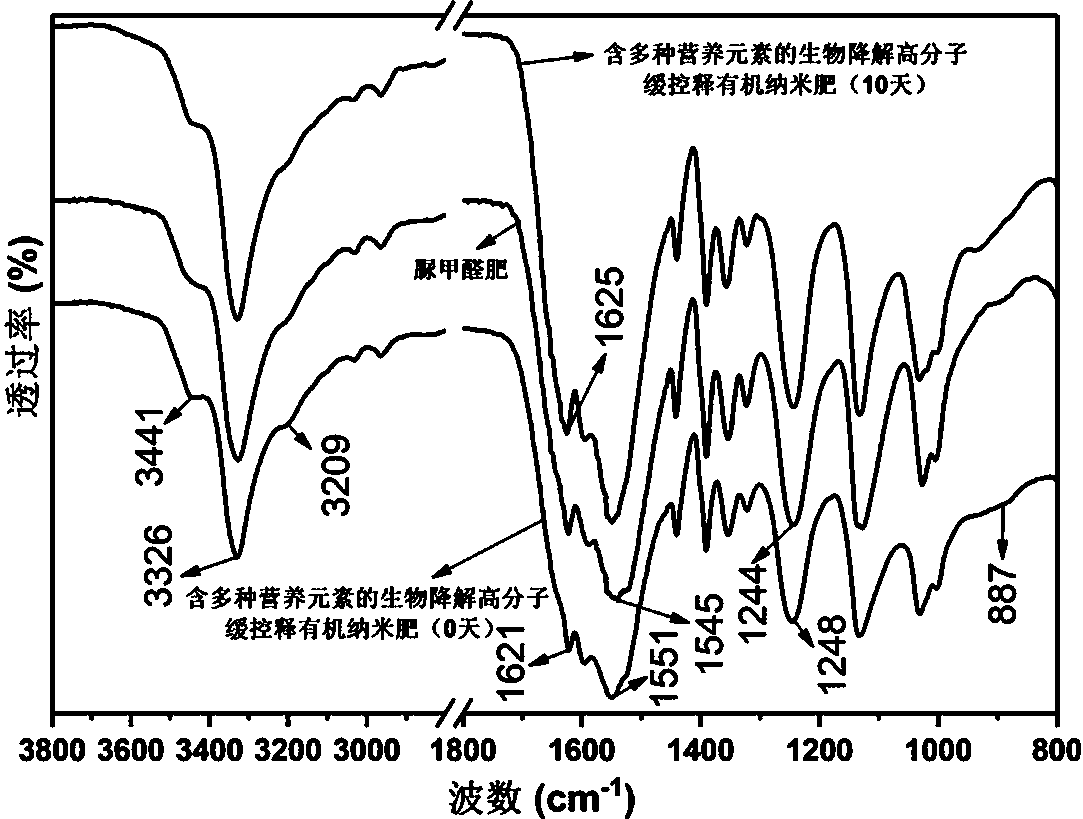
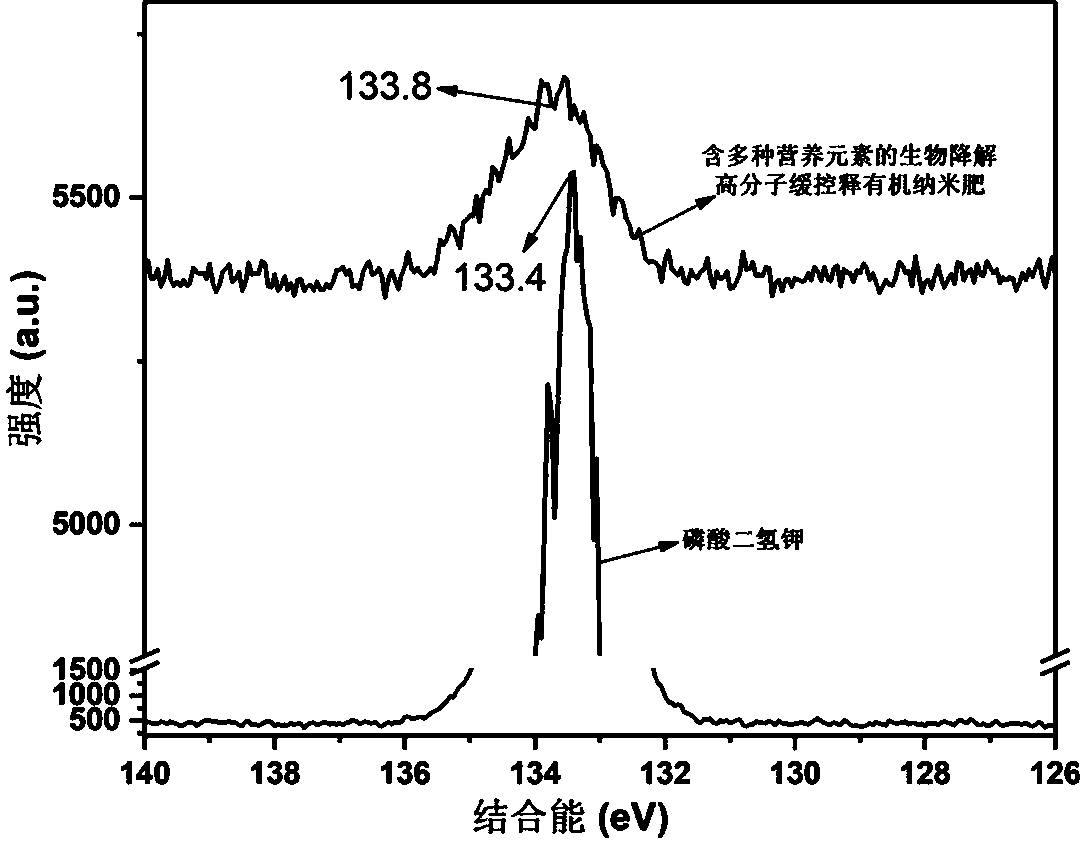
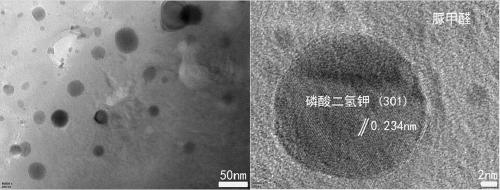
Preparation of biological degradable macromolecule slow-controlled release organic nano fertilizer with multiple nutrient elements
A nutrient element, biodegradation technology, applied in urea compound fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer and other directions, can solve the problems of complex process, expensive equipment, difficult to large-scale industrial production, etc., achieve simple and efficient preparation process, reduce crystallinity, The effect of excellent sustained release properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The method for preparing a biodegradable polymer slow and controlled release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements includes the following steps:
[0034] (1) Add 83.1g formaldehyde solution (37wt%) and 123.0g urea into the reactor respectively, adjust the pH of the system to 8, and react at 60℃ for 2h; then raise the temperature of the reaction system to 80℃, and add 10.0g diphosphoric acid Potassium hydrogen continues to react until the system is viscous;
[0035] (2) The obtained viscous product is granulated and dried to a constant weight at 100°C to obtain a biodegradable polymer slow-release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements.
[0036] The nitrogen content of the obtained biodegradable polymer slow and controlled release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements is 35.0wt%, and P 2 O 5 The calculated phosphorus content is 3.2wt%, in K 2 The potassium content based on O is 2.1 wt%.
Embodiment 2
[0038] The method for preparing a biodegradable polymer slow and controlled release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements includes the following steps:
[0039] (1) Add 83.1g formaldehyde solution (37wt%) and 73.8g urea into the reactor, adjust the pH of the system to 10, and react at 40℃ for 2h; then raise the temperature of the reaction system to 60℃, and add 10.0g phosphoric acid Calcium continues to react until the system is viscous;
[0040] (2) The obtained viscous product is granulated and dried to a constant weight at 40°C to obtain a biodegradable polymer slow-release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements.
[0041] The nitrogen content of the obtained biodegradable polymer slow-release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements was 29.4wt%, 2 O 5 The calculated phosphorus content is 2.4wt%, based on K 2 The potassium content based on O is 0.0wt%.
Embodiment 3
[0043] The method for preparing a biodegradable polymer slow and controlled release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements includes the following steps:
[0044] (1) Add 83.1g formaldehyde solution (37wt%) and 73.8g urea into the reactor, adjust the pH of the system to 8, and react at 40°C for 2h; then raise the temperature of the reaction system to 60°C, and add 66.0g diphosphoric acid Potassium hydrogen continues to react until the system is viscous;
[0045] (2) The obtained viscous product is granulated and dried to a constant weight at 100°C to obtain a biodegradable polymer slow-release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements.
[0046] The nitrogen content of the obtained biodegradable polymer slow and controlled release organic nano-fertilizer containing multiple nutrient elements is 21.3wt%, 2 O 5 The calculated phosphorus content is 21.0wt%, in K 2 The potassium content based on O is 13.9% by weight.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com