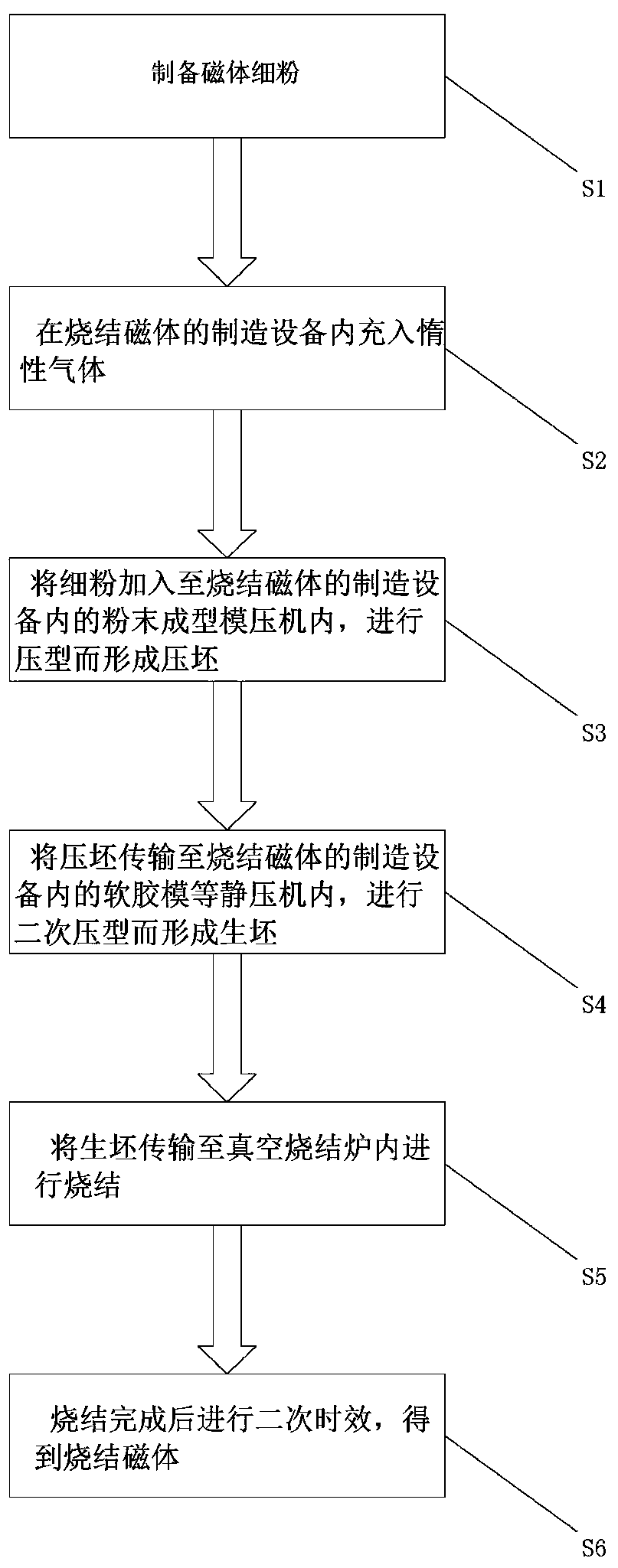
Method and equipment for manufacturing continuous sintered magnet
A technology of sintered magnets and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic objects, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the production cost of magnetic steel, environmental pollution, and poor static pressure working conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
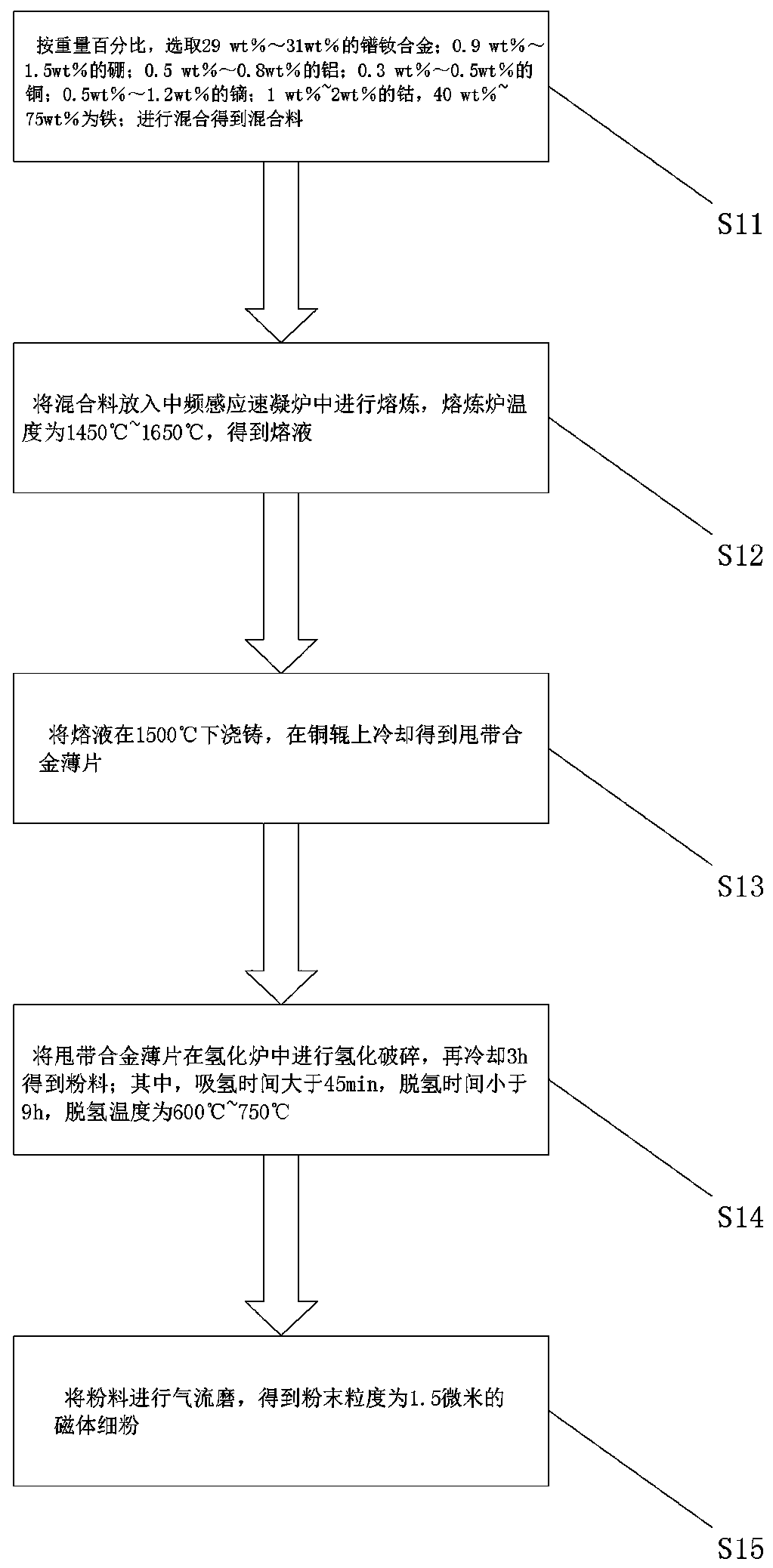
[0059] Step S11, by weight percentage, select 30wt% praseodymium neodymium alloy; 1wt% boron; 0.7wt% aluminum; 0.5wt% copper; 0.8wt% dysprosium; 1wt% cobalt, 66wt% iron; mix get the mixture;
[0060] Step S12, put the mixed material into an intermediate frequency induction quick-setting furnace for melting, and the temperature of the melting furnace is 1600° C. to obtain a melt;
[0061] Step S13, casting the melt at 1500°C, and cooling it on a copper roll to obtain stripped alloy flakes;
[0062] Step S14, carry out hydrogenation crushing of stripped alloy flakes in a hydrogenation furnace, and then cool for 3 hours to obtain powder; wherein, the hydrogen absorption time is 45 minutes, the dehydrogenation time is 9 hours, and the dehydrogenation temperature is 700°C;
[0063] Step S15, jet milling the powder to obtain fine magnet powder with a particle size of 2.5 microns.
[0064] In embodiment one, by weight percentage, select 30wt% praseodymium neodymium alloy; 1wt% boro...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Step S11, by weight percentage, select 29wt% praseodymium neodymium alloy; 1.5wt% boron; 0.8wt% aluminum; 0.5wt% copper; 1.2wt% dysprosium; 2wt% cobalt, 65wt% is iron; mix to obtain a mixture;
[0067] Step S12, putting the mixed material into an intermediate frequency induction quick-setting furnace for melting, and the temperature of the melting furnace is 1500° C. to obtain a melt;
[0068] Step S13, casting the melt at 1500°C, and cooling it on a copper roll to obtain stripped alloy flakes;
[0069] Step S14, carry out hydrogenation crushing of stripped alloy flakes in a hydrogenation furnace, and then cool for 3 hours to obtain powder; wherein, the hydrogen absorption time is 180 minutes, the dehydrogenation time is 8 hours, and the dehydrogenation temperature is 700°C;
[0070] Step S15, jet milling the powder to obtain fine magnet powder with a particle size of 2.5 microns.
[0071] In embodiment two, by weight percentage, choose the praseodymium neodymium allo...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Step S11, by weight percentage, select 29wt% praseodymium neodymium alloy; 0.9wt% boron; 0.5wt% aluminum; 0.3wt% copper; 0.5wt% dysprosium; 1.8wt% cobalt, 67wt% is iron; mixing to obtain a mixture;
[0074] Step S12, putting the mixed material into an intermediate frequency induction quick-setting furnace for melting, and the temperature of the melting furnace is 1500° C. to obtain a melt;
[0075] Step S13, casting the melt at 1500°C, and cooling it on a copper roll to obtain stripped alloy flakes;
[0076] Step S14, carry out hydrogenation crushing of stripped alloy flakes in a hydrogenation furnace, and then cool for 3 hours to obtain powder; wherein, the hydrogen absorption time is 200 minutes, the dehydrogenation time is 7.5 hours, and the dehydrogenation temperature is 720°C;
[0077] Step S15, jet milling the powder to obtain fine magnet powder with a particle size of 2.5 microns.
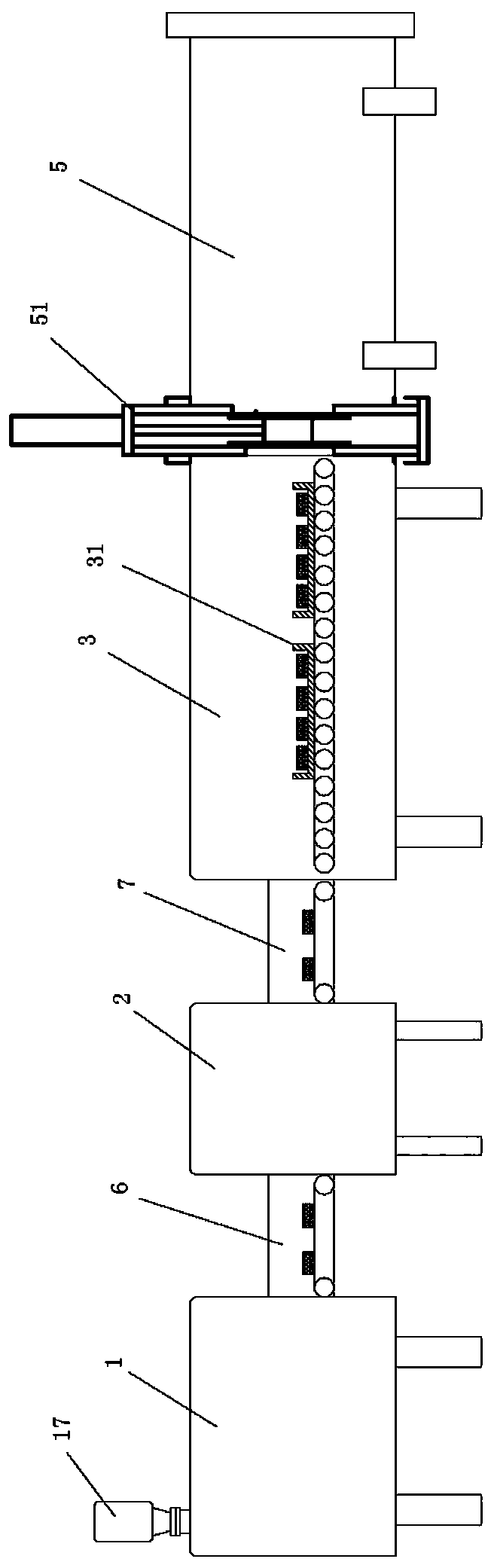
[0078] In the invention, in step S2, the continuous sintered magnet manufacturi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com