Method for magnesium removal of phosphate rock and co-production of magnesium carbonate and calcium carbonate
A technology of magnesium carbonate and calcium carbonate, which is applied in the field of phosphorus chemical industry, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of waste liquid, high loss rate of phosphorus, and high production cost, and achieve the effects of low production cost, low loss rate of phosphorus, and short treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
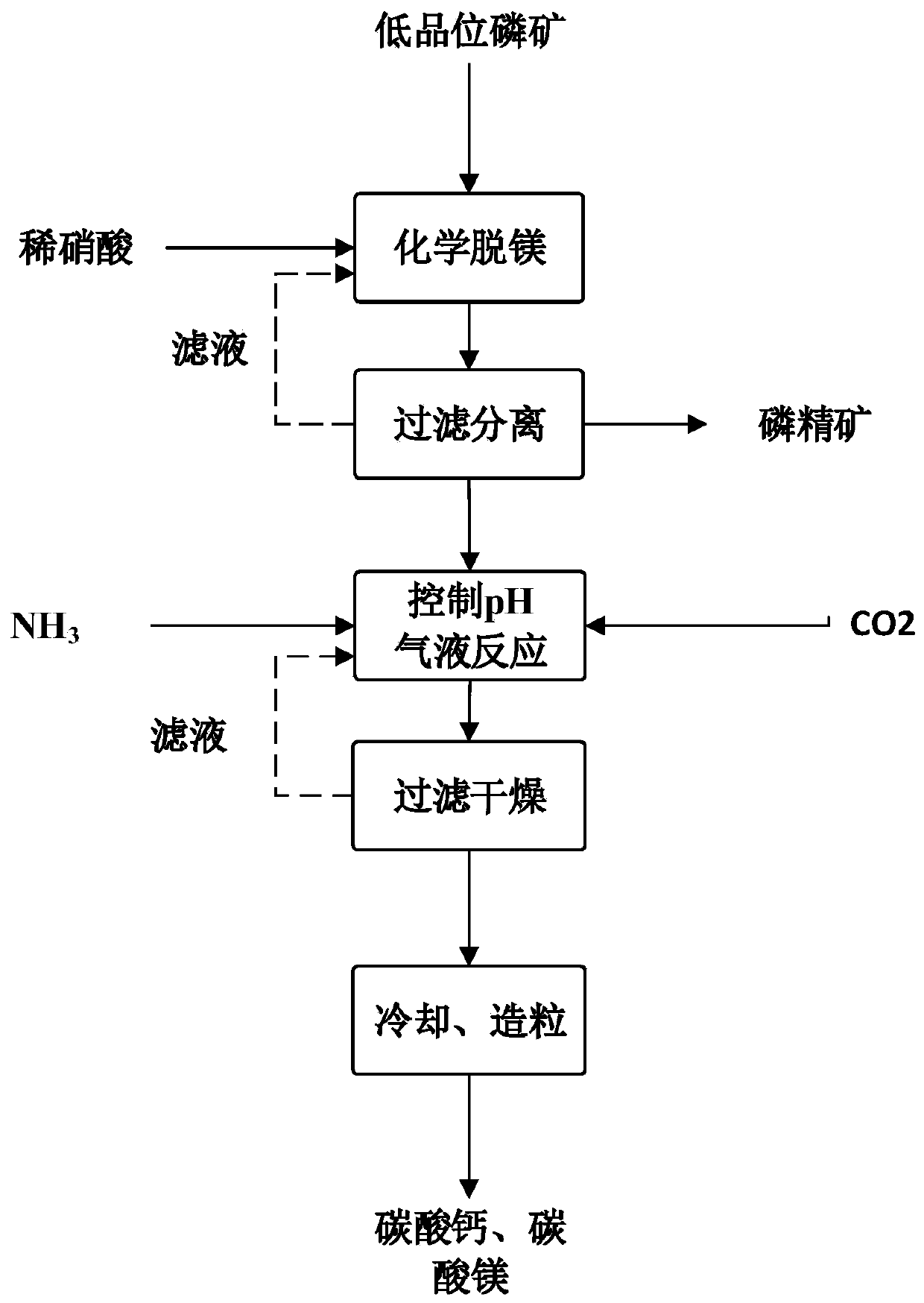
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, after the low-grade phosphate rock is crushed, crushed, and sieved, the phosphate rock powder with a particle size of 60-80 mesh is obtained, and water is added to prepare a slurry with a water content of 35%.
[0054] Add the nitric acid solution to the phosphate rock slurry with a water content of 35%, and fully mix it at a speed of 300r / min for reaction. The reaction time is 2 hours, and the temperature of the control process is 45°C. To control the pH of the reaction system to be 2, the liquid-solid ratio is 3:1.
[0055] After the reaction is completed, the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification is obtained; the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification flows out from the reaction tank and is transferred to the solid-liquid separator, and is separated to obtain a solid phase a with a moisture content of 10wt%-20wt% and a solid phase a containing For magnesium solution b, wash the solid phase a with distilled water until the wa...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Such as figure 1 As shown, after the low-grade phosphate rock is crushed, crushed, and sieved, the phosphate rock powder with a particle size of 80-100 mesh is obtained, and water is added to prepare a slurry with a water content of 35%.
[0063] Add the nitric acid solution to the phosphate rock slurry with a water content of 35%, and fully mix it at a speed of 300r / min for reaction. The reaction time is 4 hours, and the temperature of the control process is 40°C. To control the pH of the reaction system to be 3.5 and the liquid-solid ratio to be 4:1.
[0064] After the reaction is completed, the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification is obtained; the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification flows out from the reaction tank and is transferred to the solid-liquid separator, and is separated to obtain a solid phase a with a moisture content of 10wt%-20wt% and a solid phase a containing For magnesium solution b, wash the solid phase a with distilled water unt...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Such as figure 1 As shown, after jaw crushing, crushing, and screening, phosphate rock powder with a particle size between 40 and 60 meshes is obtained, and water is added to prepare a slurry with a water content of 35%.
[0072] Add the nitric acid solution into the phosphate rock slurry with a water content of 35%, and fully mix it at a speed of 300r / min for reaction. The reaction time is 3 hours, and the temperature of the control process is 55°C. To control the pH of the reaction system to be 2.5, the liquid-solid ratio is 2.5:1.
[0073] After the reaction is completed, the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification is obtained; the phosphate rock slurry after demagnesification flows out from the reaction tank and is transferred to the solid-liquid separator, and is separated to obtain a solid phase a with a moisture content of 10wt%-20wt% and a solid phase a containing For magnesium solution b, wash the solid phase a with distilled water until the washing wate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com