Application of gene GmLMM1 related to soybean phytophthora resistance
A technology of Phytophthora and soybean, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, to suppress plant cell death and active oxygen outbreak, promote research and application, and enhance the effect of plant PTI immune response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Construction and phenotype analysis of embodiment 1 Gmlmm1 mutant population
[0048] By screening the mutant library obtained by EMS mutagenesis Williams82, the mutant Gmlmm1 was obtained, and its leaves showed a lesion-like phenotype ( figure 1 ), continuously self-planted for 4 generations for background purification. The F2 segregation population used for map-based cloning was constructed by crossing with the distant variety "Hedou 12". Phenotype observation and statistical analysis showed that it was stable genetically and conformed to the Mendelian law of inheritance (3:1 segregation ratio), indicating the Gmlmm1 mutation The somatic phenotype is controlled by a recessive single gene.
Embodiment 2
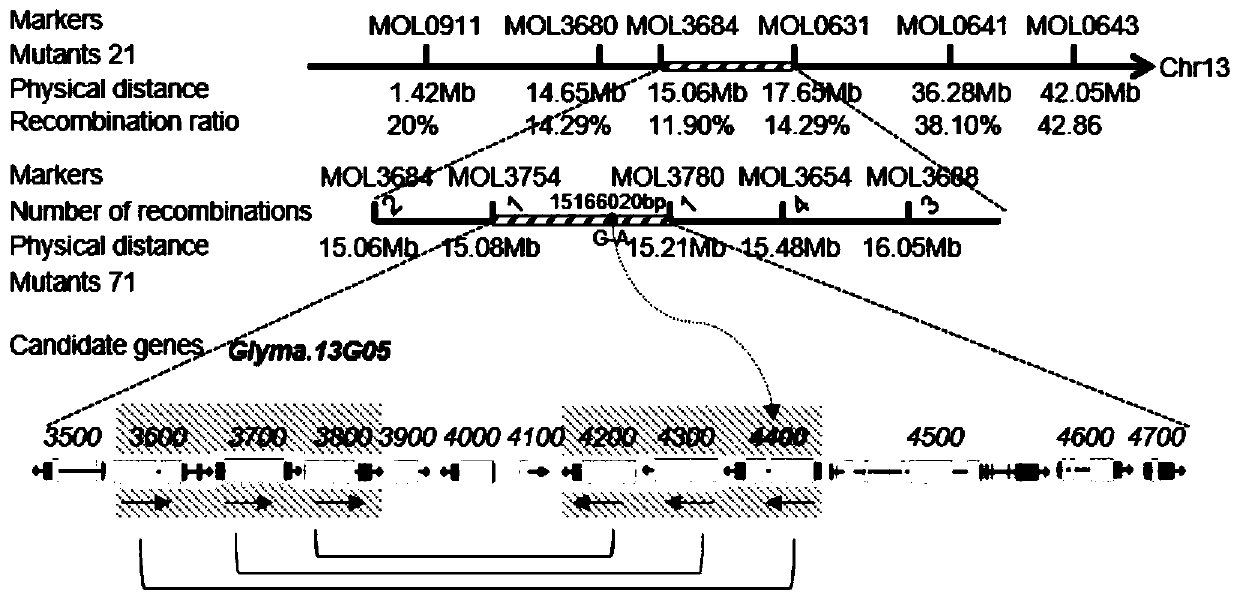
[0049] Example 2 Location of Soybean Phytophthora Resistance-Related Gene GmLMM1
[0050] The F2 segregation population crossed with Gmlmm1 and "Hedou 12" was used for gene mapping. The rough mapping results showed that the mutation site was located between 15.06Mb and 17.65Mb on chromosome 13. In order to further determine the position of the Gmlmm1 mutant gene, a new Indel molecular marker was designed in the region between 15.06Mb-17.65Mb on chromosome 13 to fine-map the mutant individual plants, and finally the GmlMM1 gene was located on chromosome 13 at 15.08Mb-17.65Mb. 131kb interval between 15.21Mb ( figure 2 ). In this 131kb interval, there are a total of 13 candidate genes. Combined with the results of whole genome resequencing, it is found that there is only Glyma.13G054400 in this 131kb interval, that is, the GmLMM1 gene (the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the CDS sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 ID NO.2) in the second ex...
Embodiment 3
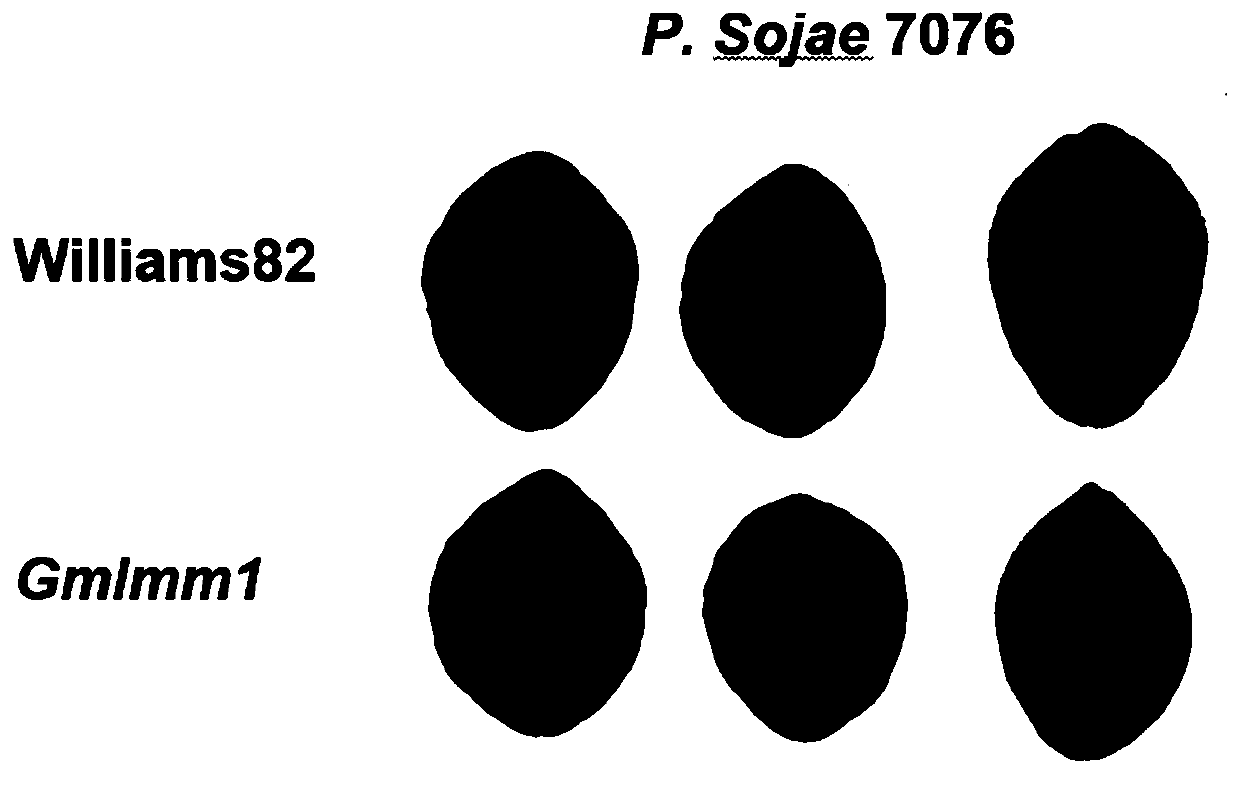
[0051] Example 3 Identification of Phytophthora Phytophthora Resistance Phenotypes of Gmlmm1 Mutants
[0052] The wild-type "Williams82" leaves and Gmlmm1 mutant leaves were inoculated with Phytophthora sojae P.Sojae 7076 mycelium block, and the infection difference was observed by observing the size of the lesion and staining with trypan blue after 60 hours of infection ( image 3 ), the observation statistics found that the resistance level of the Gmlmm1 mutant was significantly increased compared with the wild type. Further statistics were made on the lesion area after 60 hours of mycelium block infection, and it was found that the lesion area of the mutant Gmlmm1 was significantly smaller than that of the wild type "Williams82" ( Figure 4 ).
[0053] Use zoospores of Phytophthora soybean P.Sojae 7076 to infect the root hairs of soybean mutant Gmlmm1 and wild-type "Williams82", and induce zoospores after growing for about 3 days. Infect the root hairs with basically th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com