A kind of sphingobacterium and its application and method in catalytic synthesis of l(+)-tartaric acid or its salt
A technology of sphingosine and tartaric acid, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low conversion rate and achieve the effect of avoiding the use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Strain screening.
[0021] Collect the root soil of wisteria in Yuhang District, Hangzhou City, add 0.5g to 50mL of seed medium, and enrich and cultivate in a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 2 days. The enriched culture solution was diluted with sterile water for 10 6 Afterwards, it was spread on a solid plate medium, and incubated at a constant temperature of 30°C for 2 days. A single colony was picked and placed in a test tube containing 5 mL of seed medium, and cultured at 30 °C and 200 rpm for 16 h. Pipette 3 mL of seed culture liquid into 30 mL of fermentation medium containing 30 g / L 5-keto-D-gluconate potassium, cultivate at 30°C and 200 rpm, and regularly sample and detect the L(+)-tartaric acid content in the fermentation liquid. After 20 rounds of screening, a total of 2680 strains were selected from the soil for the above fermentation experiments, and several strains of microorganisms that can generate L(+)-tartrate from 5-keto-D-gluconate were screened, amon...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Sphingobacterium BK99 utilizes potassium 5-keto-D-gluconate to generate L(+)-potassium tartrate.
[0028] A single colony was picked from the solid medium and placed in a 250mL shake flask containing 50mL of seed medium, and shaken and cultivated in a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 16h to obtain a seed culture solution.
[0029] Pipette 5 mL of seed culture solution into 50 mL of fermentation medium containing different concentrations of 5-keto-D-potassium gluconate, and culture in a shaker at 30°C and 200 rpm for 10 days. After the fermentation broth was centrifuged to remove bacteria, the content of L(+)-tartaric acid in the supernatant was measured by HPLC method, and the results are shown in Table 1-5. The HPLC detection conditions are: chromatographic column Astec CLC (150 9 4.6mm), column temperature 30°C, injection volume 10 μL, mobile phase 3mM CuSO 4 Aqueous solution (pH 3.2), flow rate 1.0mL / min, detection wavelength 254nm.
[0030] Table 1 Fermentation resul...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Sphingobacterium BK99 utilizes potassium 5-keto-D-gluconate to generate L(+)-potassium tartrate.
[0042] A single colony was picked from the solid medium and placed in a 250mL shake flask containing 50mL of seed medium, and shaken and cultivated in a shaker at 30°C and 200rpm for 16h to obtain a seed culture solution.
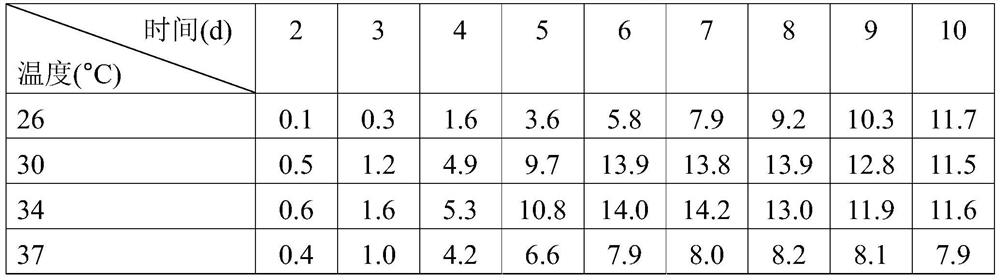
[0043] Pipette 5 mL of seed culture solution into 50 mL of fermentation medium containing 70 g / L 5-keto-D-gluconate potassium, and culture in a shaker at 200 rpm at different temperatures for 10 days. After the fermentation broth was centrifuged to remove bacteria, the content of L(+)-tartaric acid in the supernatant was measured by HPLC, and the results are shown in Table 6.
[0044] Table 6 The influence of fermentation temperature on the fermentation of Sphingobacterium to produce L(+)-tartaric acid
[0045]
[0046] Note: The data in the above table is the concentration of L(+)-tartaric acid in the fermentation broth.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com