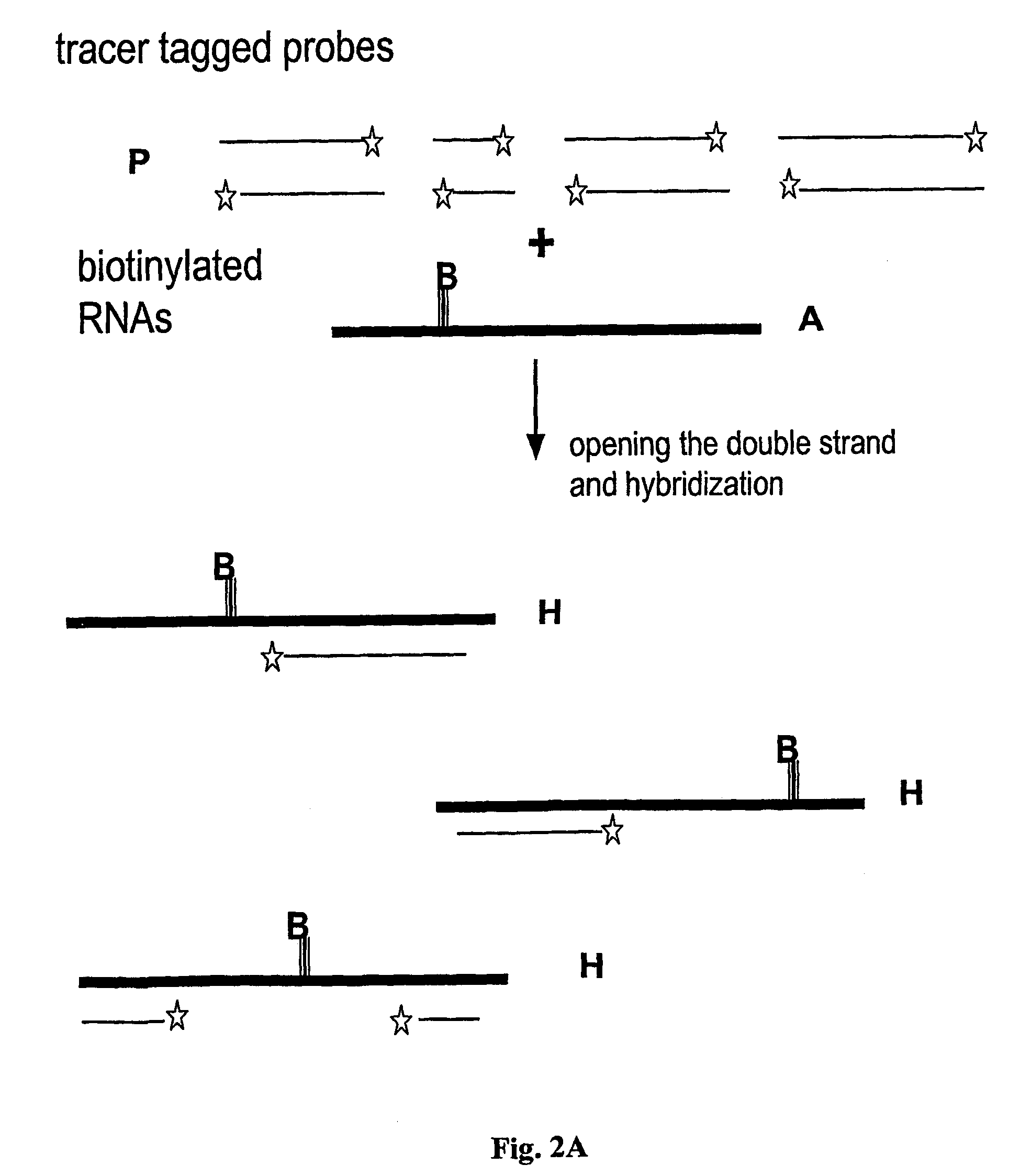
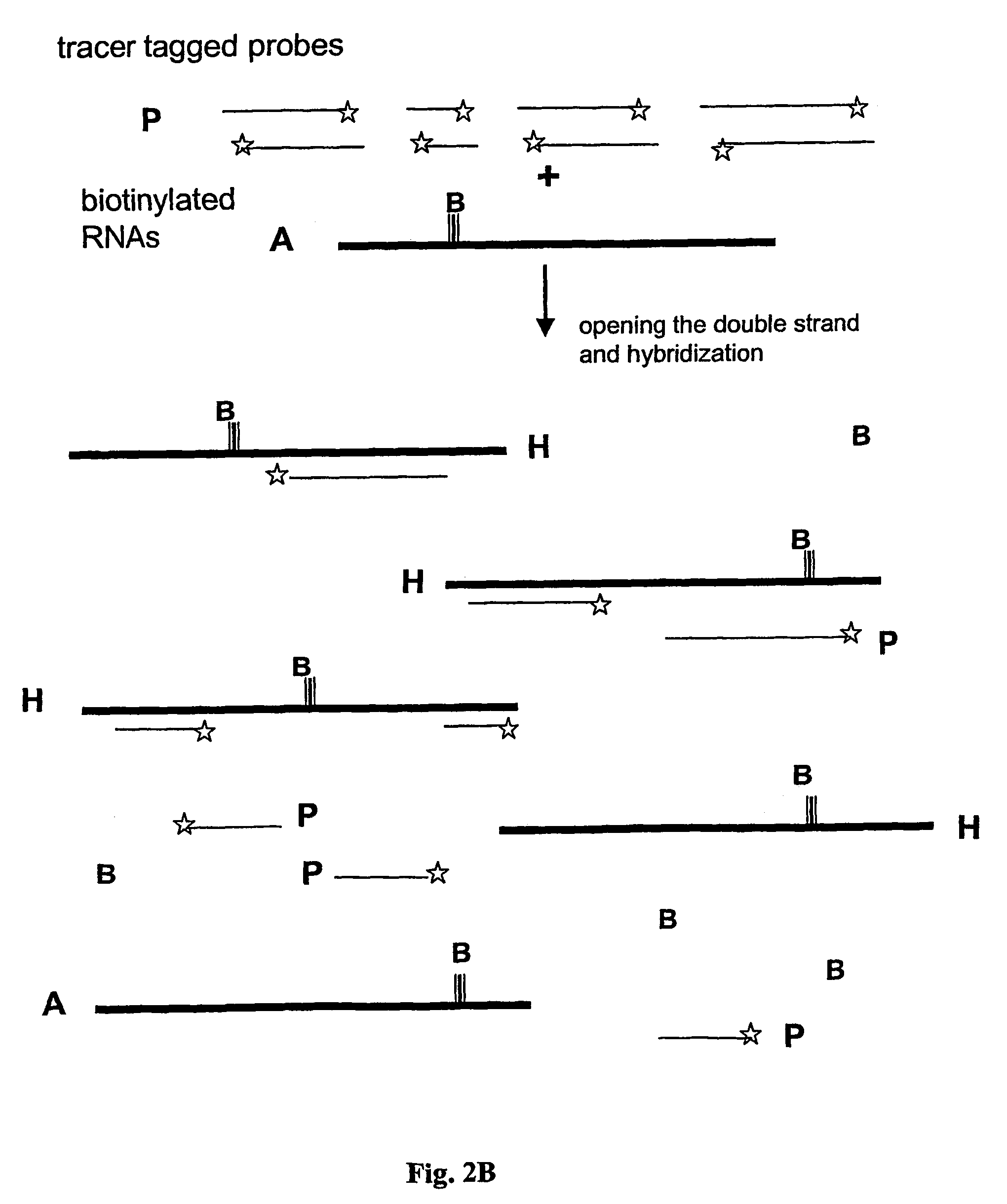
Method and test kit for quantitative determination of variations in polynucleotide amounts in cell or tissue samples
ActiveUS20040053300A1Easy to adaptContinue processMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorComponent separationAnalyteQuantitative determination
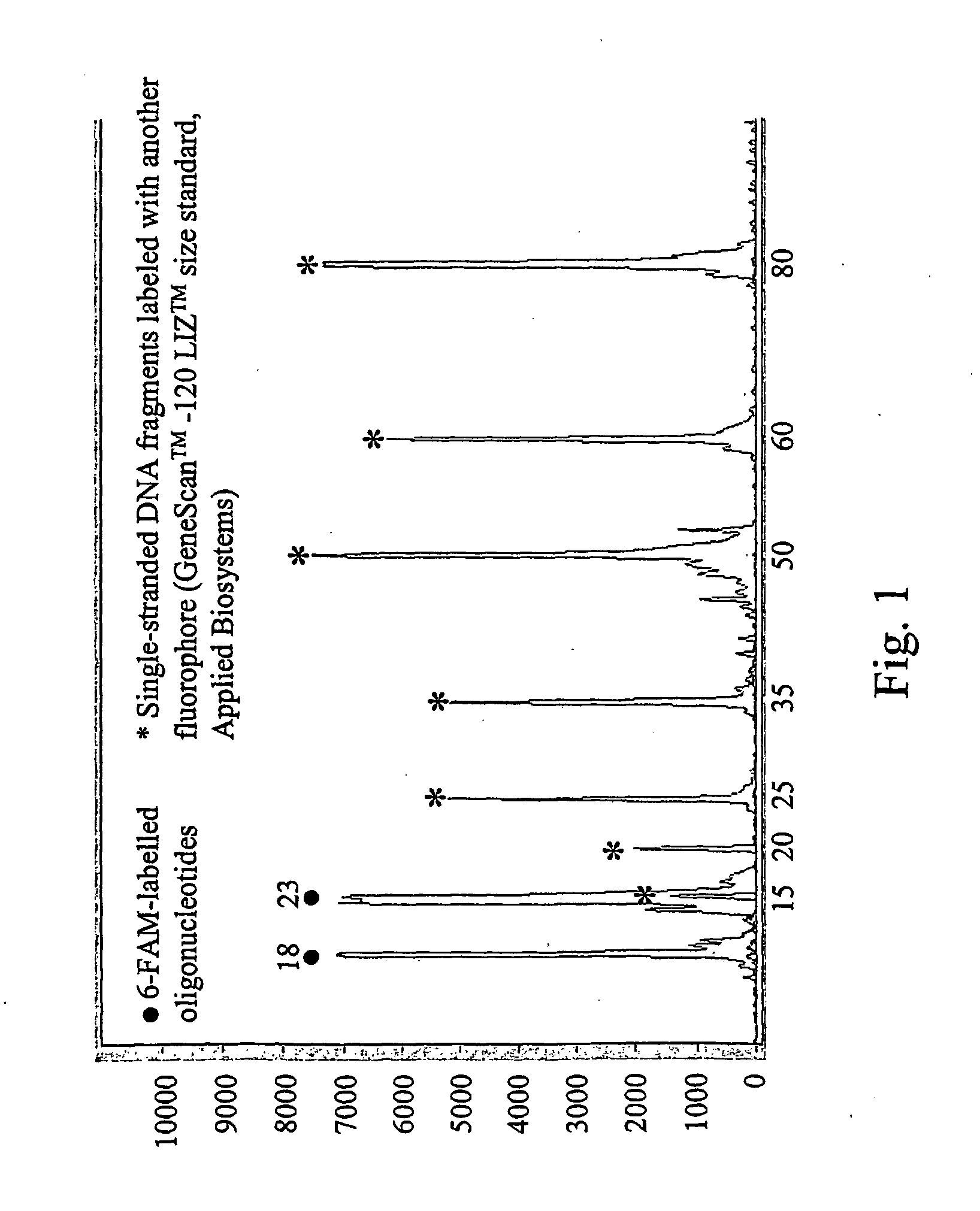
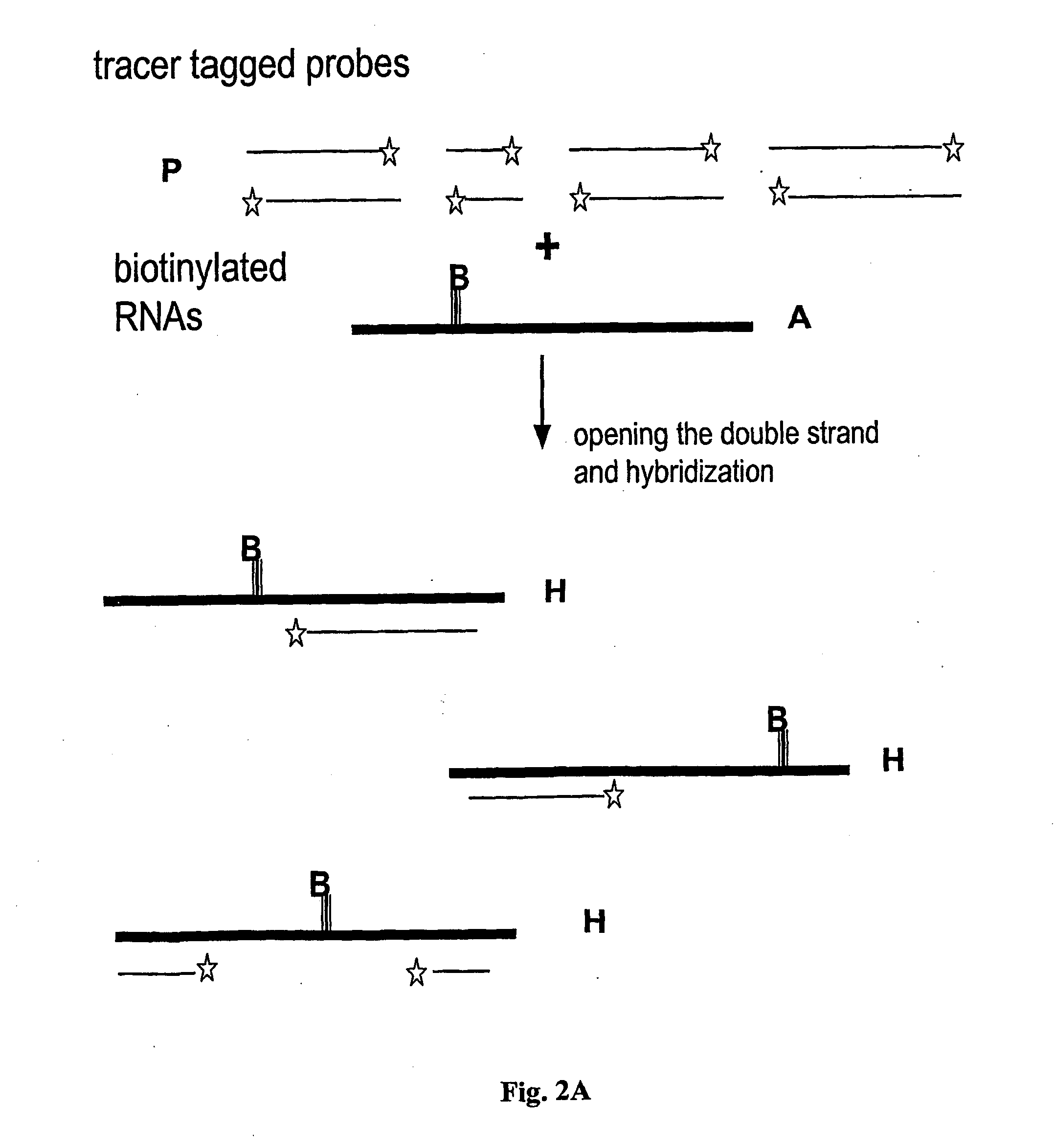
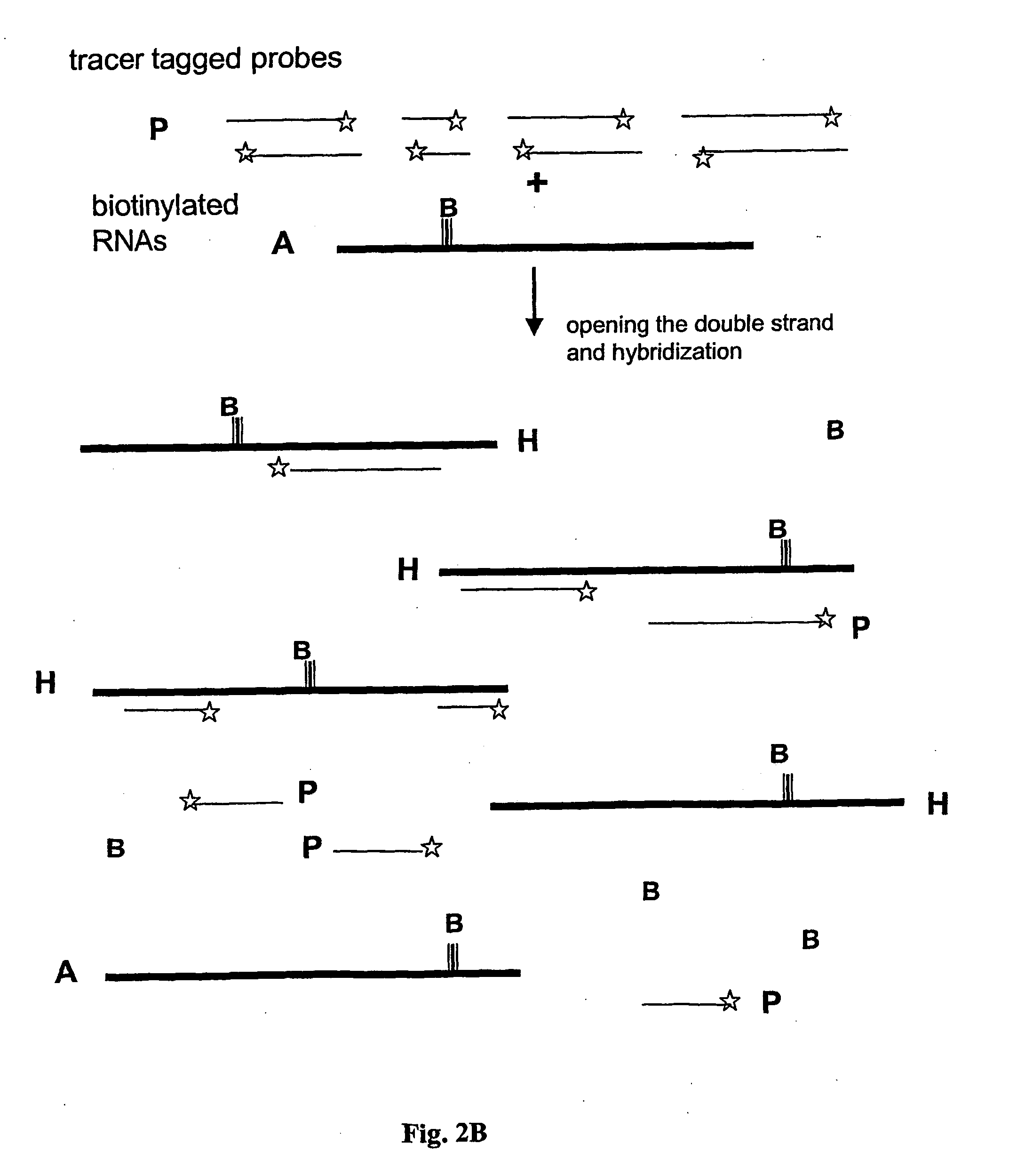
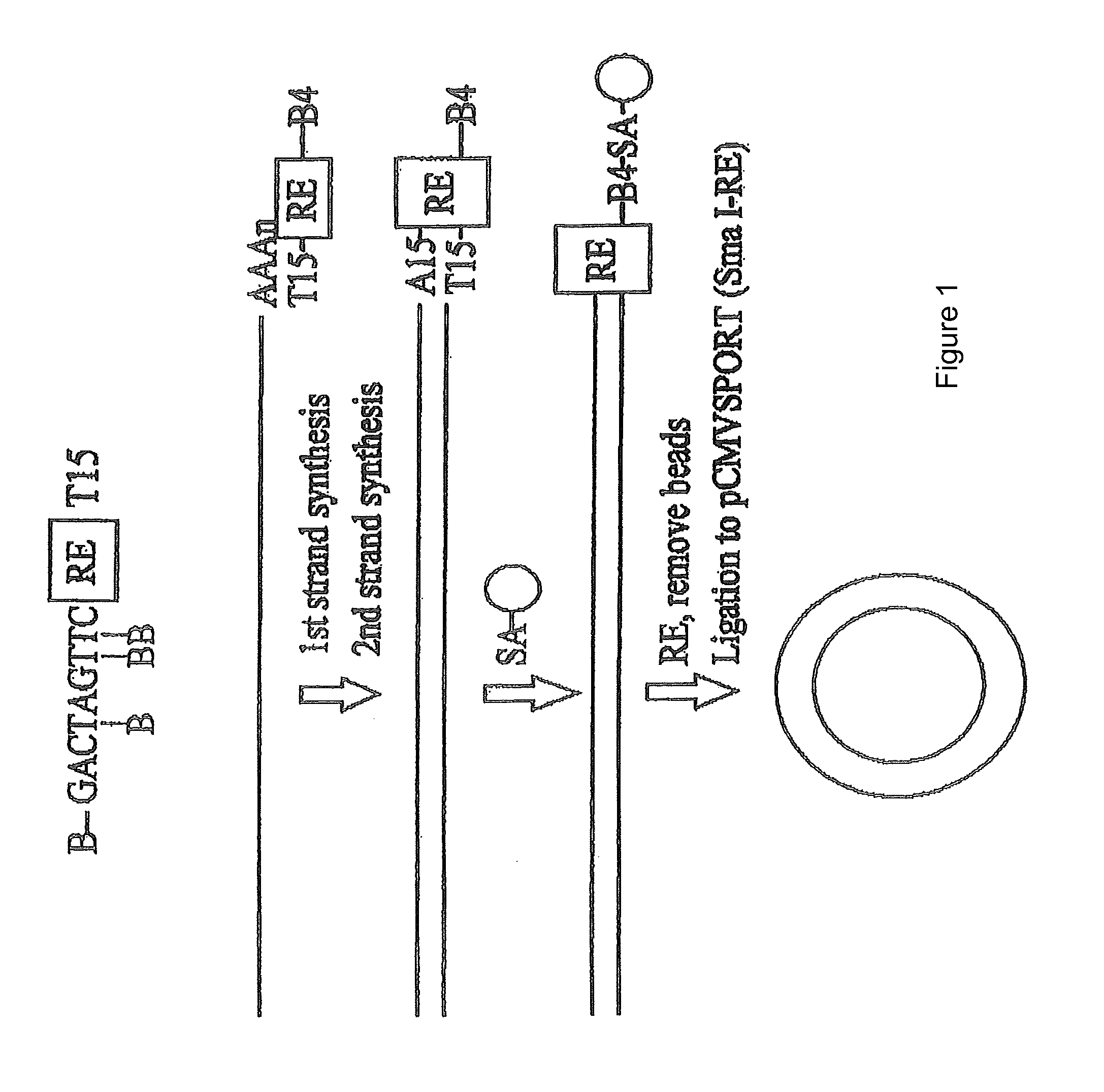
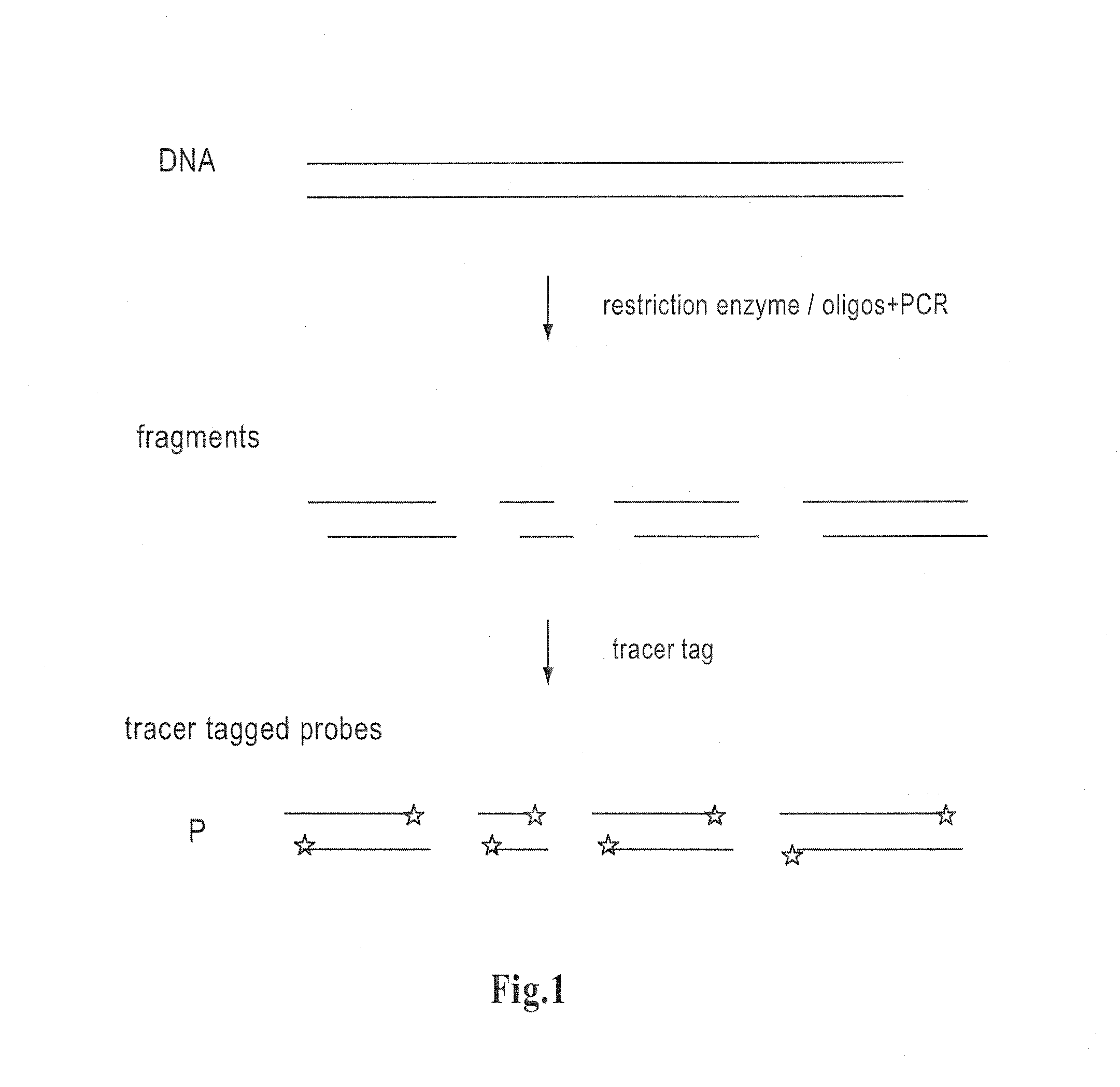
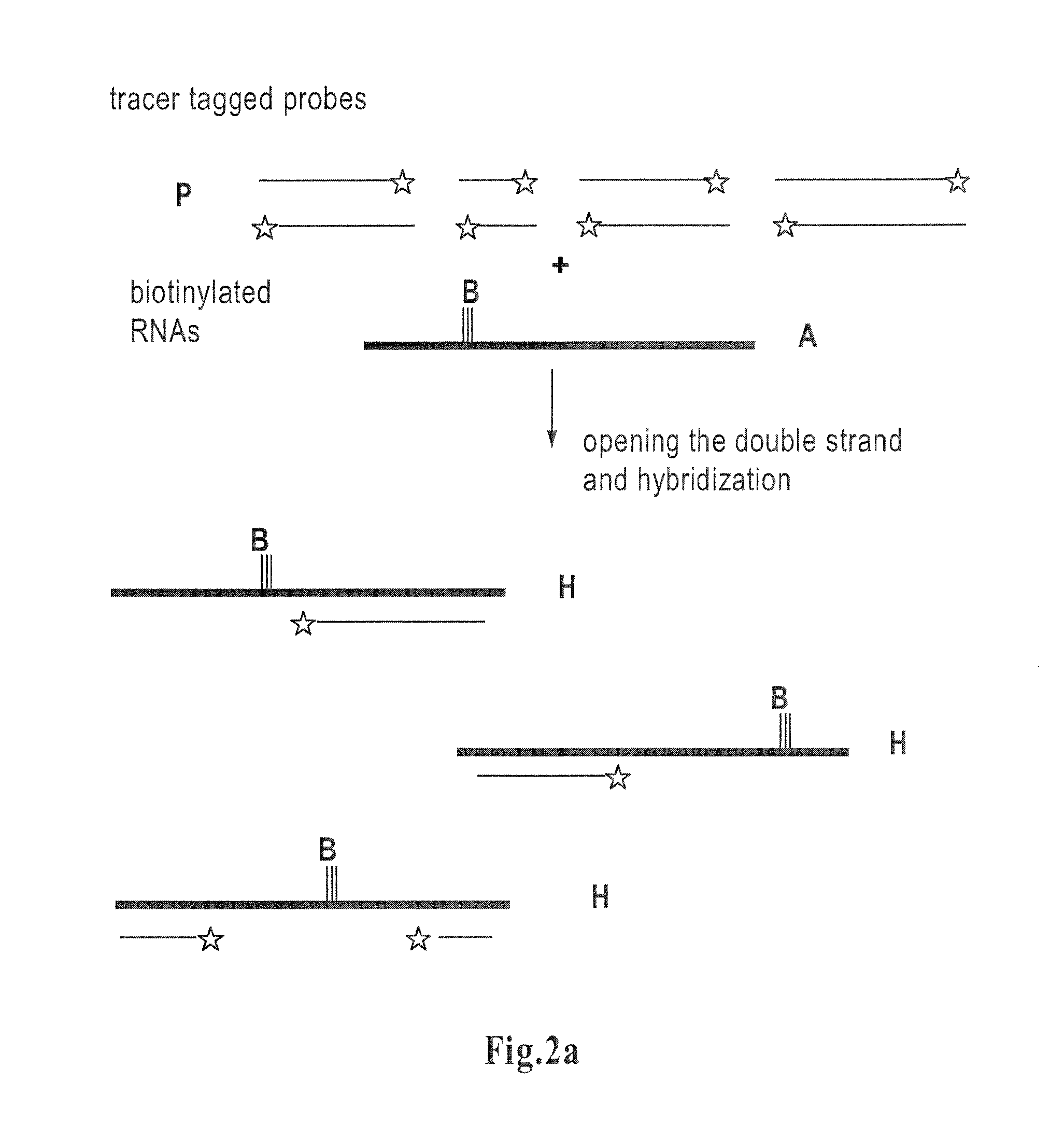
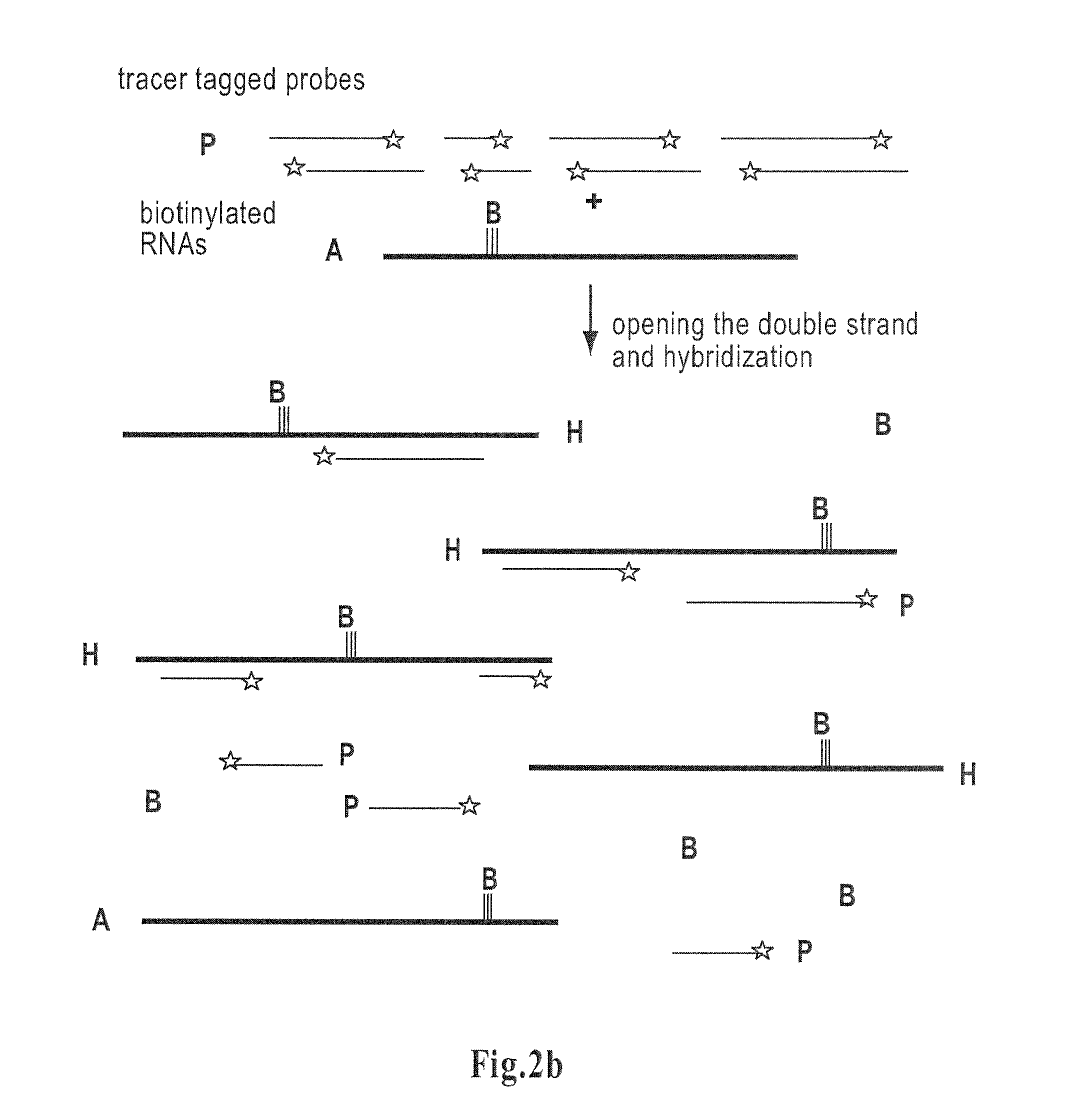
The invention is related to a method and test kits for quantitative determination of polynucleotide amounts present in a sample. The test kit comprises organized pools with polynucleotide probes having distinct sizes and optionally provided with tracer tags or primer tags. The probes are allowed to hybridize with affinity tagged analyte polynucleotides from the sample. The result is hybrids, which can be recovered on a separation aiding tool provided with the pair of the affinity tag. After the quantitative release of the probes, the probes are either directly recorded, or if primer tagged, they are amplified and optionally provided with a tracer tag before recording. The invention provides a sensitive and quantitative determination of the amount polynucleotides present in a cell or tissue sample and allows a quantitative assessment of variations in the amounts of polynucleotides as a response to inherent changes or due to external stimuli.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
One class of light affinity labelling double function probe molecules, preparing and use
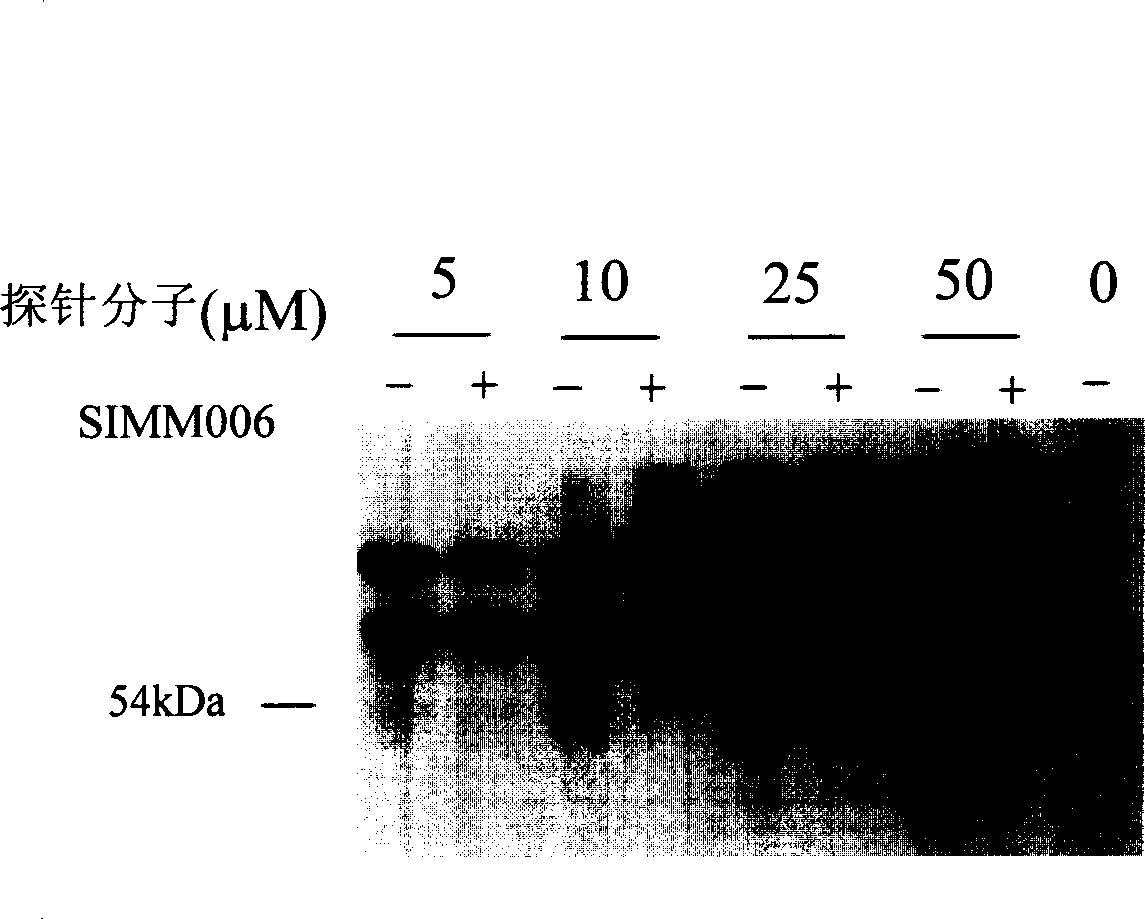
InactiveCN1900101ANovel structureReasonable structureSugar derivativesBiological testingReactive siteAffinity labeling
The present invention discloses preparation process and application of light affinity labeling double function probe molecule in the structural expression as shown. The probe molecule is used in screening penoniflorin and similar compounds for correlative proteinogram research and in researching and finding the action target sport, action mode, active site and other structure information of active compound penoniflorin. The present invention provides important way for searching penoniflorin and similar compounds.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and test kit for quantitative determination of polynucleotides in a mixture
InactiveUS20060035228A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyAntibiotics therapyEpidemiology
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
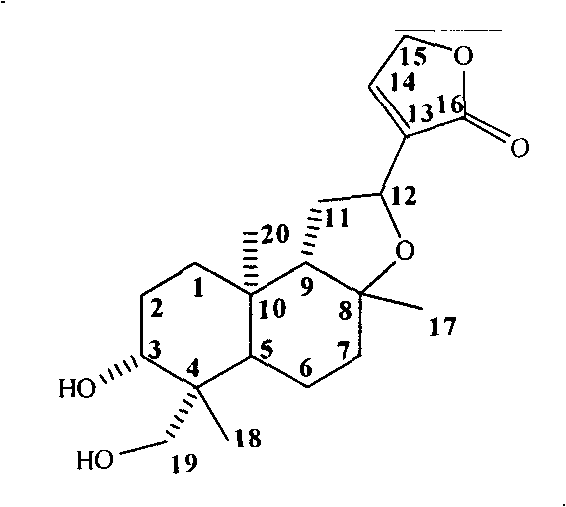
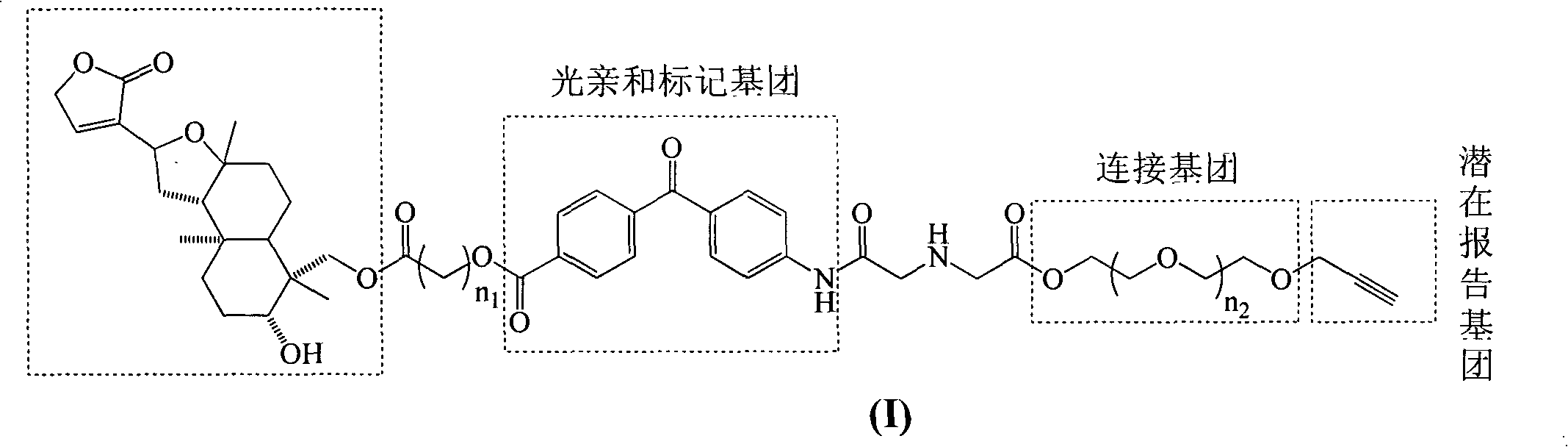
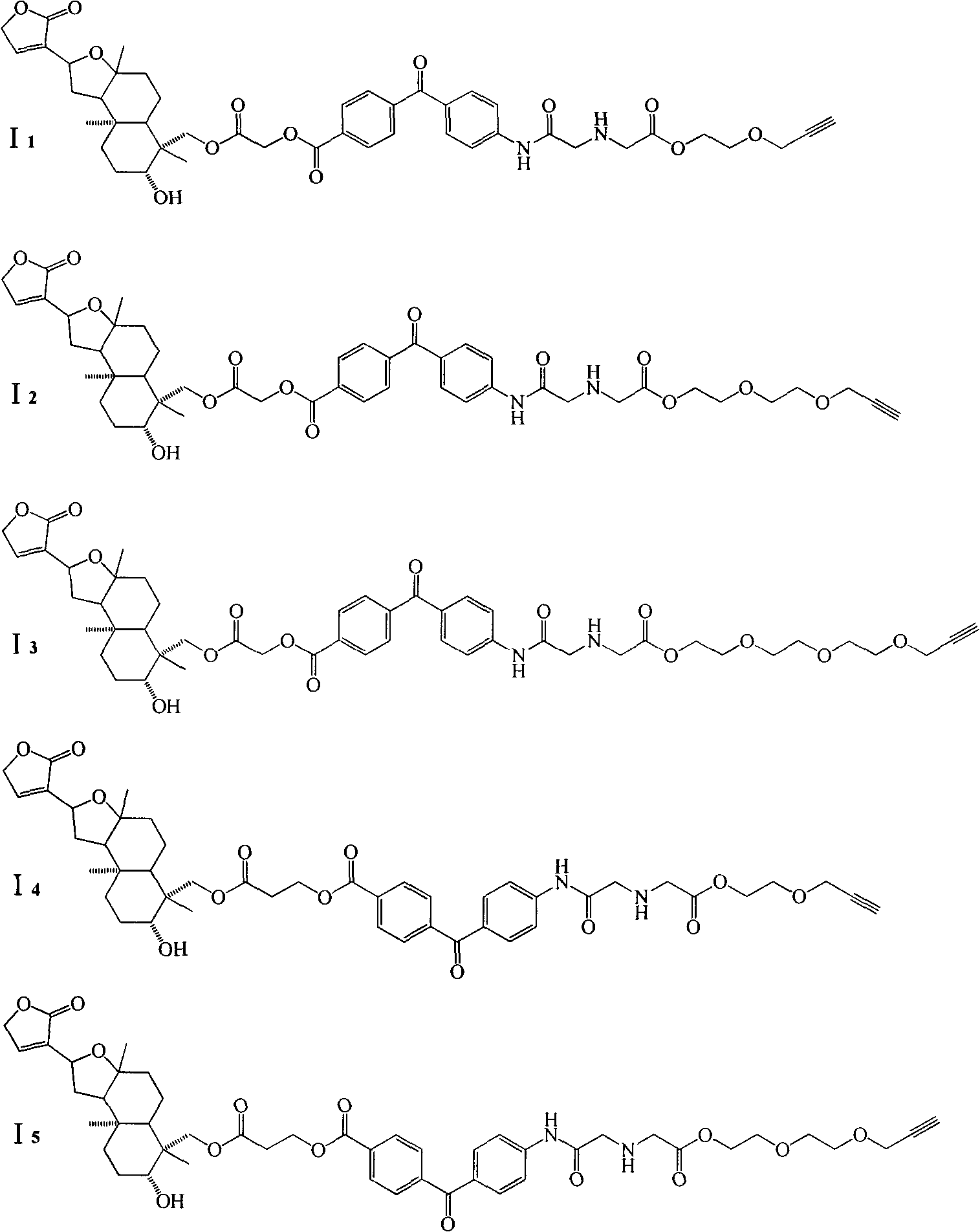
Isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe, preparation method and pharmaceutical composition of molecular probe
The invention discloses an isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe. The structure of the molecular probe is represented in a formula (I), wherein n1 ranges from 1 to 5 and n2 ranges from 0 to 2. Furthermore, the invention discloses a preparation and a pharmaceutical composition of the isoandrographolide photoaffinity labeling molecular probe. The compound, which is excellent in TNF-alpha inhibitory activity, can be used for researching and discovering target protein of isoandrographolide having an action of regulating macrophage function, and the compound, as a tool medicine, can be used for medicine development of a diagnostic reagent of the target protein as well as a regulator thereof.
Owner:XIAMEN JSY PHARMA TECH CO LTD
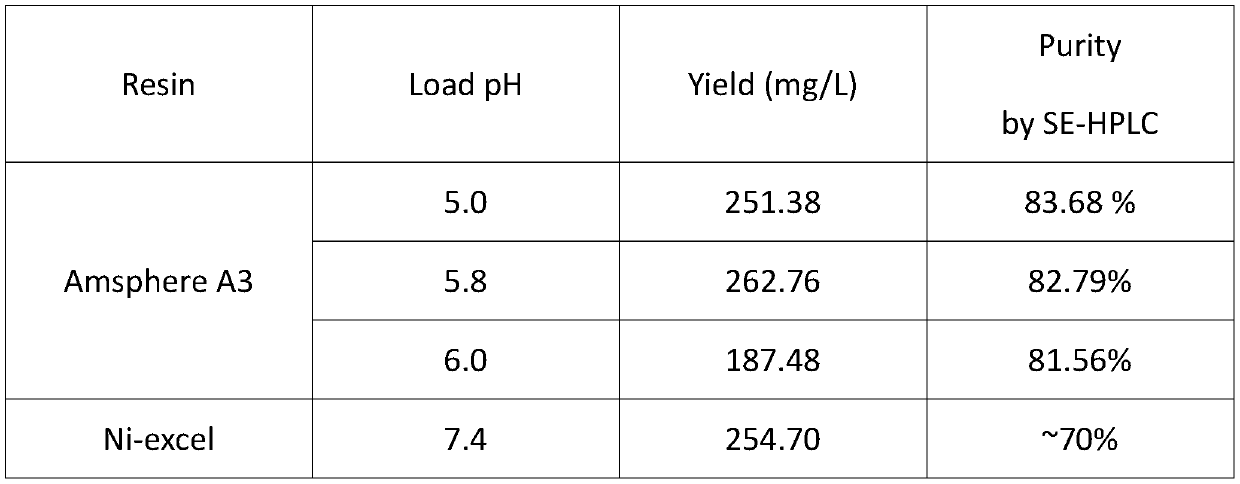
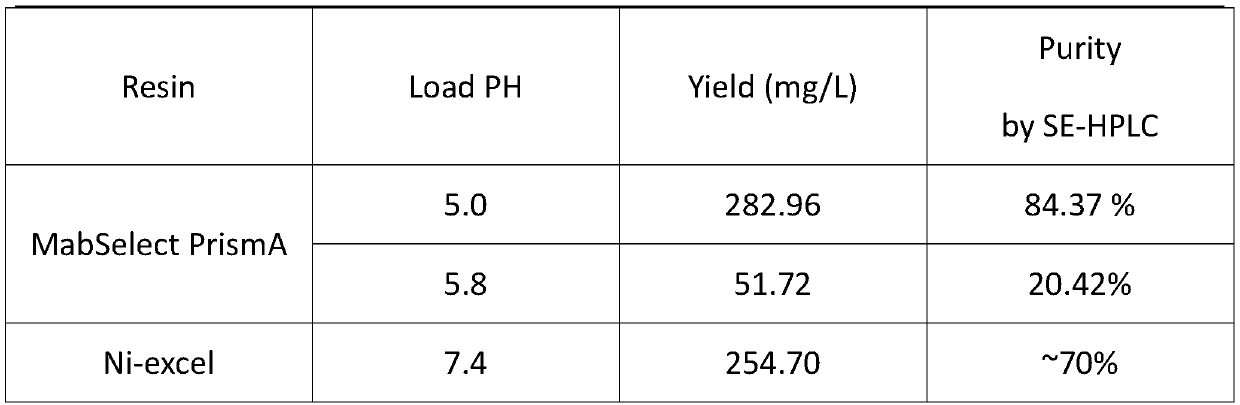
Method for purifying nano-antibody drug by employing Protein A affinity chromatography
InactiveCN110204612AAchieving High AffinityImprove the purification effectPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsElutionAffinity labeling
The invention discloses a method for purifying a nano-antibody drug by employing Protein A affinity chromatography. The method comprises the steps of: (1) adjusting the pH of a nano-antibody sample; (2) equilibrating the chromatography column with an equilibration buffer solution; (3) loading a sample adjusted by the step (1) to the chromatography column; (4) washing the product with a washing buffer solution; and (5) eluting the material with an elution buffer solution. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, affinity purification without additional affinity labeling, higher purity and easy process amplification.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUXI BIOLOGIC TECH CO LTD +2
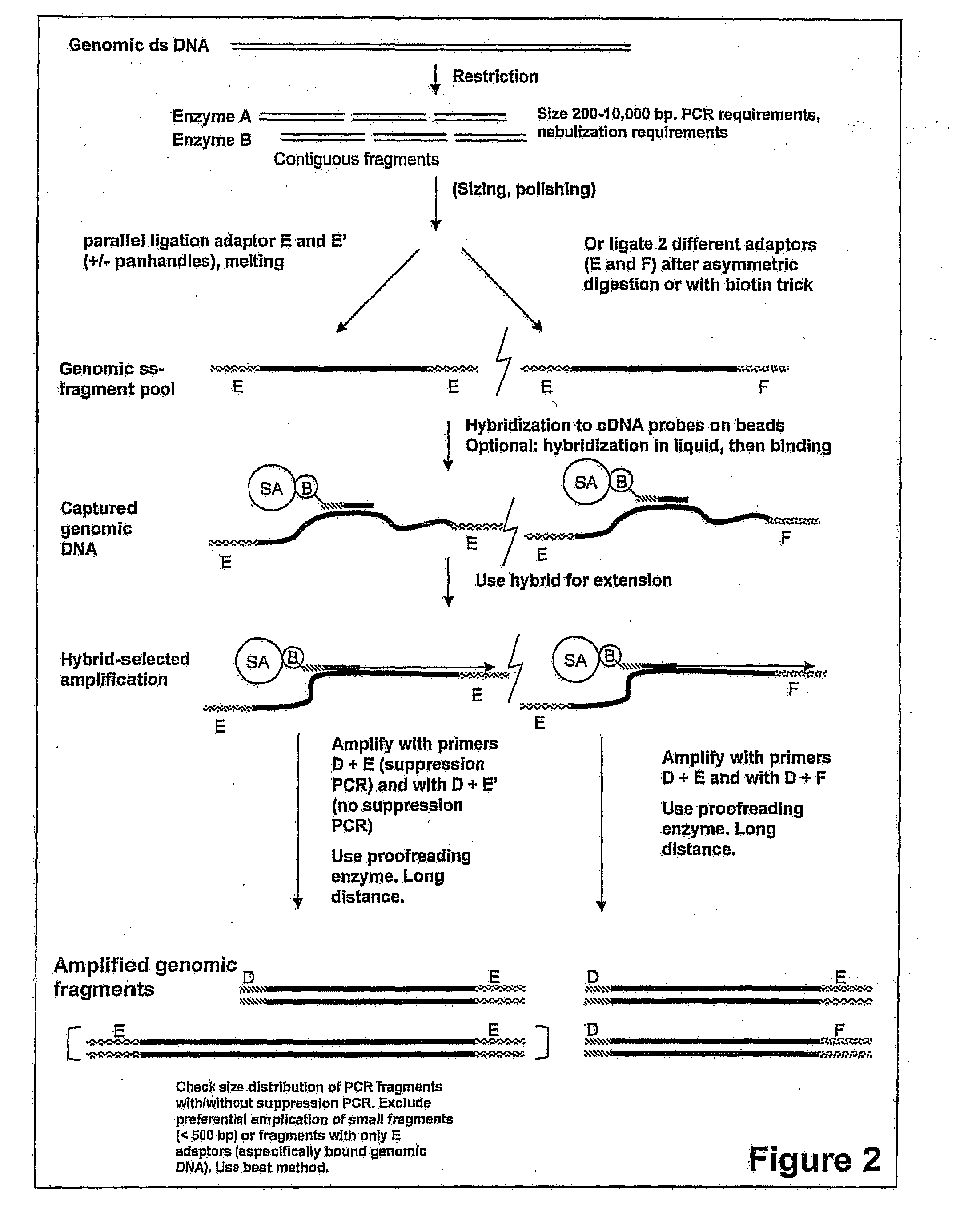
Expression-linked gene discovery
InactiveUS20110105338A1Increase volumeImprove cloning efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentAssociated organism
The invention relates to a method for analyzing a genomic region of an organism, comprising four major parts. The first part involves the isolation of mRNA from a selected organism that is used for the preparation of small single stranded DNA fragments with one adaptor containing an affinity label. These DNA fragments are used in part three. In the second part, genomic DNA from the same or a related organism is isolated. This genomic DNA is fragmented and ligated to adaptor molecules. In the third part, these genomic fragments are hybridized with single stranded DNA fragments from part one, and the hybrids formed in this process are used for synthesis of DNA fragments. These fragments will be used in part four which involves sequencing of these fragments using one of the available high throughput sequencing methods.
Owner:STICHTING GENETWISTER IP
Fusion collagenase to which affinity tag is attached, and method for producing same
ActiveCN102216454AEfficient productionConnective tissue peptidesBacteriaAffinity labelingAntibody Affinity Chromatography
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD +1
Sequencing method based on gene capture technology
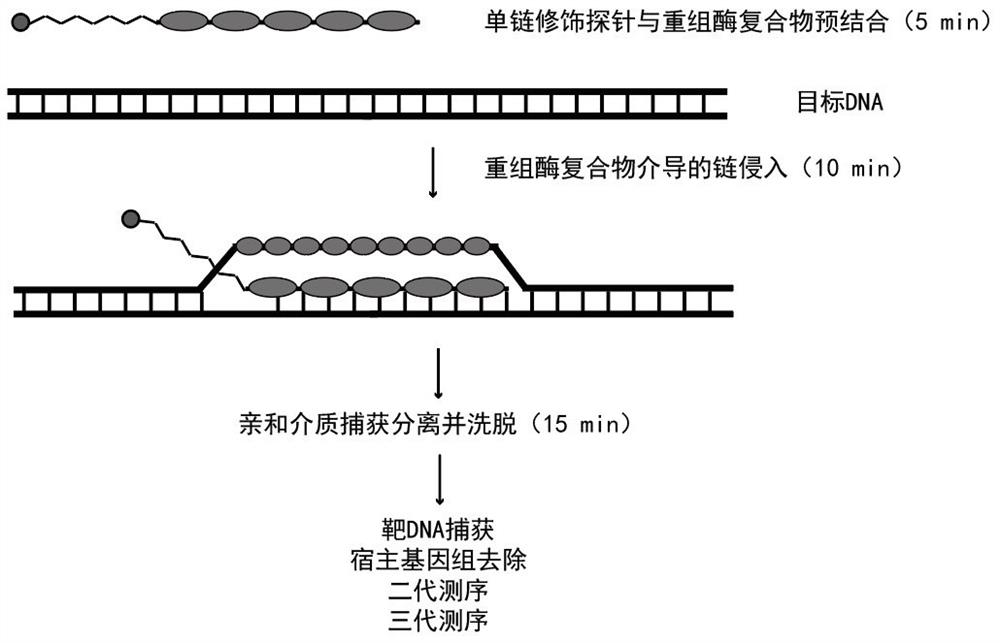
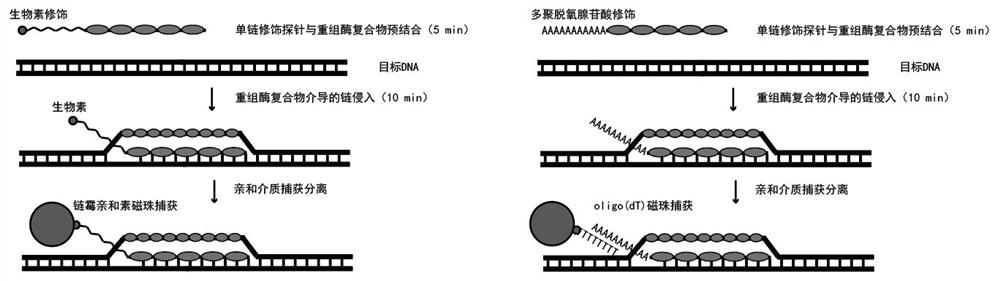
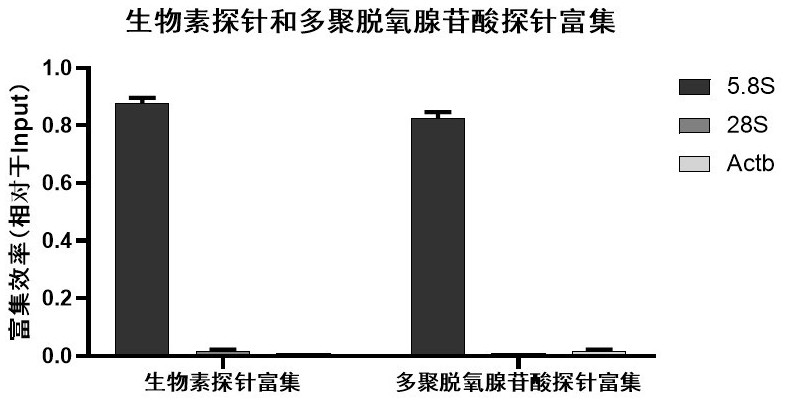
InactiveCN113699214AEasy to operateShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismThermal denaturation
The invention provides a sequencing method based on a gene capture technology. The sequencing method has the principle that a recombinase compound is used for assisting a single-stranded DNA probe with a closed 3' end to efficiently and specifically hybridize into a double-stranded target DNA molecule under the condition of 37 DEG C, and then an affinity label on the single-stranded DNA probe is used for carrying out specific enrichment on the target DNA. The method not only has the advantages of relatively strong long probe pairing, low probe design requirement and the like of a probe hybridization capture technology, but also has the advantages of simplicity in operation, short time consumption, no need of thermal denaturation of DNA, high capture efficiency, low cost and the like of a CRISPR / dCas9 system, and the probe does not participate in subsequent amplification, so that the identification accuracy is improved. Therefore, compared with other capture technologies, the RATE-seq has the obvious advantages of simplicity in operation, high capture efficiency, extremely short consumed time (30 minutes), good stability, low cost and the like, and is very suitable for gene capture and automatic application. In addition, the RATE-seq can effectively separate and remove human host DNA in a pathological sample, and the detection rate of pathogenic microorganisms is increased.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Progressive compression driven flow in vitro diagnosis method
InactiveCN108369191AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical reactionAnalyte
A cartridge and method for conducting a labeled molecular affinity binding test such as antibody / antigen, ligand / receptor, and colorometric reactions, and other chemical reactions for which one or more analytes is present in a liquid sample formate. A progressive compression structure progressively forces a liquid flow out of a conjugate pad toward a reaction region to more thoroughly and rapidlymix the liquid, encouraging specific first affinity binding to the analytes in question. A specially dimensioned constricting passageway surrounding the reaction region including the result zones provides an additional siphoning force to the flow. These combined forces rapidly and more evenly guide the flow of liquid through the reaction region so that the rushed rate of uptake of analytes at thestrip lines are more evenly distributed, adhesive attachment of non-specific molecules is largely avoided, vastly improving sensitivity and specificity, and providing quantitative results in some tests.
Owner:DNT SCI RES
Irreversible affinity labeling agent for labeling GST and application and irreversible affinity labeling agent
InactiveCN106754853AAvoid combiningChemical industryCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesMicro nanoAffinity labeling
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Triazole active molecule-based photoaffinity probe molecule as well as preparation method and application thereof
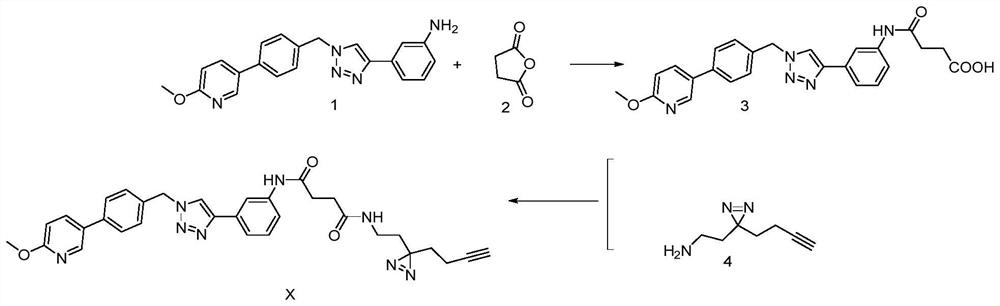
PendingCN111675696AEasy to prepareEasy to implementOrganic chemistryBiological testingButanedioic acidProtein target
The invention discloses a triazole active molecule-based photoaffinity probe molecule as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps thattriazole active molecules and succinic anhydride are stirred in acetonitrile to obtain an intermediate product with monocarboxylic acid; and the triazole active molecule-based photoaffinity probe molecule is prepared from a linker containing photoaffinity group diaziridine and alkynyl and the intermediate product with monocarboxylic acid under the condensation action of EDC.HCl. The preparation method of the triazole active molecule-based photoaffinity probe molecule is simple, easy to implement and high in yield. The triazole active molecule-based photoaffinity probe can be used for confirming the target protein of the triazole active molecule and verifying the feasibility of a photoaffinity labeling technology in the aspect of confirming a small molecule target.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
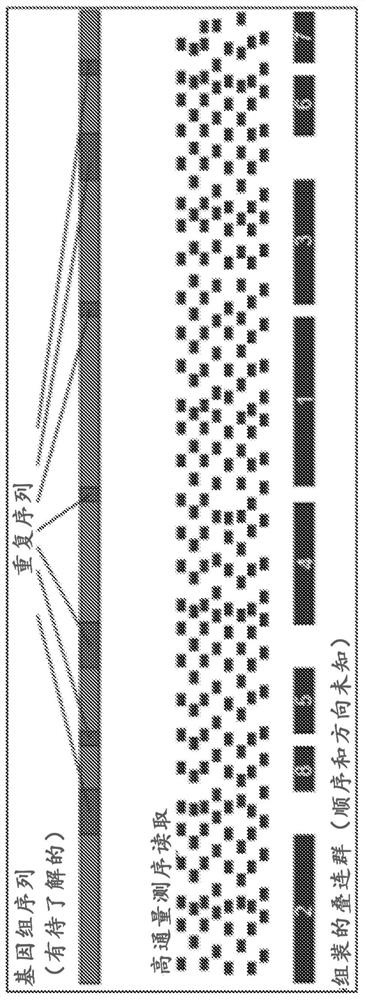
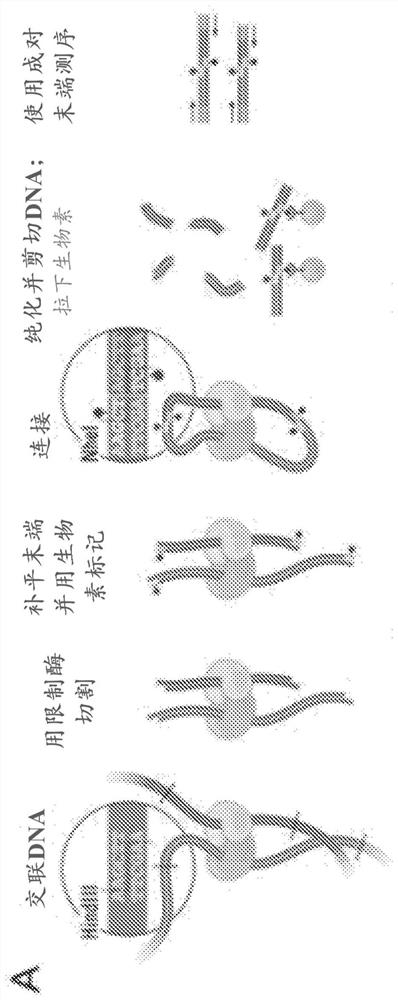
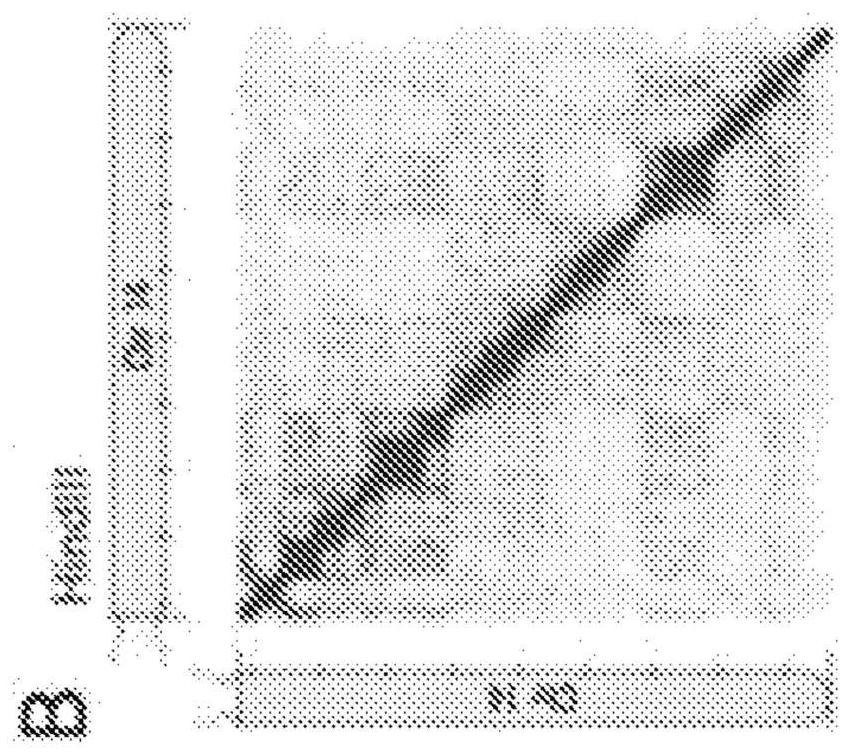
Methods for genome assembly, haplotype phasing, and target independent nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN108368542AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisGenomicsNucleic acid detection
The disclosure provides methods to assemble genomes of eukaryotic or prokaryotic organisms. The disclosure provides methods for haplotype phasing and meta-genomics assemblies. The disclosure providesa streamlined method for accomplishing these tasks, such that intermediates need not be labeled by an affinity label to facilitate binding to a solid surface. The disclosure also provides methods andcompositions for the de novo generation of scaffold information, linkage information, and genome information for unknown organisms in heterogeneous metagenomic samples or samples obtained from multiple individuals. Practice of the methods can allow de novo sequencing of entire genomes of uncultured or unidentified organisms in heterogeneous samples, or the determination of linkage information fornucleic acid molecules in samples comprising nucleic acids obtained from multiple individuals.
Owner:DOVETAIL GENOMICS
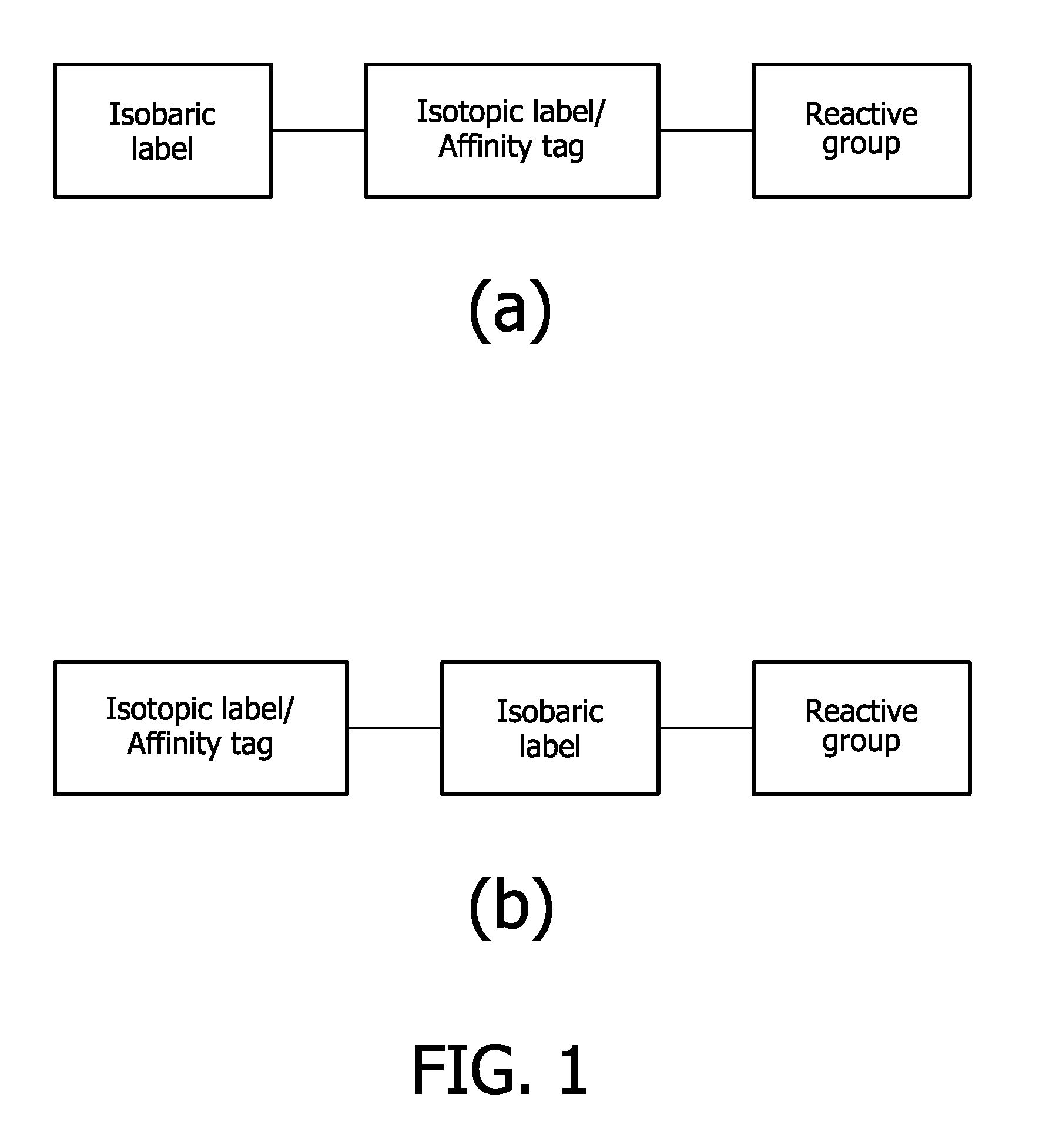
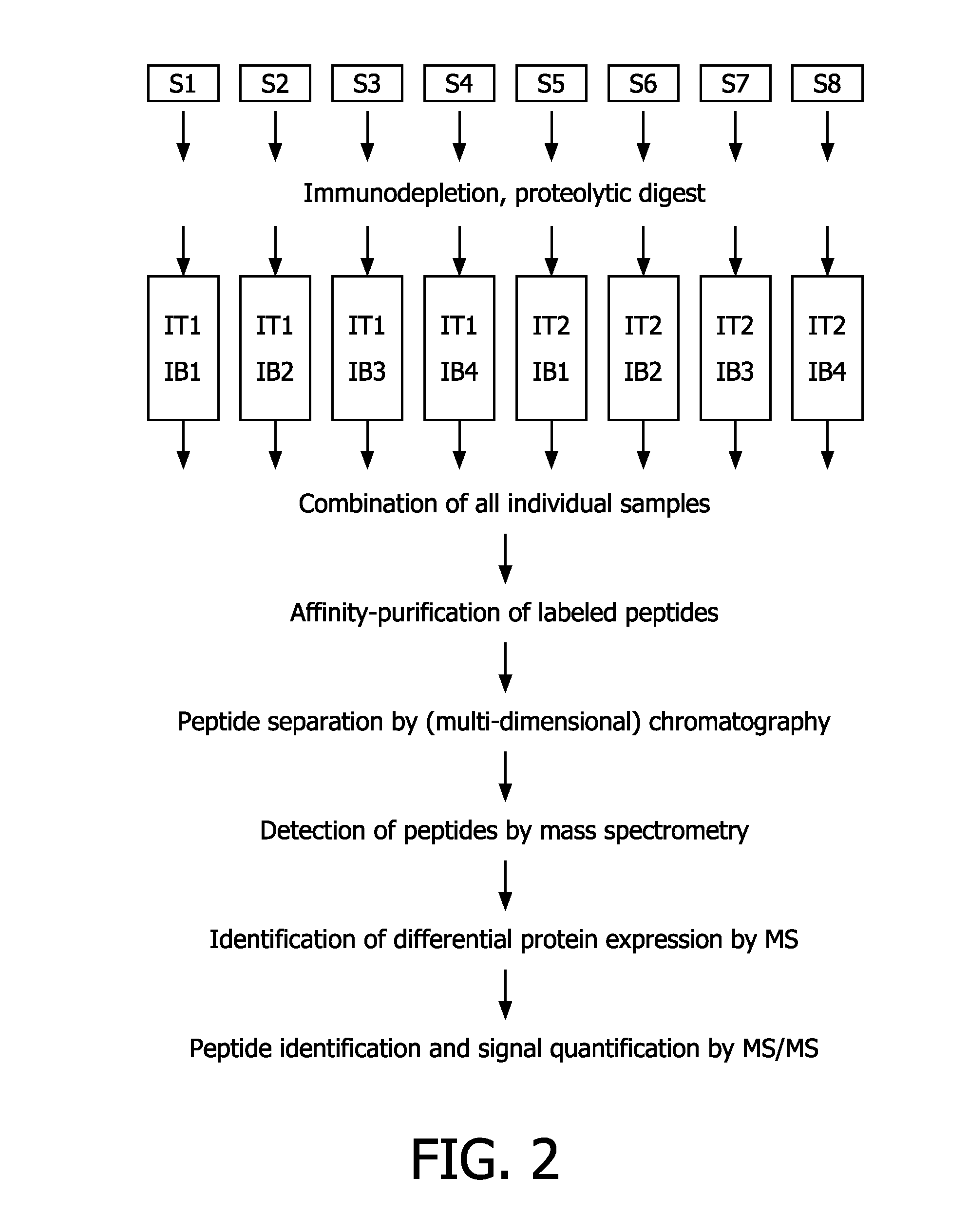
Compounds and methods for the labelling and affinity-selection of proteins
The present invention relates to kits and methods for the isotopic / isobaric labeling and the subsequent affinity selection and analysis of proteinaceous molecules. In particular, the invention relates to a kit-of-parts comprising a combinatorial plurality of labeling reagent for the labeling of proteinaceous molecules, each labeling reagent comprising an isobaric label component, an isotopic label component, and a reactive group capable of reacting with a proteinaceous molecule, wherein the isotopic label component concomitantly is an affinity tag. The invention is also directed to a corresponding method for the analysis of proteinaceous molecules, comprising labeling at least one subset of the proteinaceous molecules present by employing a kit-of-parts as defined herein and subsequently separating the labeled molecules by affinity purification via the affinity tag comprised in the label. Finally, the invention relates to the uses of such methods for protein expression profiling or proteomic analyses.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Modified protein and method for altering genome of cell
ActiveUS20210062169A1Reduced nuclease activityStrong specificityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAStaphylococcusPeptide sequence
A modified Streptococcus aureus Cas9 (SaCas9) protein with a mutation at an N413 position, and optionally one or more of a nuclear localization sequence, a cell penetrating peptide sequence, an affinity tag and / or a fusion base editor protein, and a kit that comprises said modified protein. A method for altering the genome of a cell, the method including the step of using the modified protein of the invention.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
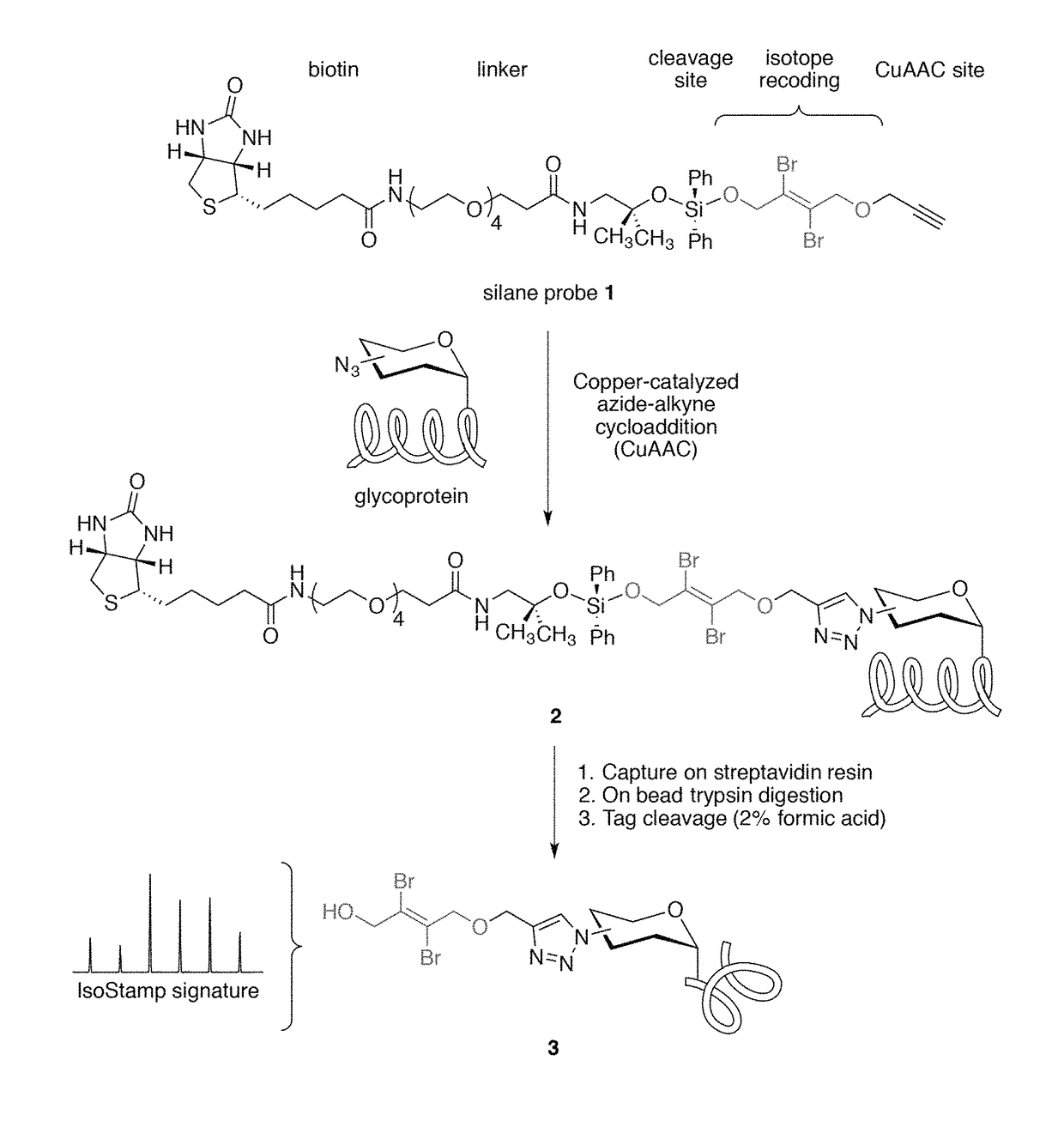
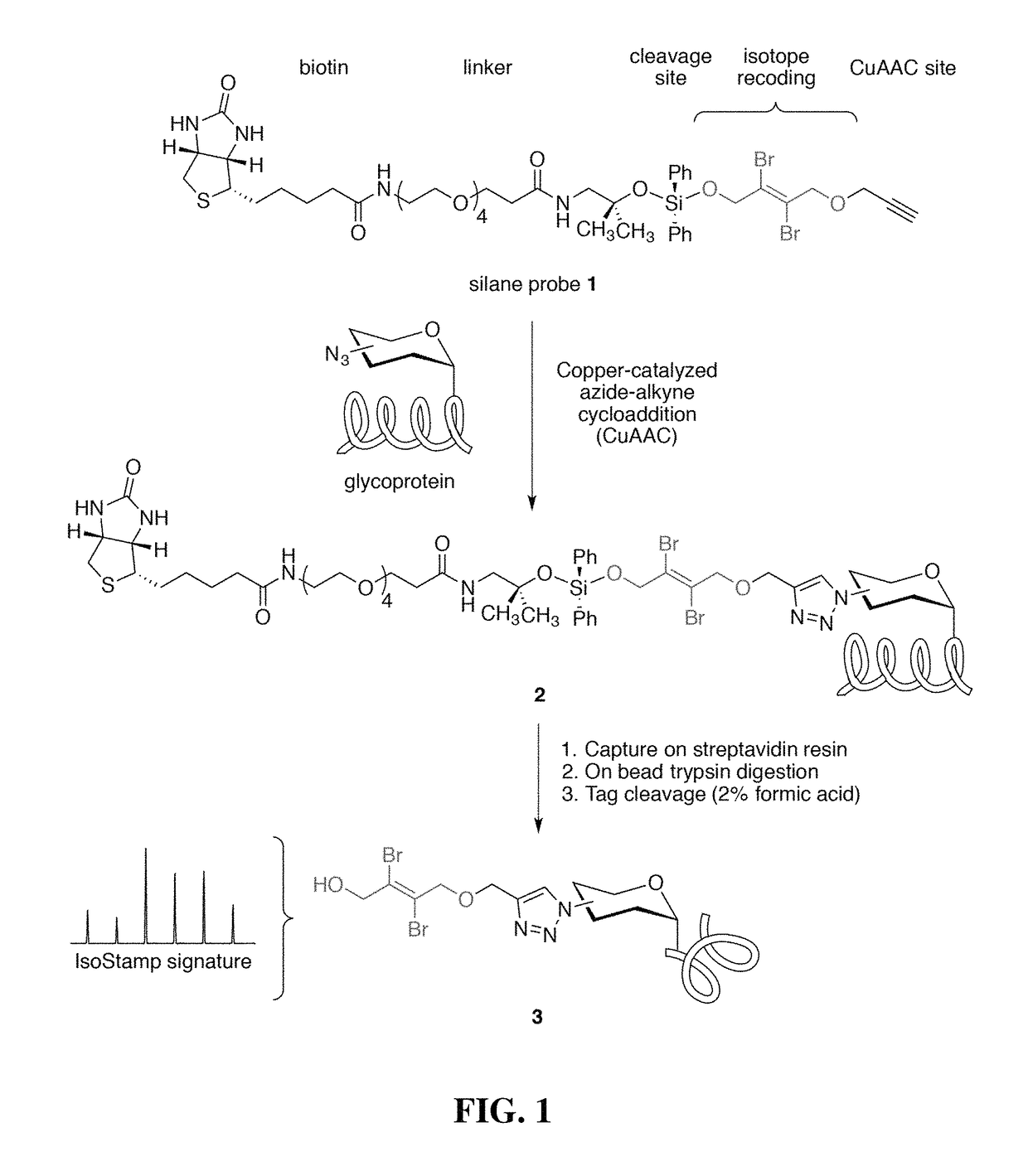
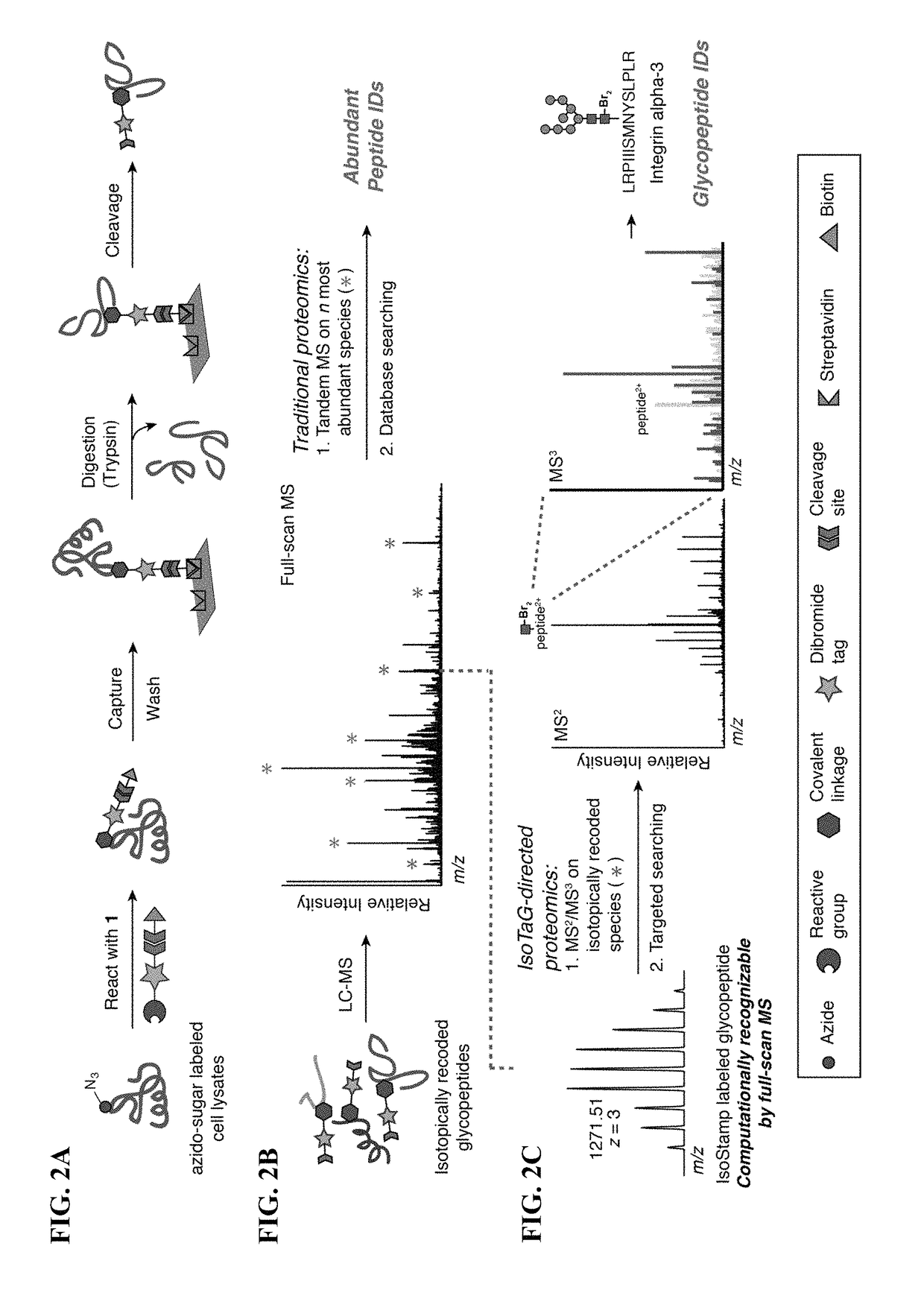
Cleavable probes for isotope targeted glycoproteomics and methods of using the same
ActiveUS10114026B2Reduce detectionLow efficiencyGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPeptide preparation methodsCross-linkIsotopic labeling
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
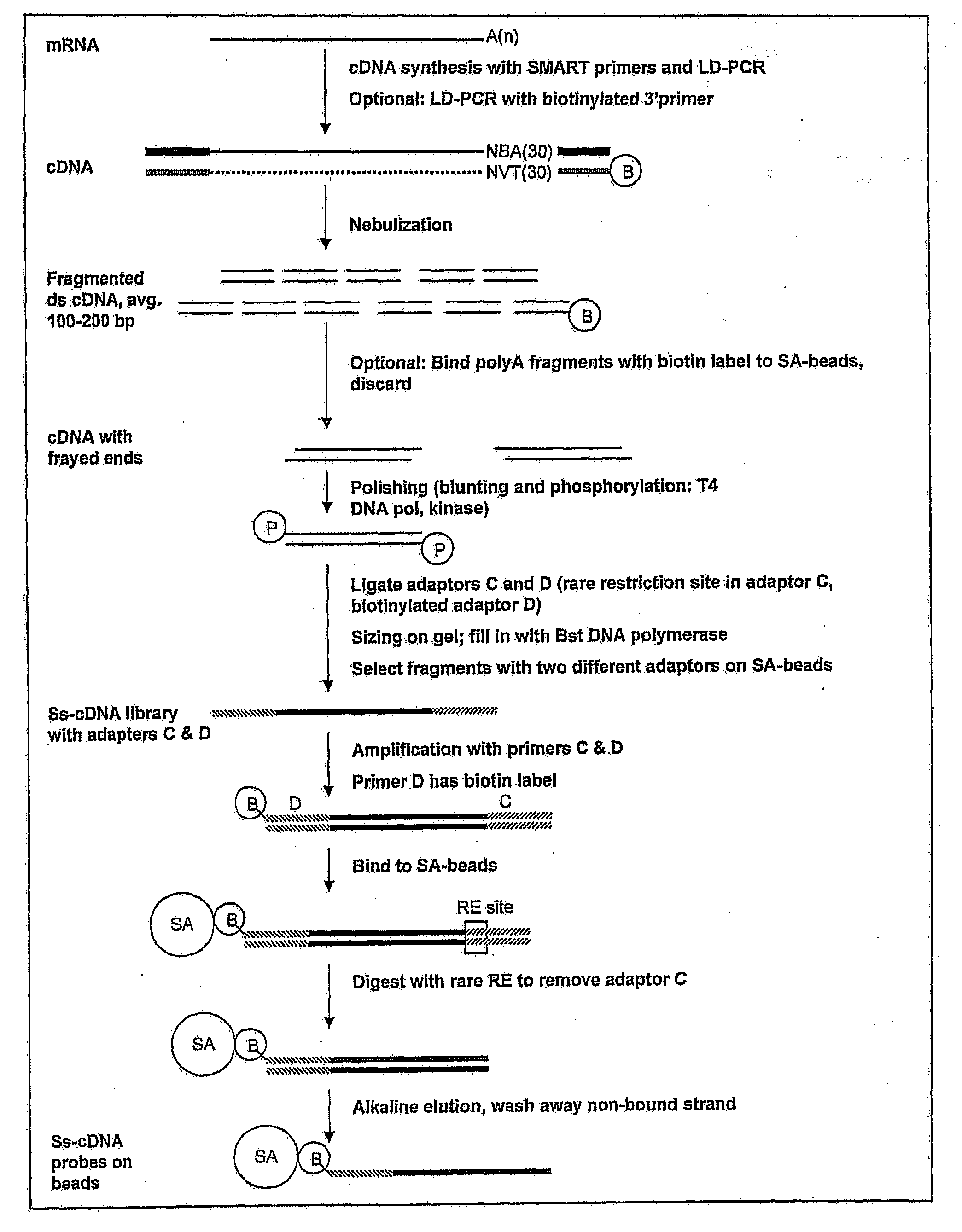
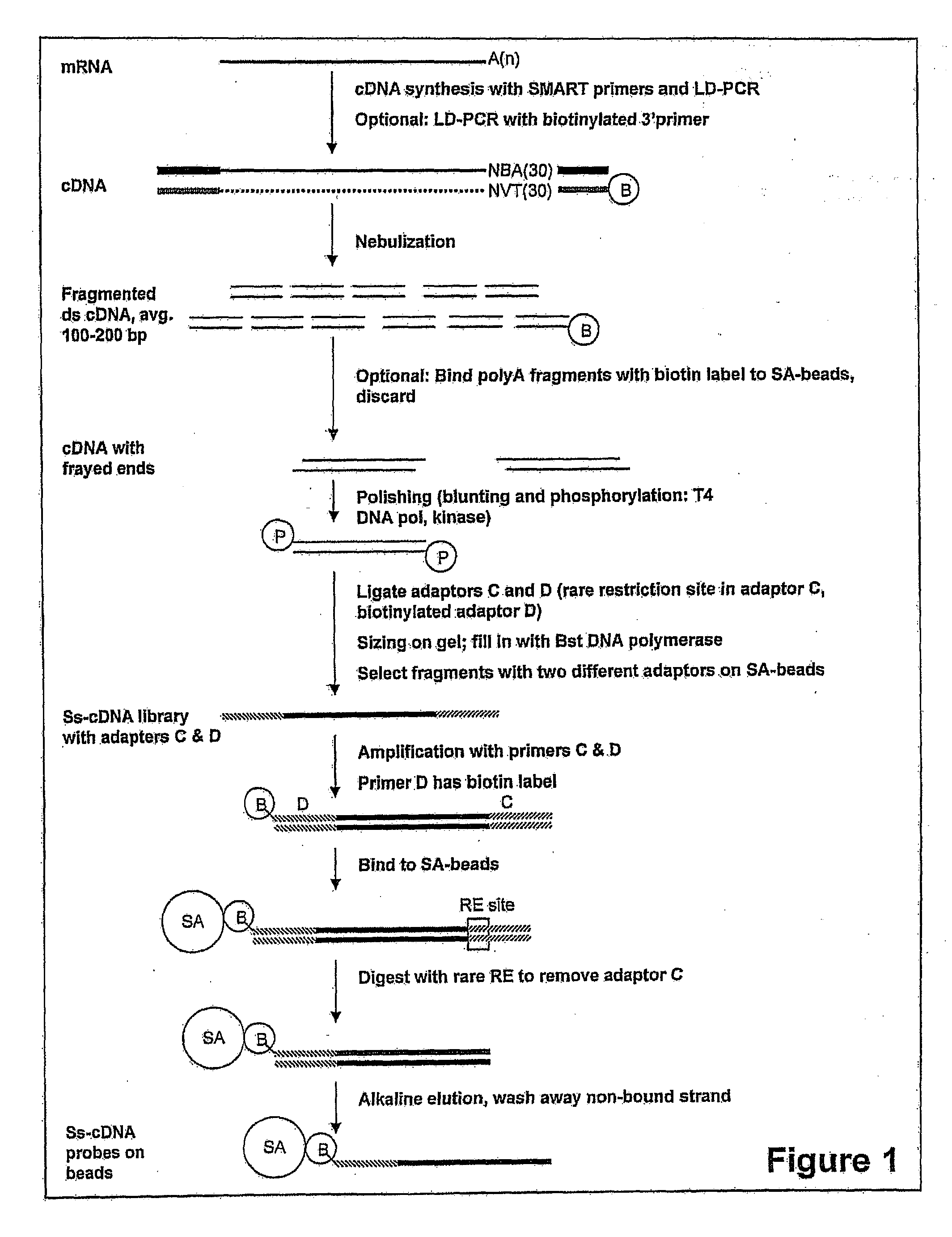
Methods For Production And Purification Of Nucleic Acid Molecules
InactiveUS20100093989A1Good choiceReduce contaminationSugar derivativesFermentationAffinity labelingSingle strand
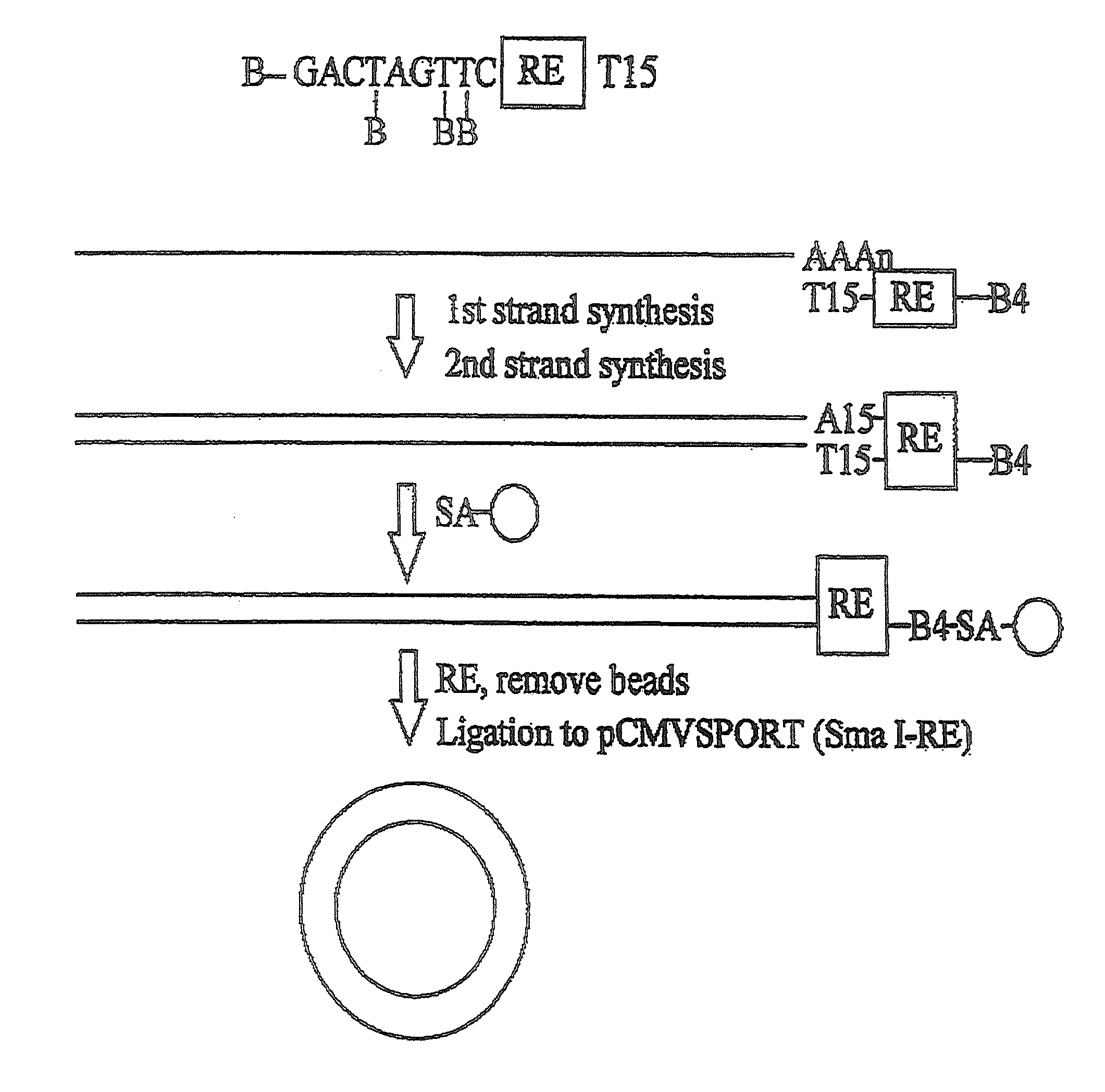
The present invention is directed to methods for the production and isolation of nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the invention concerns isolation of mRNA molecules and the production and isolation of nucleic acid molecules (e.g., cDNA molecules or libraries), which may be single- or double-stranded. Additionally, the invention concerns selection and isolation of particular nucleic acid molecules of interest from a sample which may contain a population of molecules. Specifically, the invention concerns affinity-labeled primer-adapter molecules which allow improved isolation and production of such nucleic acid molecules, increasing both product recovery and speed of isolation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Monomolecular mechanics method for measuring accurate length of human telomere
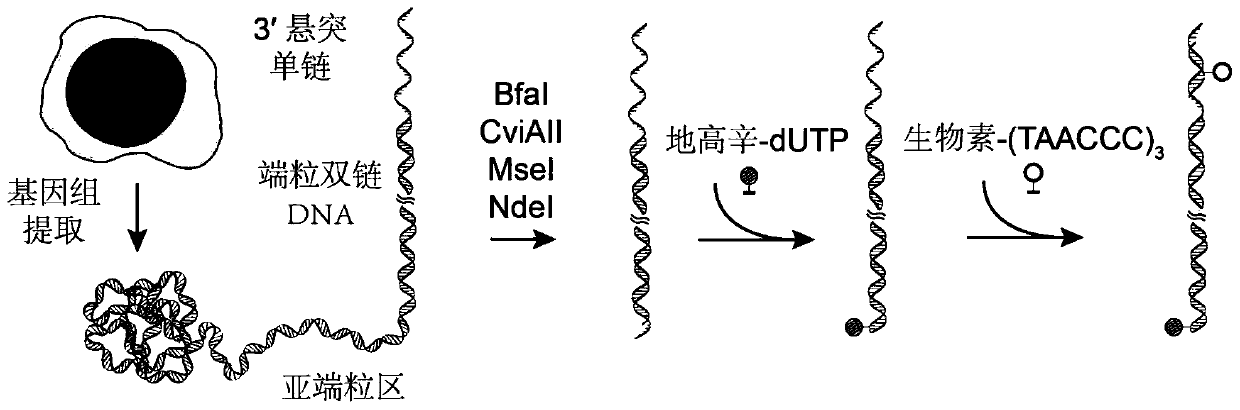
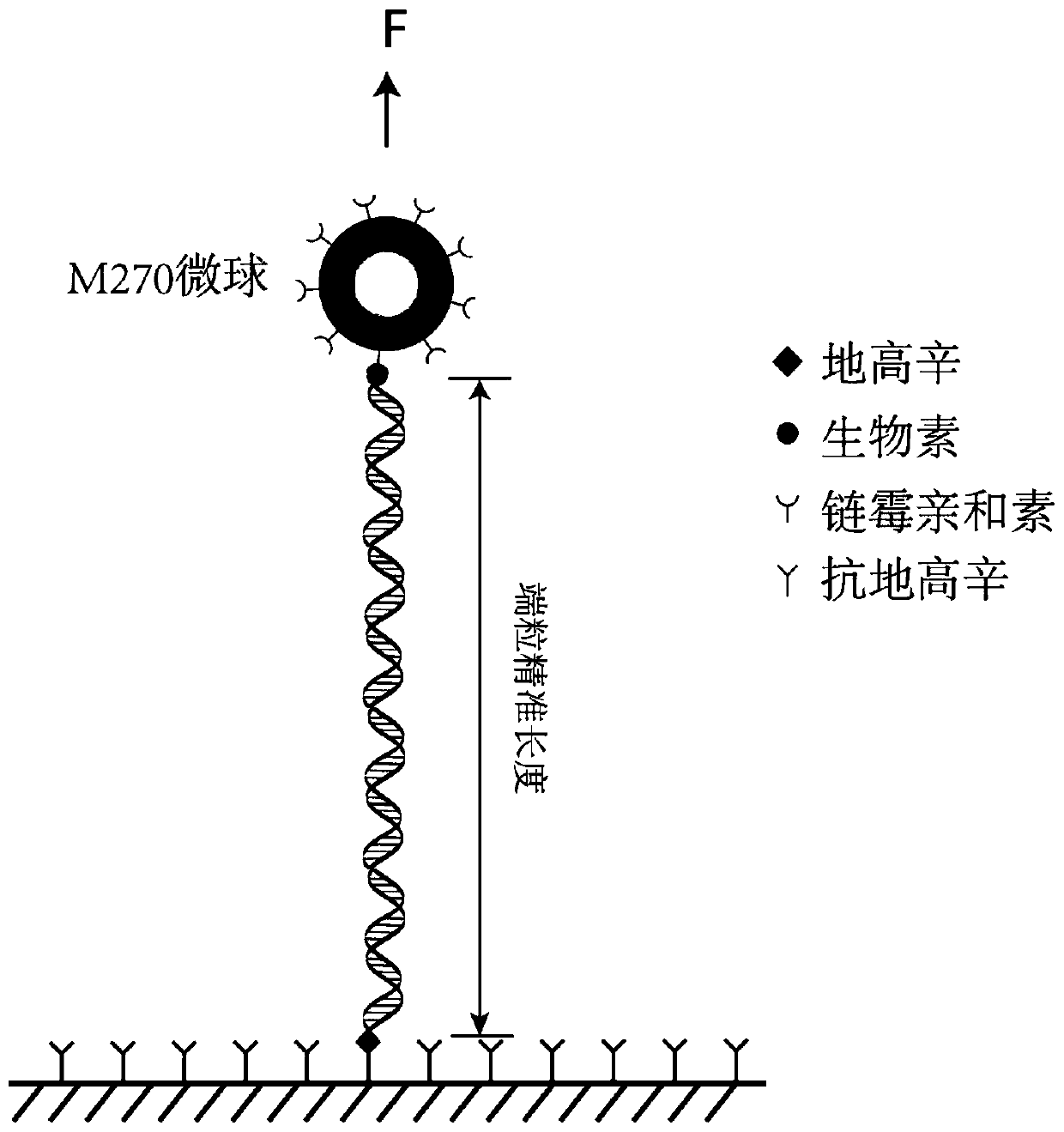
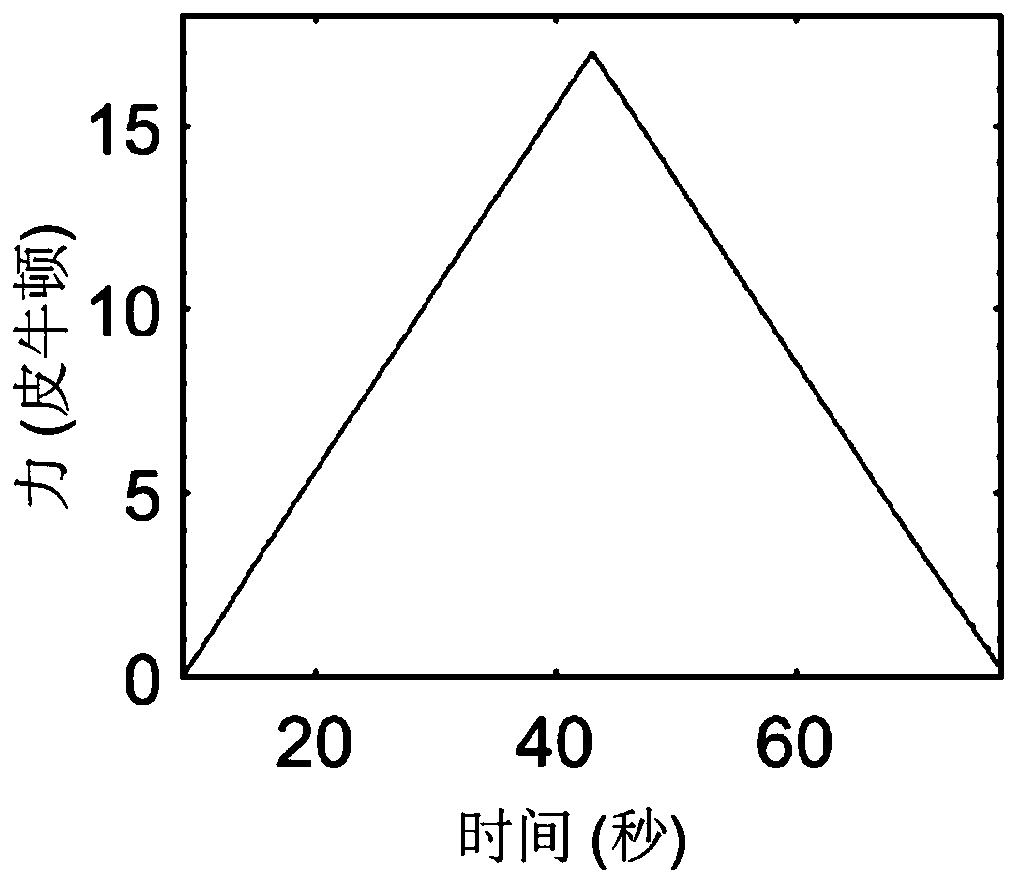
PendingCN111549098ALow influence of length measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisEnzyme digestionAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to a monomolecular mechanics method for measuring the accurate length of human telomere. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, extracting genome DNA of a target cell; digesting the genome by using combined enzyme digestion, and reserving telomere DNA; carrying out affinity labeling on the two ends of telomere DNA by adopting digoxin and biotin respectively soas to obtain a telomere DNA structure capable of being used for Monomolecular mechanical measurement; secondly, fixing the telomere structure between streptavidin-coated magnetic beads and the glass surface paved with the anti-digoxin antibody, and carrying out a DNA mechanical tensile experiment on a monomolecular instrument; and finally, using a worm model to perform length conversion between nanometer and basic group pairs on the actually measured telomere length, so as to realize accurate measurement of the telomere length. The invention belongs to the field of precise instrument measurement and analysis and cell molecular biology, and develops a new method for directly measuring the accurate length of telomere for cell research, health screening and clinical drug therapeutic effect evaluation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Methods for genome assembly, haplotype phasing, and target-independent nucleic acid detection
ActiveCN108368542BMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisProkaryote organismsAffinity labeling
The present disclosure provides methods for assembling the genomes of eukaryotic or prokaryotic organisms. The present disclosure provides methods for haplotype phasing and metagenomic assembly. The present disclosure provides a streamlined approach for accomplishing these tasks so that intermediates do not need to be labeled with affinity tags to facilitate binding to solid surfaces. The present disclosure also provides methods and compositions for de novo generation of scaffold information, linkage information, and genome information for unknown organisms in heterogeneous metagenomic samples or samples obtained from multiple individuals. Implementation of the method may allow de novo sequencing of the entire genome of an uncultured or uncharacterized organism in a heterogeneous sample, or determination of linkage information for nucleic acid molecules in a nucleic acid-containing sample obtained from multiple individuals.
Owner:DOVETAIL GENOMICS
Methods for production and purification of nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20120107879A1Good choiceReduce contaminationSugar derivativesOther chemical processesAffinity labelingSingle strand
The present invention is directed to methods for the production and isolation of nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the invention concerns isolation of mRNA molecules and the production and isolation of nucleic acid molecules (e.g., cDNA molecules or libraries), which may be single- or double-stranded. Additionally, the invention concerns selection and isolation of particular nucleic acid molecules of interest from a sample which may contain a population of molecules. Specifically, the invention concerns affinity-labeled primer-adapter molecules which allow improved isolation and production of such nucleic acid molecules, increasing both product recovery and speed of isolation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for determining amounts of polynucleotide sequences present in cell or tissue samples
ActiveUS9416401B2Easy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteQuantitative determination
The invention is related to a method and test kits for quantitative determination of polynucleotide amounts present in a sample. The test kit comprises organized pools with polynucleotide probes having distinct sizes and optionally provided with tracer tags or primer tags. The probes are allowed to hybridize with affinity tagged analyte polynucleotides from the sample. The result is hybrids, which can be recovered on a separation aiding tool provided with the pair of the affinity tag. After the quantitative release of the probes, the probes are either directly recorded, or if primer tagged, they are amplified and optionally provided with a tracer tag before recording. The invention provides a sensitive and quantitative determination of the amount polynucleotides present in a cell or tissue sample and allows a quantitative assessment of variations in the amounts of polynucleotides as a response to inherent changes or due to external stimuli.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
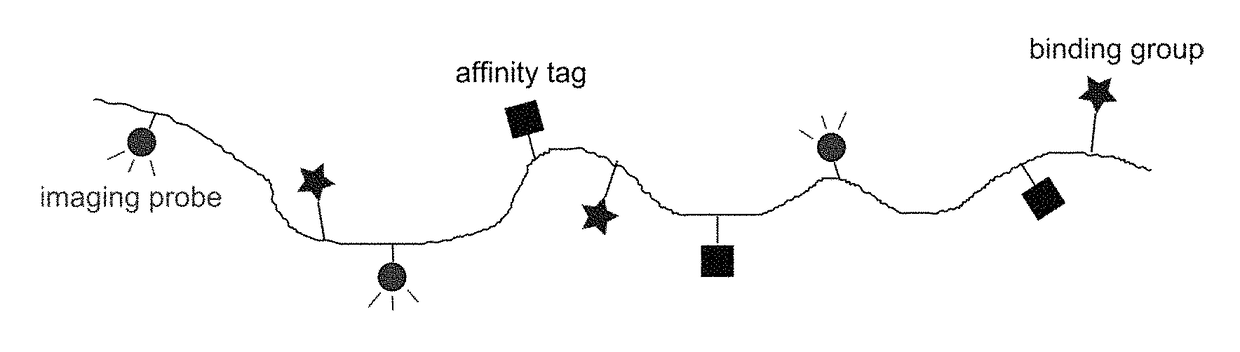
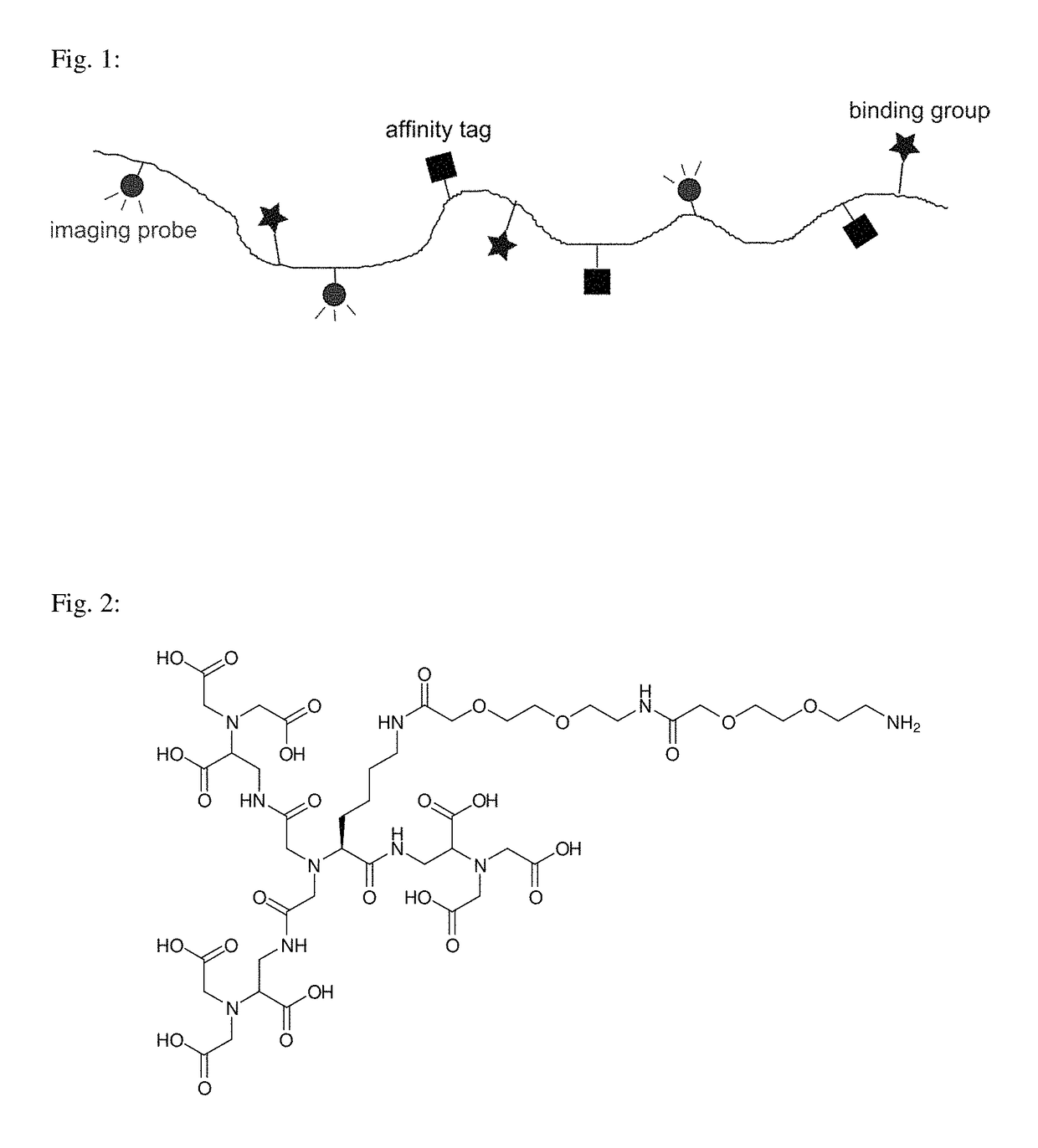
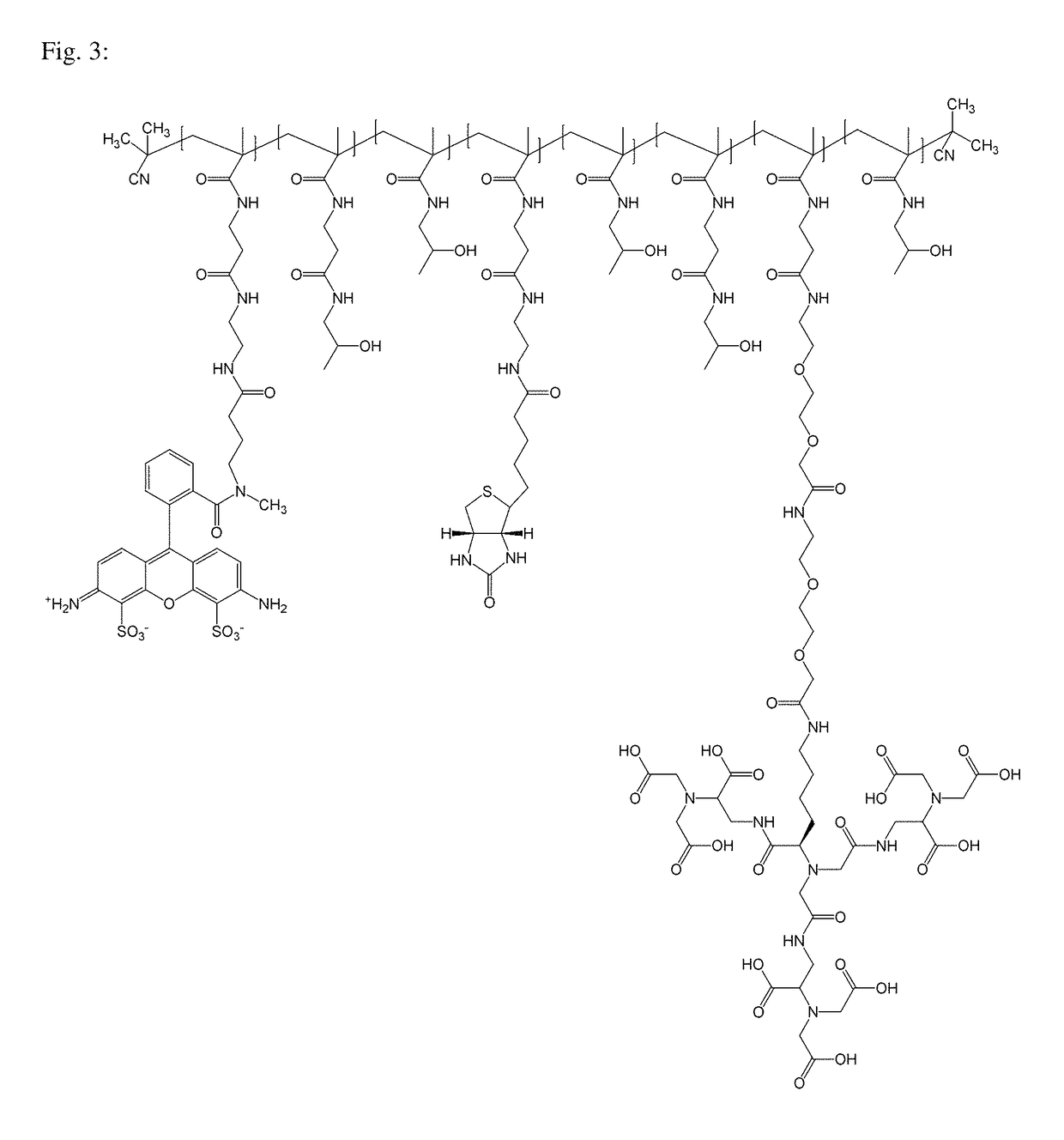
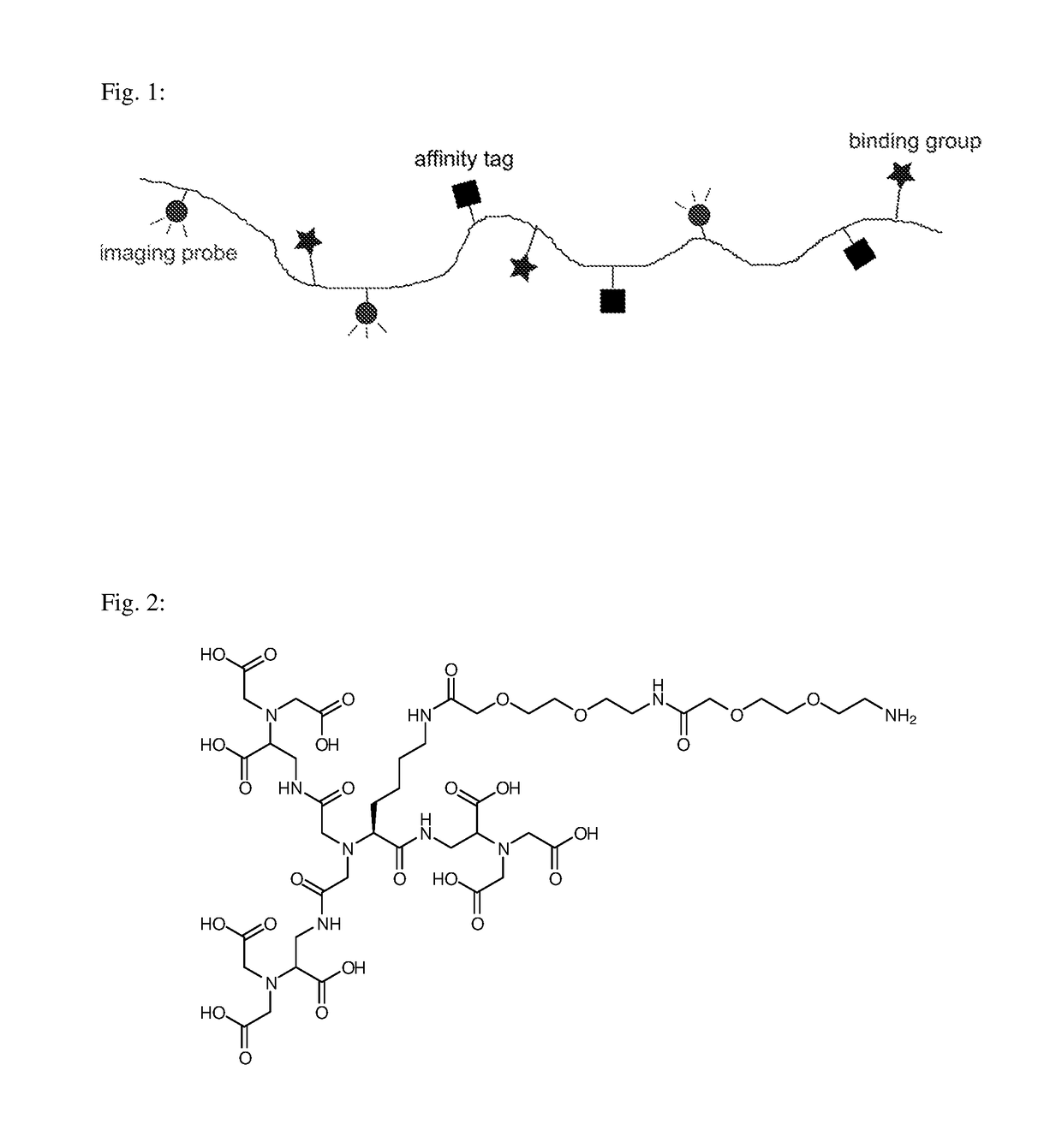
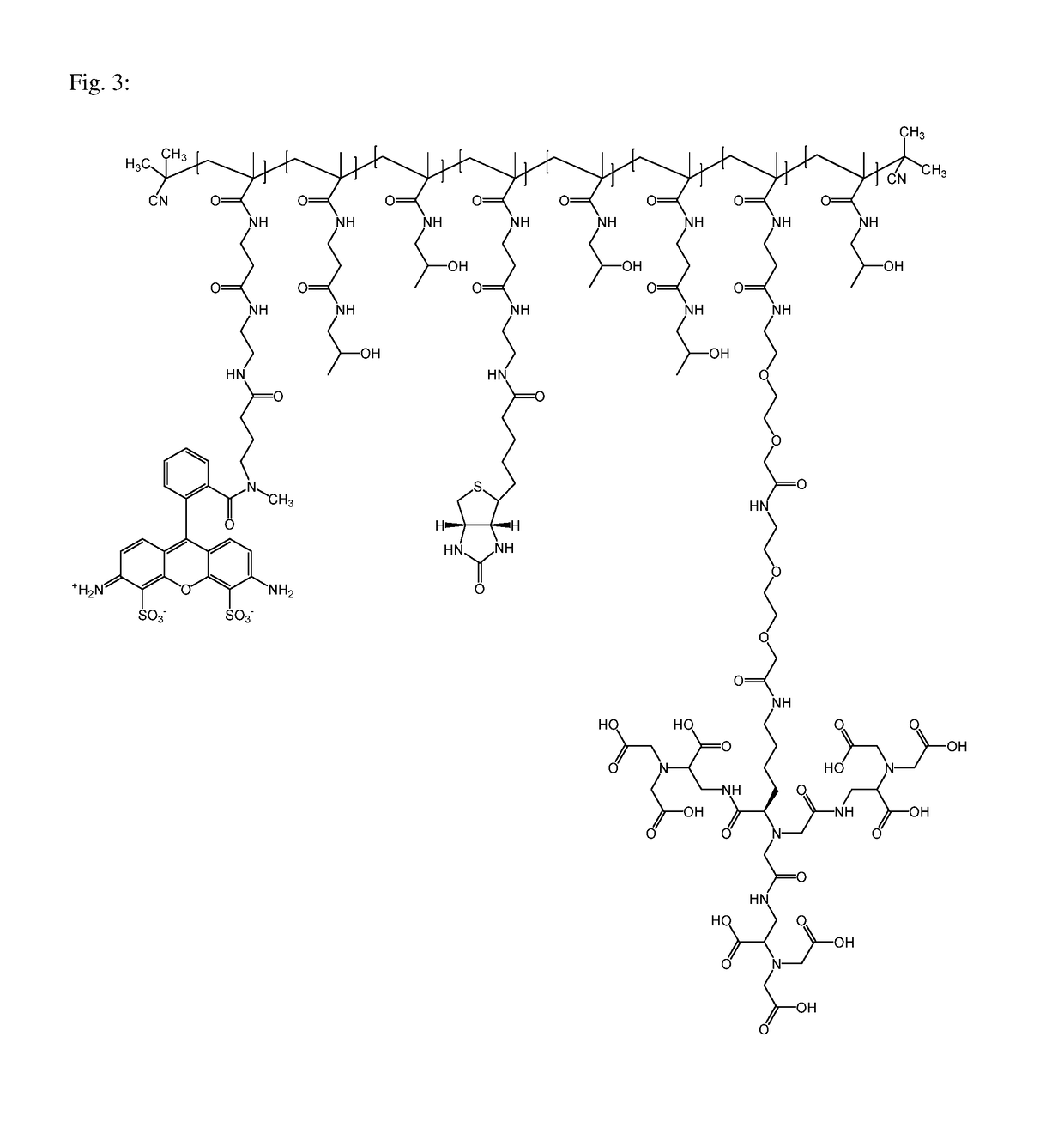
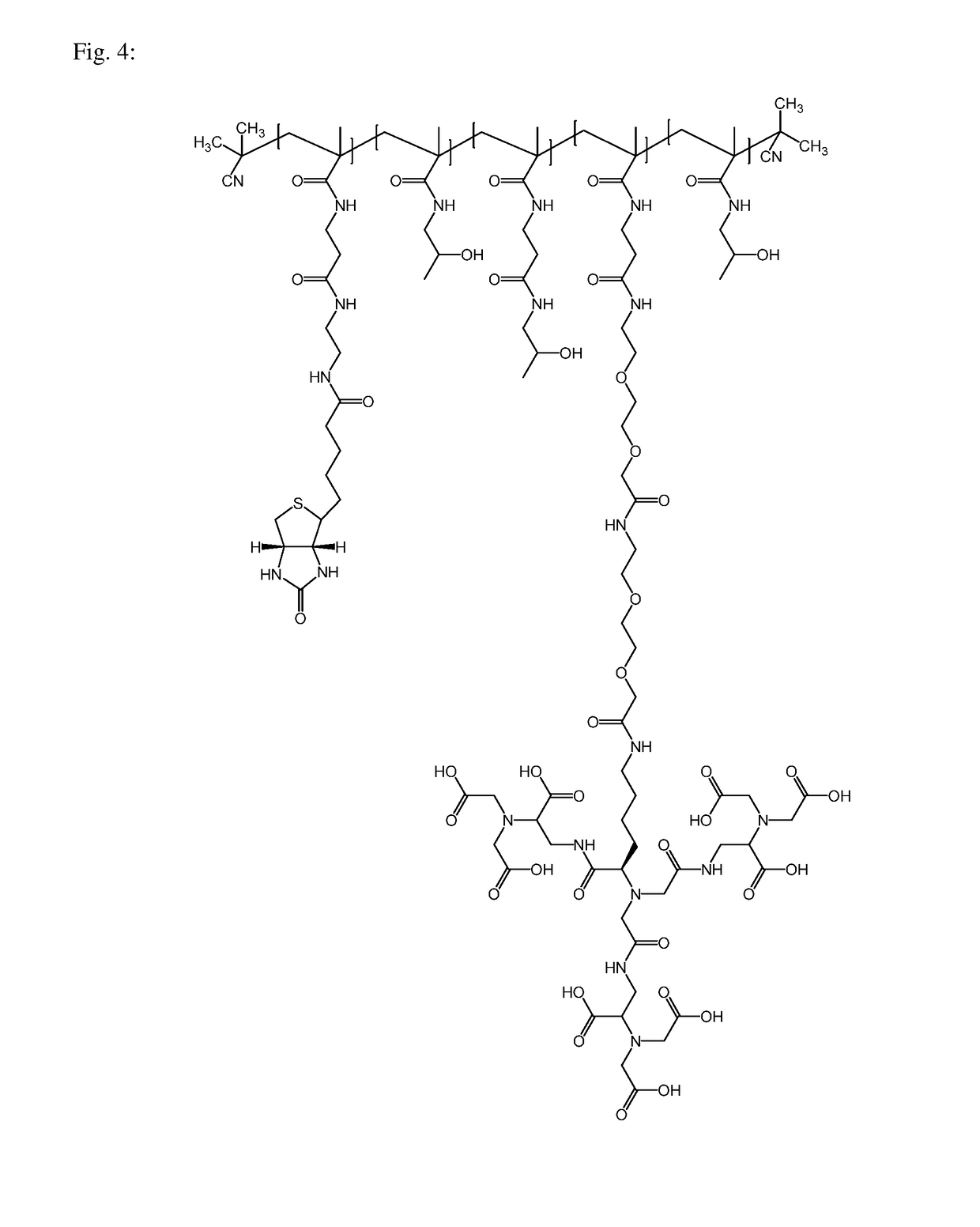
Macromolecular conjugates for isolation, immobilization and visualization of proteins
ActiveUS10114014B2Avoid steric hindranceReduce lightPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesAffinity labelingCombinatorial chemistry
Synthetic macromolecular conjugate for selective interaction with proteins has a synthetic copolymer, and at least one binding group and at least one further group selected from an affinity tag and an imaging probe, and at least one binding group and at least one further group being bound via covalent bond to the synthetic copolymer. The macromolecular conjugate is suitable in particular for identification, visualization, quantification or isolation of proteins and / or cells.
Owner:USTAV ORGANICKE CHEM A BIOCHEM AV CR +2
Method and test kit for quantitative determination of polynucleotides in a mixture
InactiveUS7361461B2Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySolution hybridizationAnalyte
The invention relates to a method and test kit for quantitative determination of the amounts or relative proportions of polynucleotides in a mixture. The invention enables assessment of dynamic variations in a mixed population of organisms using affinity aided solution hybridization. The test kit comprises organized pools of polynucleotide probes having approximately the same number of nucleotides, which are distinguishable using resolution enabling tags providing the probes with different sizes. The resolution enabling tags may simultaneously act as tracer, affinity or primer tags. The probes are allowed to hybridize with affinity tagged analyte polynucleotides. The result is hybrids, recoverable on separation aiding tools provided with counterparts of the affinity tag. After the quantitative release of the probes, the individual probes can be amplified and recorded. The method and test kit are useful for determining hygienic and epidemiologic situations and evaluating the effect of antibiotic treatment and sanitary measures.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
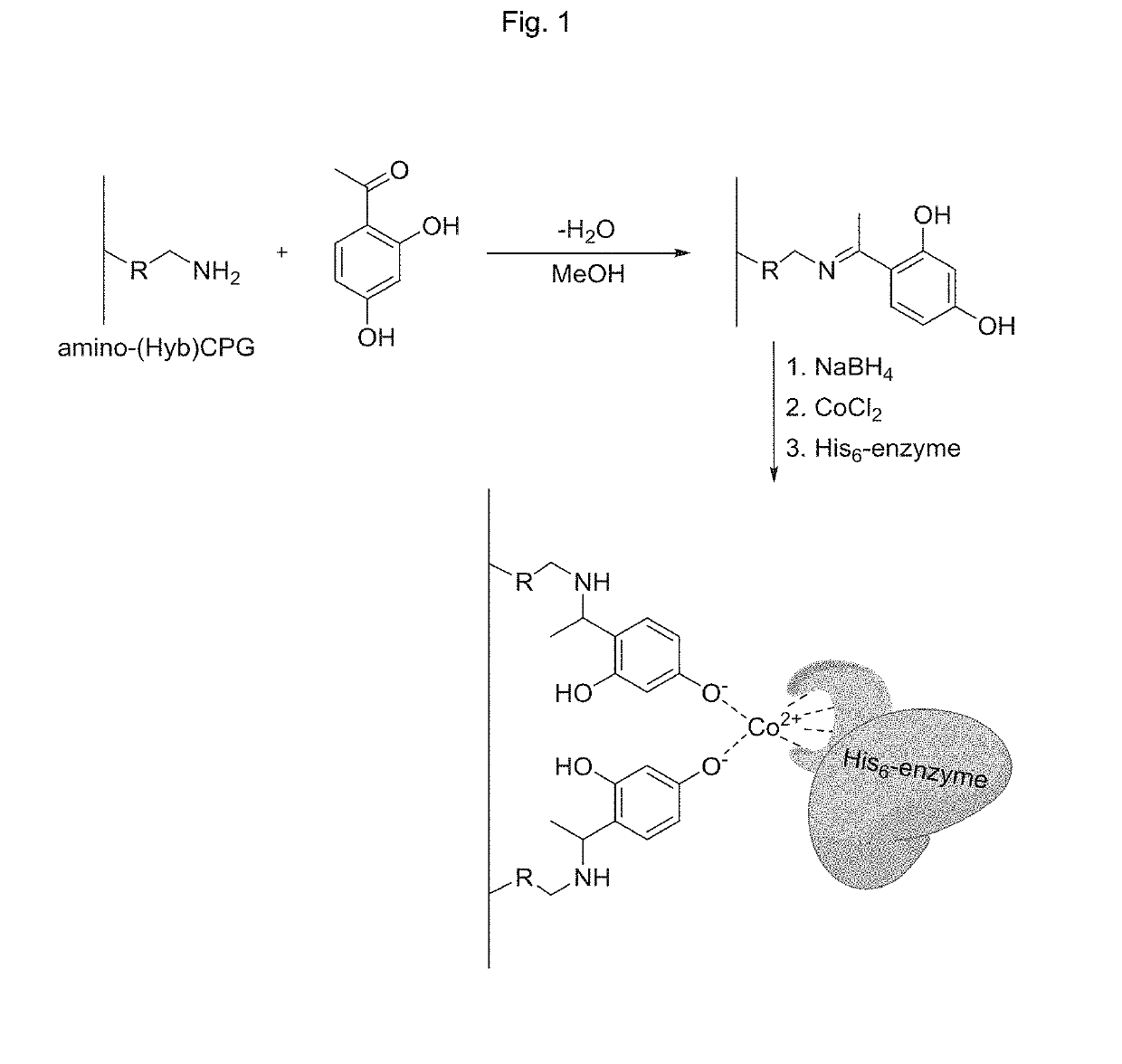
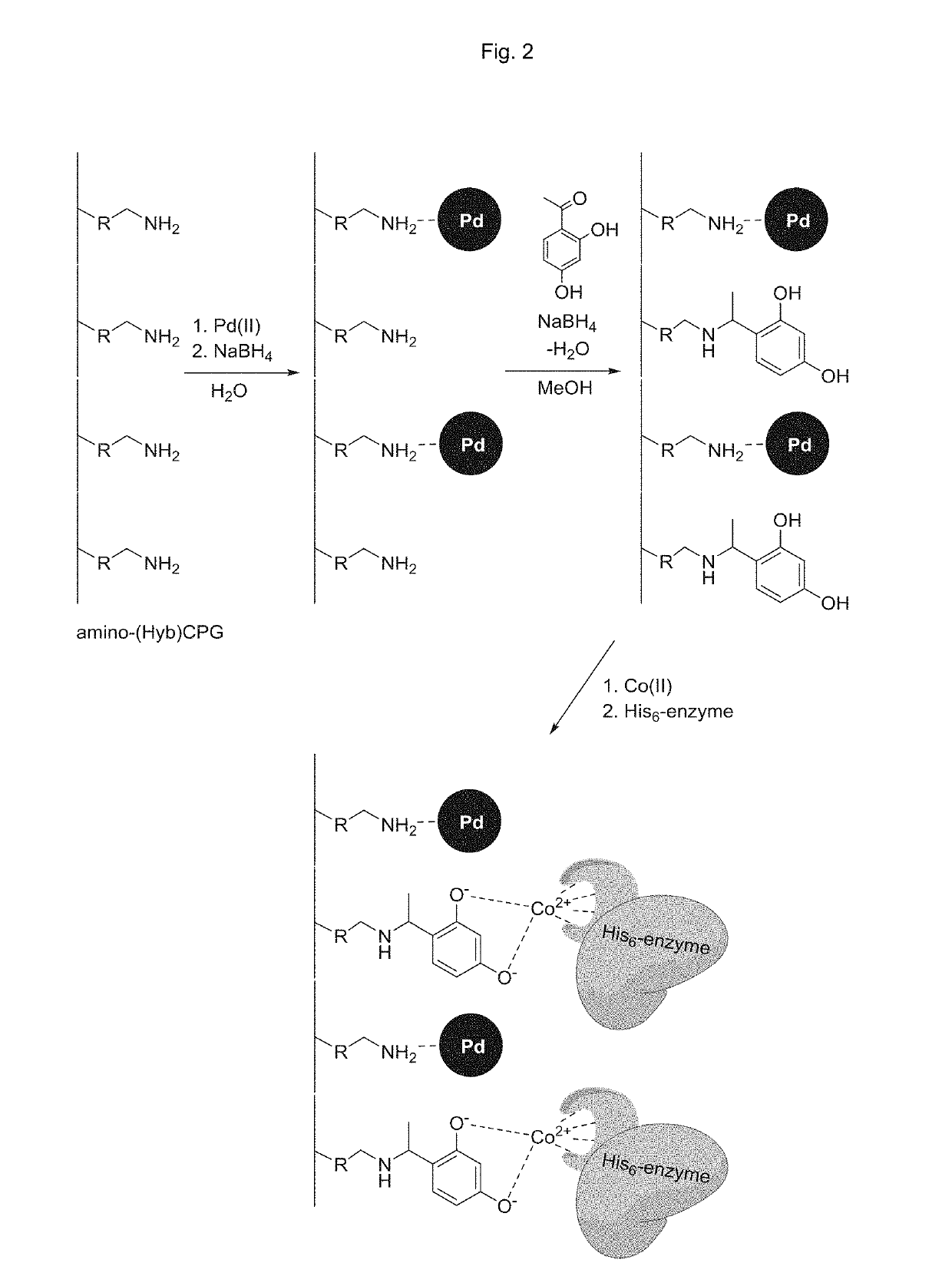
Immobilized proteins and use thereof
InactiveUS20190241884A1Easy to recycleImprove bindingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical synthesisAffinity labeling
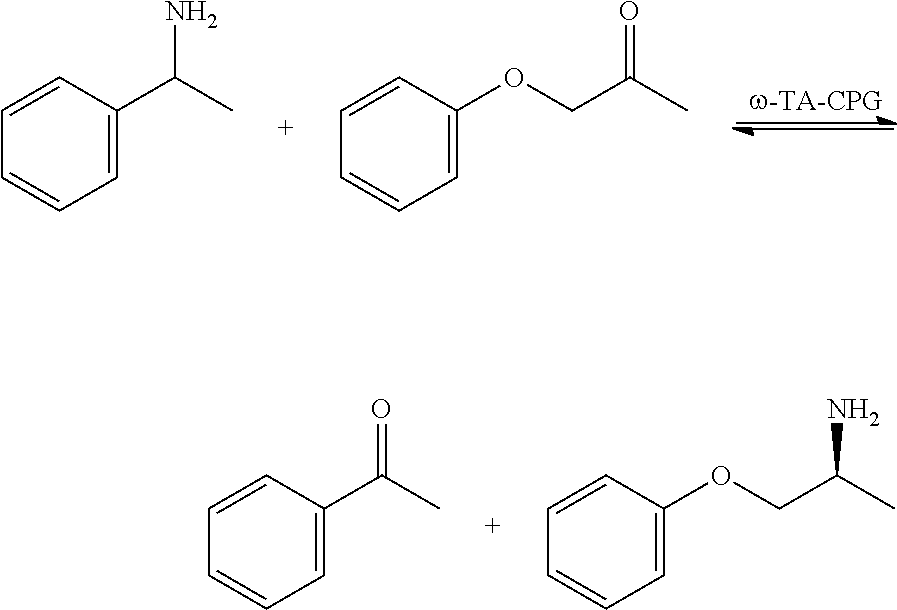
The invention relates to an immobilized protein material comprising a protein that is immobilized on a glass material or organic polymer through affinity tag binding. The glass material may be a porous glass material such as (hybrid) controlled porosity glass. The invention also relates to the use of an immobilized enzyme material as a heterogeneous biocatalyst in chemical synthesis. The invention further relates to a method for the immobilization of affinity tagged proteins on a glass material or organic polymer, and to a method for the purification and isolation of affinity tagged proteins by the immobilization of such proteins on a glass material or organic polymer.
Owner:ENGINZYME
Macromolecular conjugates for isolation, immobilization and visualization of proteins
ActiveUS20180011085A1Good chemical stabilityLower requirementCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesBiological testingAffinity labelingCombinatorial chemistry
Synthetic macromolecular conjugate for selective interaction with proteins has a synthetic copolymer, and at least one binding group and at least one further group selected from an affinity tag and an imaging probe, and at least one binding group and at least one further group being bound via covalent bond to the synthetic copolymer. The macromolecular conjugate is suitable in particular for identification, visualization, quantification or isolation of proteins and / or cells.
Owner:USTAV ORGANICKE CHEM A BIOCHEM AV CR +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com