Method for testing water content and distribution of cellular levels in fruit and vegetable tissues based on Raman spectrum
A Raman spectroscopy, cell-level technology, applied in the field of spectral detection, can solve the problems of evaluating the binding degree of intracellular water and extracellular water, indistinguishable distribution, difficult quantitative analysis by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance response method, etc., to achieve the advantage of computing speed. , the effect of saving time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A method utilizing Raman spectroscopy to test water content and state distribution in plant tissue, comprising the steps of:
[0049] (1) Use a sampler to take a 12mm×15mm (diameter×height) sample column on the apple in the radial direction, then cut the sample column into 2mm thick slices with a self-made slicing device, and place it immediately on a constant temperature and humidity quartz. The cavity was sealed with a quartz coverslip with a thickness of 0.3 mm. Set the cavity humidity to 80%, and the temperature to 4°C, place it on the laser confocal Raman microscope stage, and wait for the test.
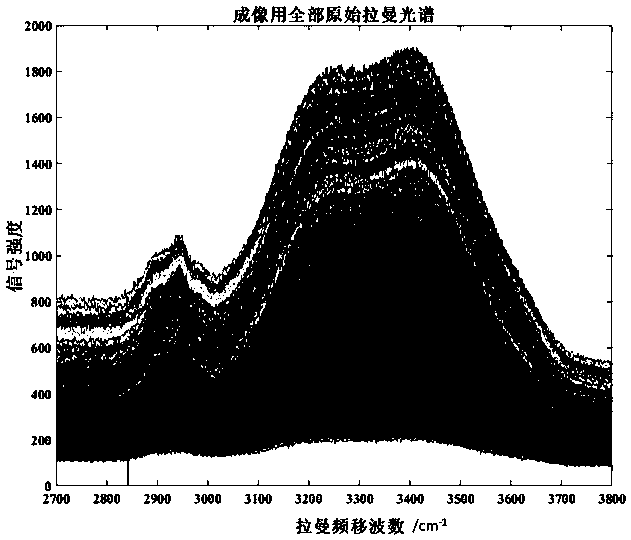
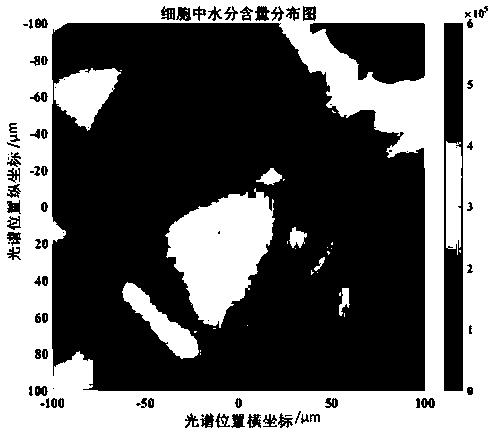
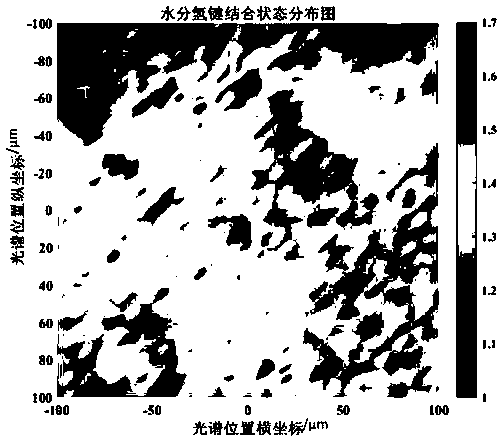
[0050] (2) Select the 10× objective lens of the laser confocal Raman microscope equipment to align with the sample, adjust the focal length to obtain a clear microscopic image of the tissue structure, and select cells with complete structure as the measurement area, such as Figure 4 As shown, the area size is 200 × 200 μm, and the selected area is meshed with a step siz...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com