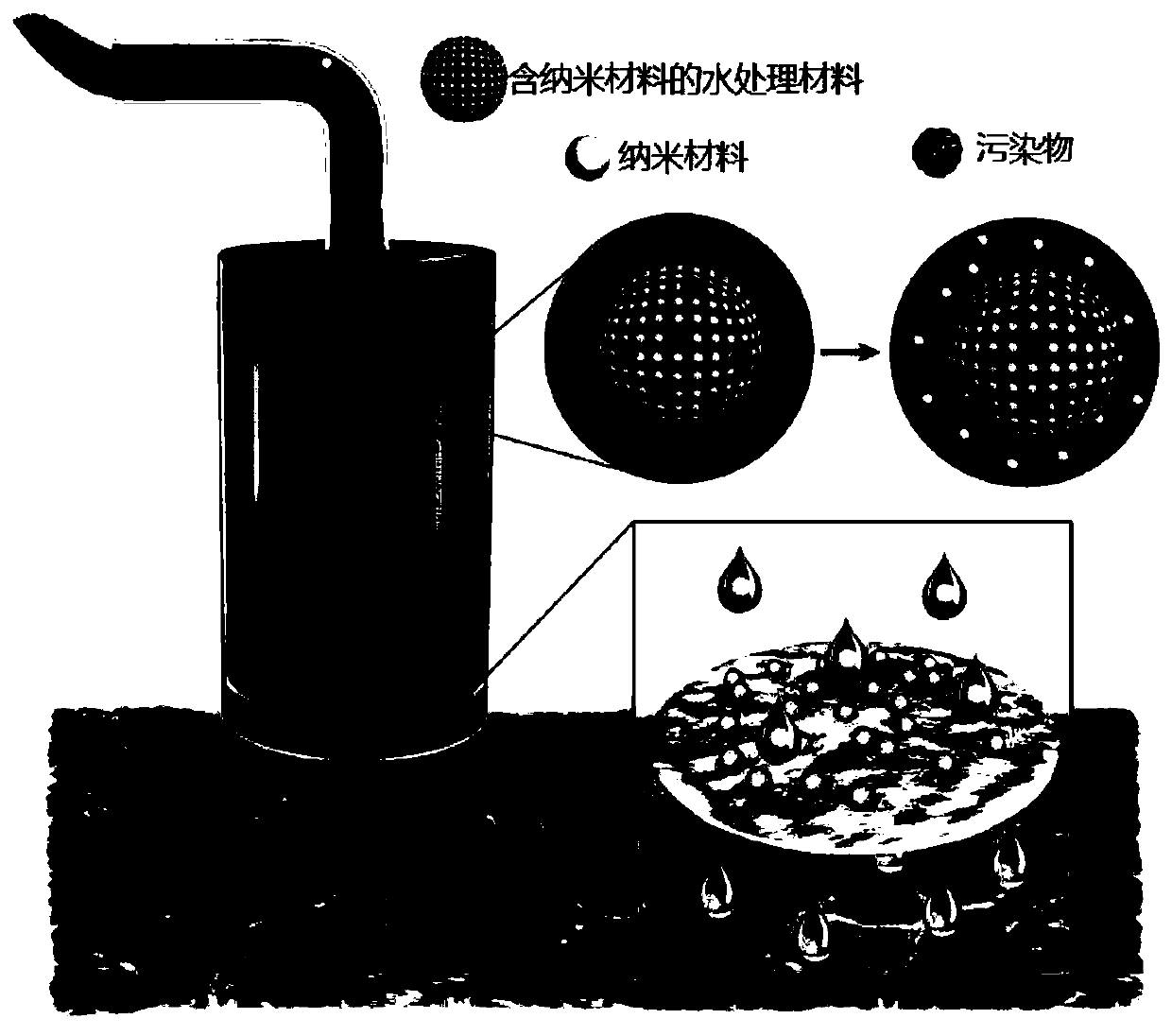
Method for rapidly removing trace nano-material in water
A nano-material and water removal technology, applied in the field of environmental chemistry, can solve problems such as no research reports, and achieve high-efficiency enrichment, good stability, and large volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The standard addition removal of nano-silver in the actual water of embodiment 1
[0031] The microporous membrane removes nano-silver in four kinds of actual water samples, and the actual water samples do not need any pretreatment. Add nano-silver to 1.0L sewage treatment plant inlet water and outlet water, river water and lake water to 1mg / L, and then add 0.1g of PVDF microporous membrane with a pore size of 0.45μm to the actual water sample containing nano-silver , shake at 300rpm at room temperature for 1h, complete the adsorption, and take out the filter membrane.
[0032] The concentration of nano-silver in the actual water sample after adsorption is measured and the filter membrane after adsorption is characterized: take 1mL of the above-mentioned actual water sample after adsorption by the microporous filter membrane, add 2.0mL concentration of 5% ( v / v) HNO 3 After the aqueous solution, the concentration of silver in the above water sample solution was measur...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 adopts microporous membrane filtration mode to remove nanoparticles in water
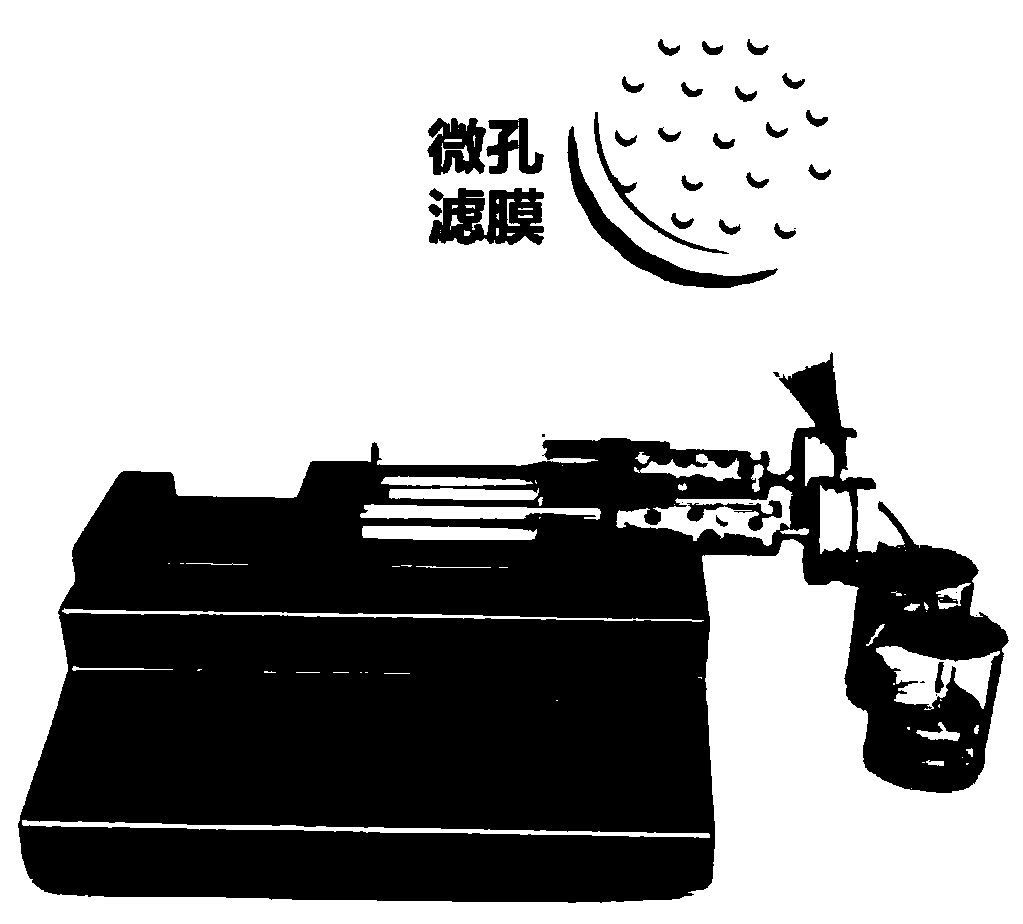
[0034] The PVDF microporous filter membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm is installed in the replaceable membrane filter head, and the construction is as follows: figure 2 device shown. After sucking 1L of samples (respectively, four kinds of actual water solutions containing 10μg / L nano-silver, river water, lake water, sewage treatment plant inlet water and outlet water) into the syringe, they were all pushed out of the syringe at a speed of 60mL / min. The content of nanomaterials in aqueous solution after microporous membrane filtration.
[0035] The experimental results show that when the concentration of nano-silver in the actual water body is 10 μg / L, the removal efficiency of nano-silver in four kinds of actual water solutions is all above 92%. Considering that the sample matrix is complex and the standard addition level ( Nano silver content) is extremely low, so this r...
Embodiment 3
[0037] a. Add 0.1g of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyethersulfone (PES), nylon (Nylon) and mixed cellulose (MCE) microporous membranes with a pore size of 0.45 μm to 1L containing 30mg / L nano silver In the aqueous solution, the pH of the aqueous solution is 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, 300rpm oscillating adsorption at room temperature for 120min, the adsorption removes the nano-silver in the aqueous solution, and the adsorption ends, and the content of the nano-silver in the aqueous solution is tested after the adsorption is completed. .
[0038] b. Add 0.1g of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyethersulfone (PES), nylon (Nylon) and mixed cellulose (MCE) microporous membranes with a pore size of 0.45 μm to 1L containing 50mg / L nano-gold In the aqueous solution, the pH of the aqueous solution is 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 respectively, 300rpm vibration adsorption at room temperature for 120min, the adsorption removes the nano-gold in the aqueous solution, the adsorption is comple...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com