Method for removing antimony in wastewater
A waste water and acid waste water technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as antimony removal capacity not meeting demand, heavy metal secondary pollution, etc., to achieve waste reuse and low cost Low cost, avoid secondary pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
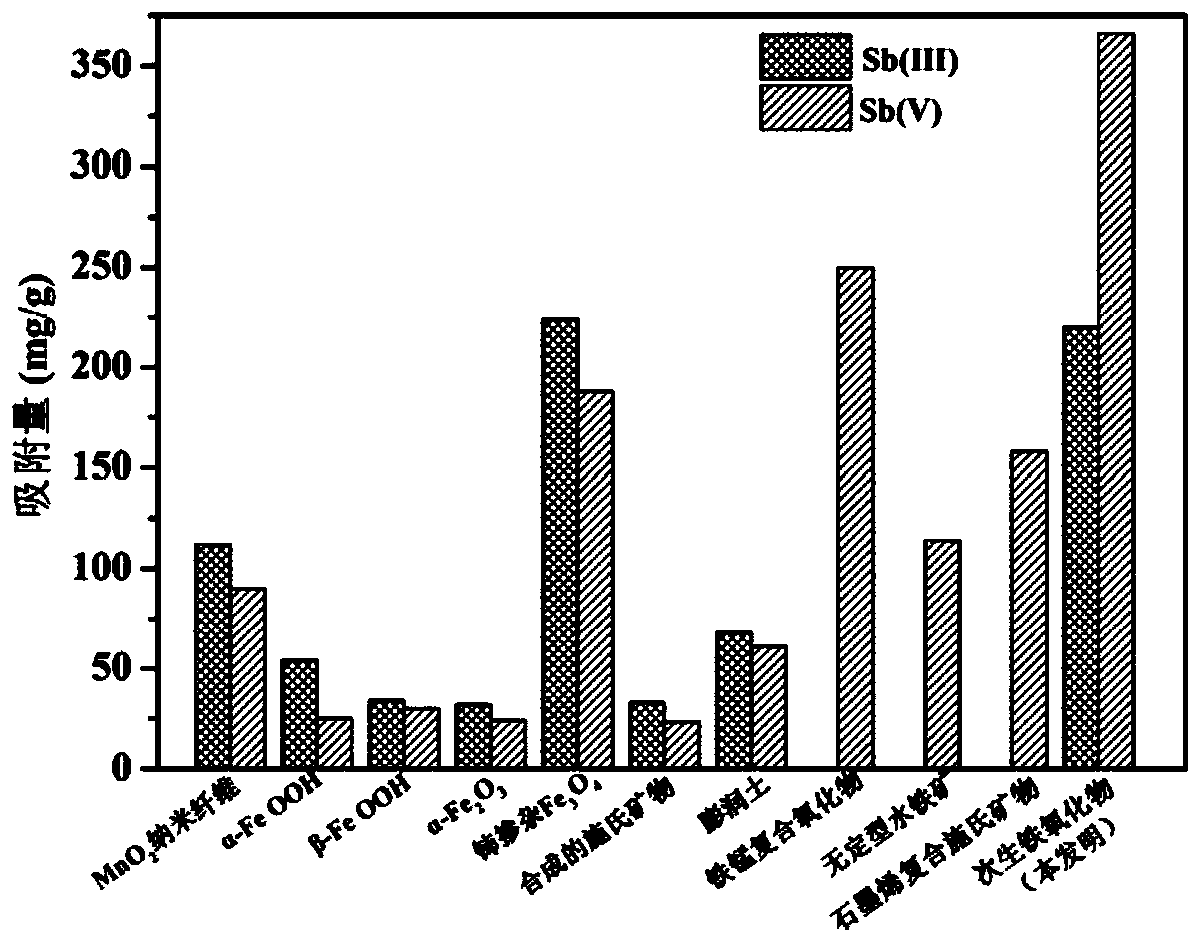
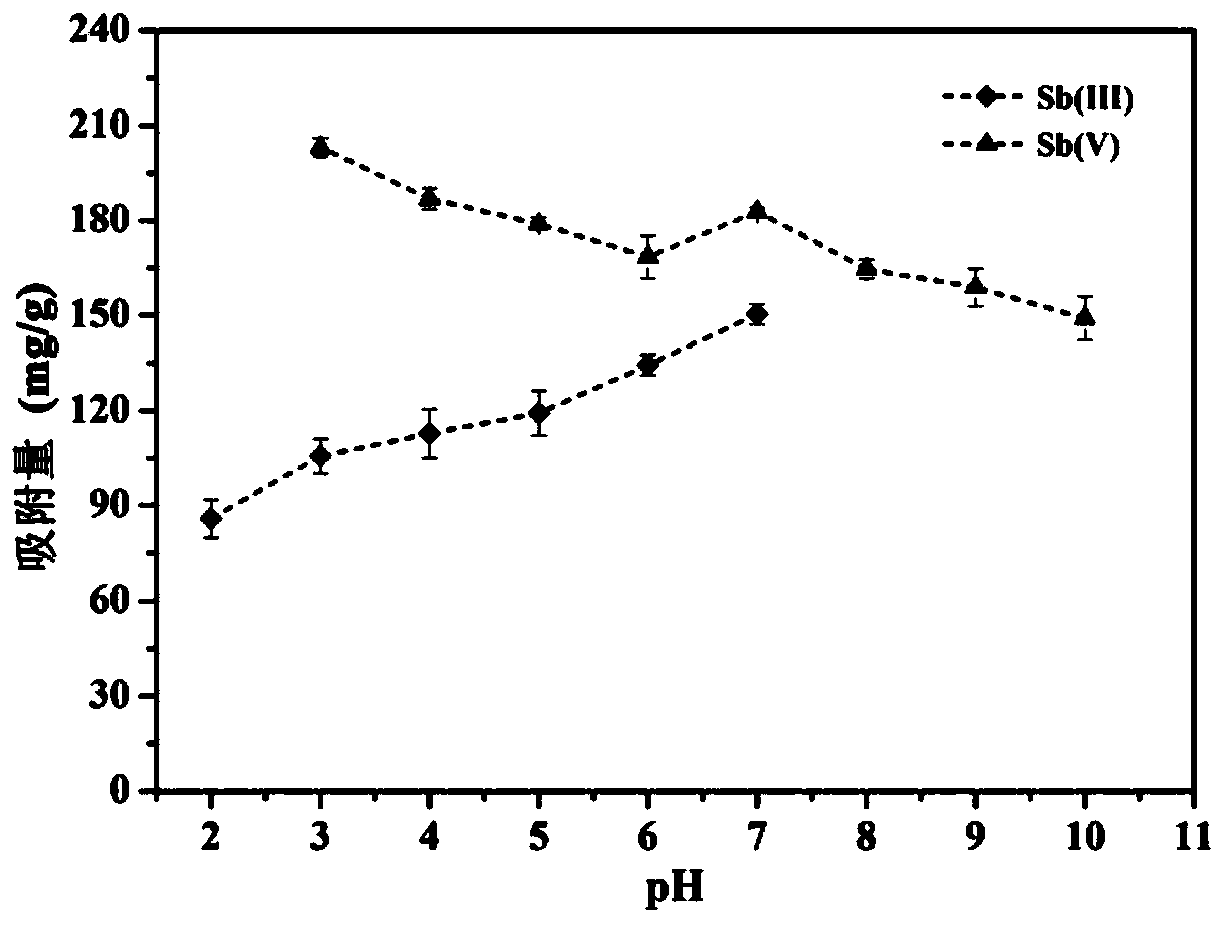
[0028] An embodiment of the method for removing antimony in waste water according to the present invention, the method is: collect the nascent secondary iron oxides in the puddle of acidic waste water in coal mines, dry and grind them, and then add Sb containing pH = 2-10 (Ⅲ) and / or Sb(Ⅴ) wastewater, shake at 25-45°C for no more than 12 hours, and then separate the solid and liquid to remove the antimony ions in the wastewater.
[0029] The applicant has studied the antimony removal performance of nascent secondary iron oxides. The nascent secondary iron oxides used in the study are formed under natural conditions from coal mine acid wastewater. The concentrations of iron ions and sulfate ions in the acid wastewater are 920 and 4905mg / L, the pH of the solution is 2.0-2.7. The acidic wastewater is collected into the puddle, and under the action of microorganisms such as sulfate-reducing bacteria and oxygen, primary ecological secondary iron oxides are generated. The primary s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com