Nucleic acid fragment sorting and purifying reagent and method
A nucleic acid fragment and purification method technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid fragment separation and purification reagents, can solve problems such as danger, time-consuming, and complicated operation, and achieve high-throughput separation of nucleic acid fragment size, high recovery rate and purity, and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
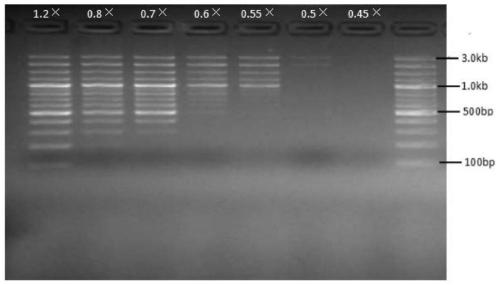
[0026] Implementation Case 1: Fragment Gradient Sorting on DNA
[0027] Use a nucleic acid mixture containing 100bp, 200bp, 300bp, 400bp, 500bp, 600bp, 700bp, 800bp, 900bp, 1kb, 1.2kb, 1.5kb, 2kb, 3kb for nucleic acid sorting templates to sort nucleic acid fragments of different segments.
[0028] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0029] 1. Binding: Take seven 1.5ml EP tubes, add 50ul nucleic acid mixture respectively, and then select a specific volume of magnetic bead binding solution according to the size of the target fragment to be sorted (see Table 1), vortex and mix, and place at room temperature for 5 minutes. The EP tube was placed on the magnetic stand for 2 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded.
[0030] 2. Washing: Take 200ul of washing liquid and vortex to mix the magnetic beads, and place at room temperature for 30s. After the end, place the centrifuge tube on the magnetic stand for 2min, discard the supernatant, and dry at room temperature for ...
Embodiment example 2
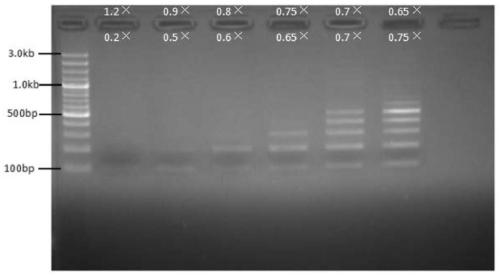
[0039] Implementation Case 2: Fragment Gradient Sorting under DNA
[0040] Use a nucleic acid mixture containing 100bp, 200bp, 300bp, 400bp, 500bp, 600bp, 700bp, 800bp, 900bp, 1kb, 1.2kb, 1.5kb, 2kb, 3kb for nucleic acid sorting templates to sort nucleic acid fragments of different segments.
[0041] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0042] 1. The first binding (remove the upper fragment): Take six 1.5ml EP tubes, add 50ul nucleic acid mixture respectively, and then select a specific volume of magnetic bead binding solution according to the size of the target fragment to be sorted (see Table 2), and vortex to mix , placed at room temperature for 5 minutes, and then placed the EP tube on the magnetic stand for 2 minutes, and transferred the supernatant to a new EP tube for later use.
[0043] 2. The second binding (binding to the lower fragment): select a specific volume of magnetic bead binding solution (see Table 2) according to the size of the target fragment, ...
Embodiment example 3
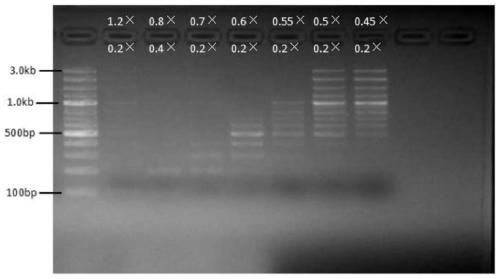
[0054] Implementation case 3: DNA intermediate fragment sorting
[0055] Use a nucleic acid mixture containing 100bp, 200bp, 300bp, 400bp, 500bp, 600bp, 700bp, 800bp, 900bp, 1kb, 1.2kb, 1.5kb, 2kb, 3kb for nucleic acid sorting templates to sort nucleic acid fragments of different segments.
[0056] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0057] 1. The first binding (remove the upper fragment): Take seven 1.5ml EP tubes, add 50ul nucleic acid mixture respectively, and then select a specific volume of magnetic bead binding solution according to the size of the target fragment to be sorted (see Table 3), and vortex to mix , placed at room temperature for 5 minutes, and then placed the EP tube on the magnetic stand for 2 minutes, and transferred the supernatant to a new EP tube for later use.
[0058] 2. The second binding (binding to the middle fragment): select a specific volume of magnetic bead binding solution according to the size of the target fragment (see Table 3), a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com