Bacterial cellulose hydrogel dressing for diabetic wound surface and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and hydrogel, applied in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problem that dressings are not suitable for diabetic wounds, and achieve the effects of reducing blood sugar on wounds, ensuring safety, and promoting healing rates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
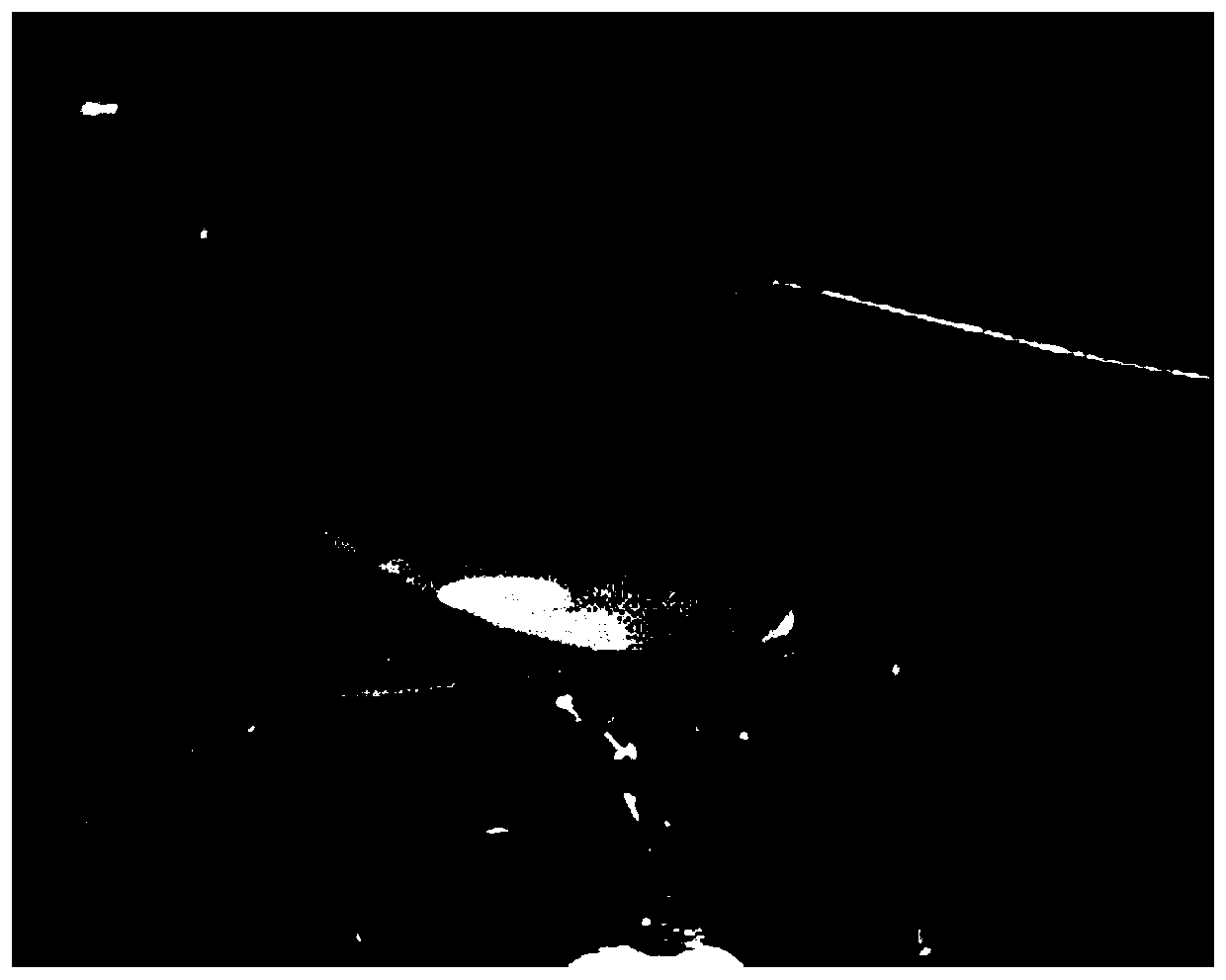
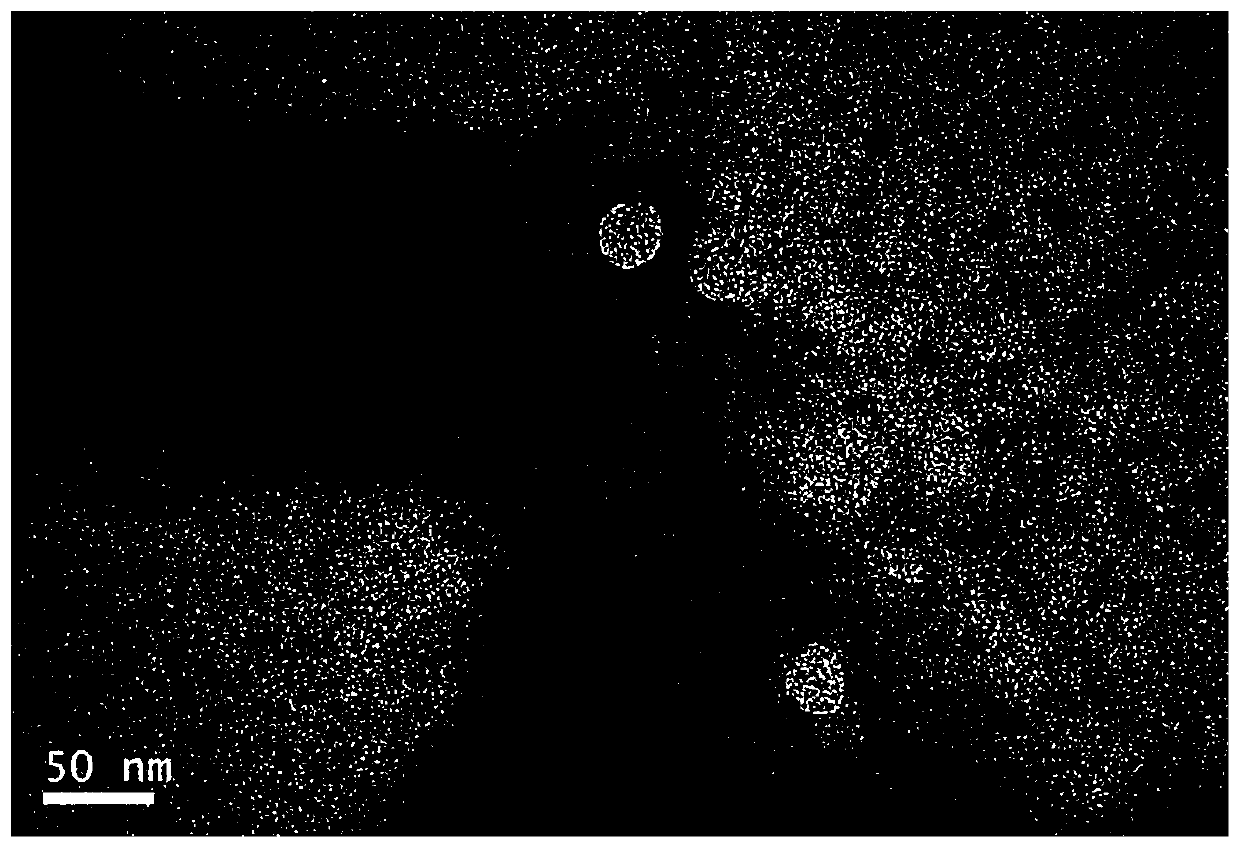
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The preparation method of the bacterial cellulose hydrogel dressing for diabetic wounds of the present invention comprises the following four steps;
[0052] The first step is to modify the raw material bacterial cellulose BC to obtain aldehyde-ylated bacterial cellulose BC-CHO;
[0053] The second step is to further oxidatively modify the aldehyde-ylated bacterial cellulose BC-CHO to obtain carboxylated bacterial cellulose BC-COOH;
[0054] The third step is to react the carboxylated BC-COOH with aminated glucose oxidase to prepare a bacterial cellulose-glucose oxidase BC-GOD hydrogel, wherein the glucose oxidase and the bacterial cellulose skeleton are separated by a amide bonds are connected;
[0055] The fourth step is to soak the BC-GOD gel in the solution of the hematopoietic stem cell mobilization drug AMD3100 overnight to obtain the BC-GOD hydrogel loaded with AMD3100.
Embodiment 1
[0057] 5g of raw bacterial cellulose gel (solid content of 0.27g) was cut into small pieces and placed in 250mL of a solution containing 0.71g of sodium periodate and stirred for 24h, wherein the molar ratio of sodium periodate to bacterial cellulose structural unit was 2 : 1. After the reaction was completed, the reaction was terminated with 10 mL of ethylene glycol and the gel was washed to prepare the aldehydeylated bacterial cellulose BC-CHO. The BC-CHO was then placed in 250 mL of a mixed solution containing sodium chlorite and hydrogen peroxide and stirred for 12 h, wherein the molar ratio of the total aldehyde groups of sodium chlorite to BC-CHO was 2:1, and the ratio of sodium chlorite to peroxide was 2:1. The molar ratio of hydrogen was 1:1, and the gel was washed after the end to prepare carboxylated bacterial cellulose BC-COOH.
[0058] A total of 100 mL of 2 mg / mL glucose oxidase solution was prepared and reacted with 0.01 mol of NAS (acryloyloxysuccinimide) at pH ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] 5g of raw bacterial cellulose gel (solid content of 0.27g) was cut into small pieces and placed in 250mL of sodium periodate solution containing 0.71g and stirred for 18h, wherein the molar ratio of sodium periodate to bacterial cellulose structural unit was 2 : 1. After the reaction was completed, the reaction was terminated with 20 mL of ethylene glycol and the gel was washed to prepare the aldehydeylated bacterial cellulose BC-CHO. The BC-CHO was then placed in 250 mL of a mixed solution containing sodium chlorite and hydrogen peroxide and stirred for 24 hours, wherein the molar ratio of the total aldehyde groups of sodium chlorite to BC-CHO was 2:1, and the ratio of sodium chlorite to peroxide was 2:1. The molar ratio of hydrogen was 1:1, and the gel was washed after the end to prepare carboxylated bacterial cellulose BC-COOH.
[0063] The carboxylated bacterial cellulose BC-COOH was placed in 250 mL of pH 5.0 phosphate buffer, and the catalysts 1-ethyl-(3-dimethyla...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com