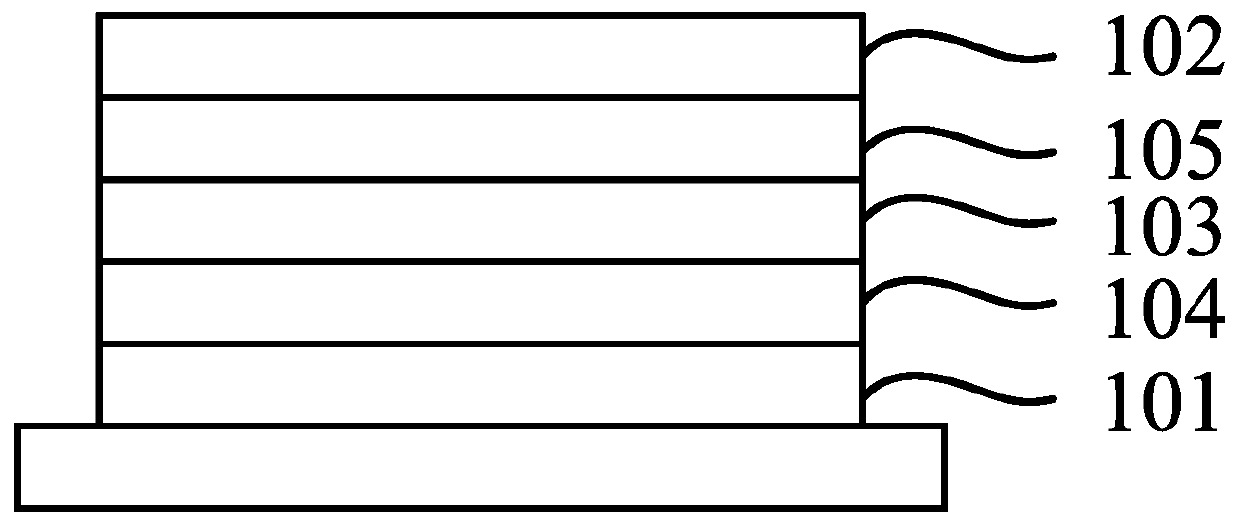
Electroluminescent compound, and thermal activation delayed fluorescence material and applications thereof
A technology of thermally activated delayed and fluorescent materials, applied in the field of organic electroluminescent materials, can solve the problems of difficult performance to meet the requirements of high-performance OLED devices, less TADF materials, etc., to achieve good compactness, improved fluorescence lifetime and improved device efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] This embodiment provides an electroluminescent compound with the following structure:
[0112]
[0113] The preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0114] (1)
[0115] Add A (0.5mmol) and B (0.5mmol) sequentially into a microwave vial, dissolve with ethanol (6mL), and then add tetrabutyl acetate (Bu 4 NOAc, 1 mmol) and palladium catalyst Pd En Cat (63 mg, 5 mol%); the reaction was irradiated with a microwave device at 120° C. for 10 minutes. After cooling to room temperature in a microwave cavity, the reaction mixture was purified on a SCXII column using dichloromethane (DCM, 10 mL) as eluent and evaporated to dryness to afford Intermediate C.
[0116] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ8.91(s,1H),8.12(d,J=4.0Hz,2H),7.84(s,1H),7.66(s,1H),7.53(s,1H),7.44(s,1H) , 7.32 (d, J=20.0Hz, 2H).
[0117] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ148.63(s), 148.12(s), 147.36(s), 143.88(s), 134.18(s), 132.82(s), 131.31(s), 130.07(s), 129.65(s), 127.95 (s), 127.51(s), 126.95(s)...
Embodiment 2
[0127] This embodiment provides an electroluminescent compound with the following structure:
[0128]
[0129] The difference between the preparation method and the preparation method in Example 1 is that the compound E in the step (3) is mixed with an equimolar amount of the compound E2 Instead, the other preparation conditions remain unchanged to obtain the target product M2.
[0130] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ8.87(s,1H),8.63(s,1H),8.55(s,1H),8.18(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.94(s,4H),7.89(s,4H) ,7.75(d,J=16.0Hz,3H),7.59(s,1H),7.51(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.41(d,J=8.0Hz,2H),7.16(dd,J= 22.0, 14.0Hz, 4H).
[0131] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ154.08(s), 151.67(d, J=7.0Hz), 146.93(s), 145.60(s), 139.35(s), 135.09(s), 134.01(s), 131.99(s), 130.97 (s), 129.86-129.49(m), 129.27(s), 127.82(s), 127.11(s), 126.91(s), 125.32(s), 124.67(s), 122.99(s), 113.74(s) .
Embodiment 3
[0133] This embodiment provides an electroluminescent compound with the following structure:
[0134]
[0135] The difference between the preparation method and the preparation method in Example 1 is that the compound E in step (3) is mixed with an equimolar amount of compound E3 Instead, the other preparation conditions remain unchanged to obtain the target product M3.
[0136] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ8.87(s,1H),8.62(s,1H),8.17(s,1H),7.94(s,1H),7.74(d,J=24.0Hz,3H),7.55(d,J= 36.0Hz, 2H), 7.42(s, 1H), 7.18(dd, J=8.0, 4.0Hz, 8H), 6.94(s, 2H), 1.69(s, 6H).
[0137] 13 C-NMR (100MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ154.08(s), 152.78(s), 151.64(s), 145.60(s), 142.44(s), 139.35(s), 135.09(s), 134.24(s), 133.37(s), 131.99 (s), 130.97(s), 29.86-129.49(m), 128.95(s), 127.82(s), 127.11(s), 126.83(d, J=15.7Hz), 125.32(s), 122.86(s) , 120.00(s), 113.74(s), 35.71(s), 29.68(s).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com