Filtering type electrochemical reactor and method for removing antibiotics from water mass
An electrochemical and filtering technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as limiting the application range of electrochemical oxidation, failing to meet practical application requirements, and failing to obtain removal effects. Good use value and application prospect, good strength, good removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
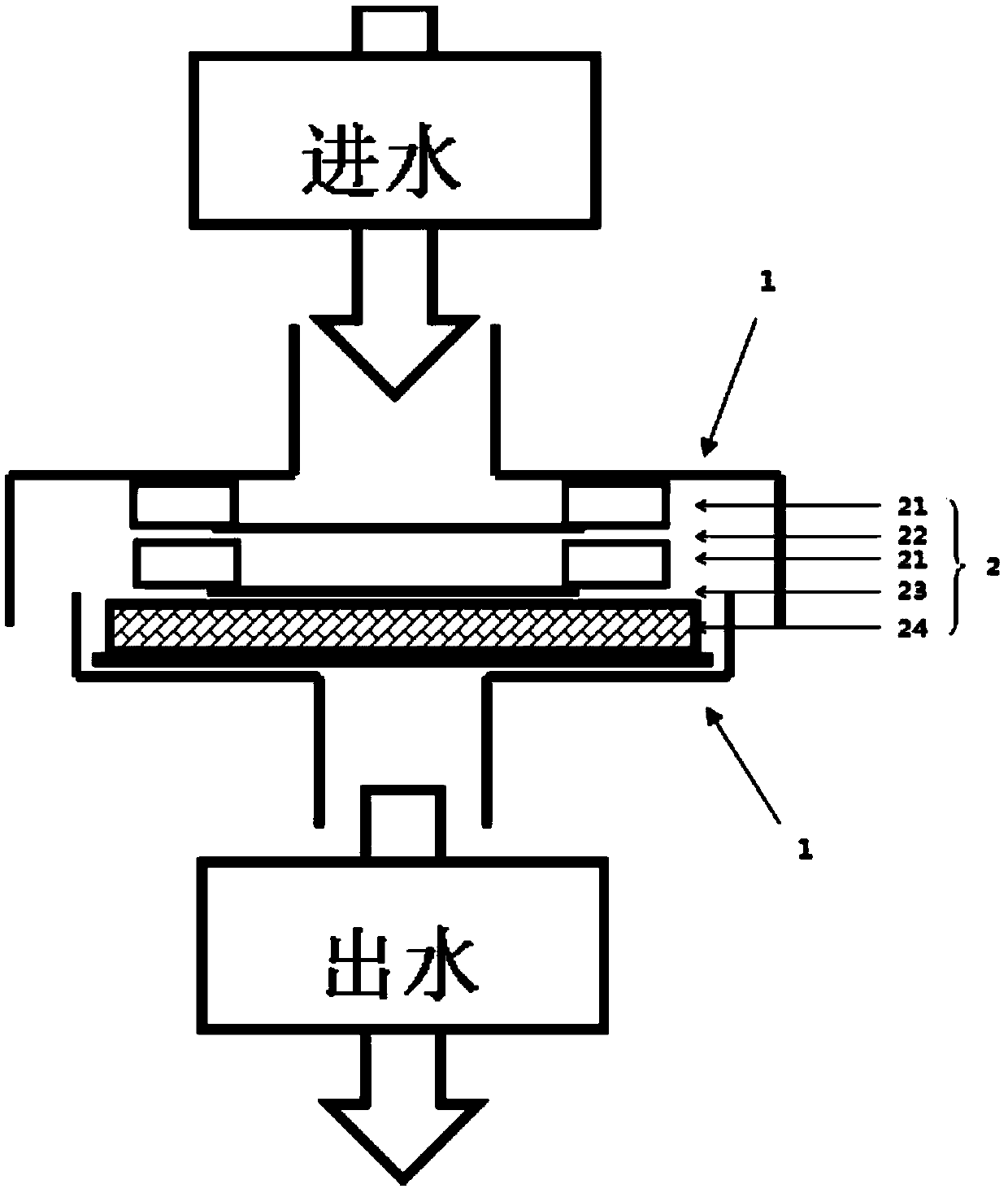
[0036] A filtered electrochemical reactor, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a pool body 1 and a filter device 2 located in the pool body 1, the filter device 2 includes a cathode 21 located at the water inlet end and an anode 24 located at the water outlet end, wherein a sealing septum 21 is provided between the cathode 21 and the anode 24, It is used to separate the cathode 21 from the anode 24 while also sealing the filter device 2 to avoid water leakage; a sealing spacer 21 is provided between the cathode 22 and the cell body 1 for separating the cathode 22 from the cell body 1 Simultaneously, the filter device 2 is also sealed to avoid water leakage.
[0037]In the present embodiment, the anode 24 is a carbon nanotube film, and the carbon nanotube film is used as the anode material to be arranged at the water outlet of the filter device 2, which can not only absorb more pollutants (such as antibiotics), but also in the process of electrochemical oxidation reaction. ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A method for removing antibiotics in water, using the filtering electrochemical reactor in embodiment 1 to process antibiotics, comprising the following steps:
[0045] (1) Mix sulfamethoxazole waste water with an initial concentration of 5 mg / L and a pH of 7 with sodium chloride to obtain a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of sodium chloride in the mixed solution is 20 mmol / L.
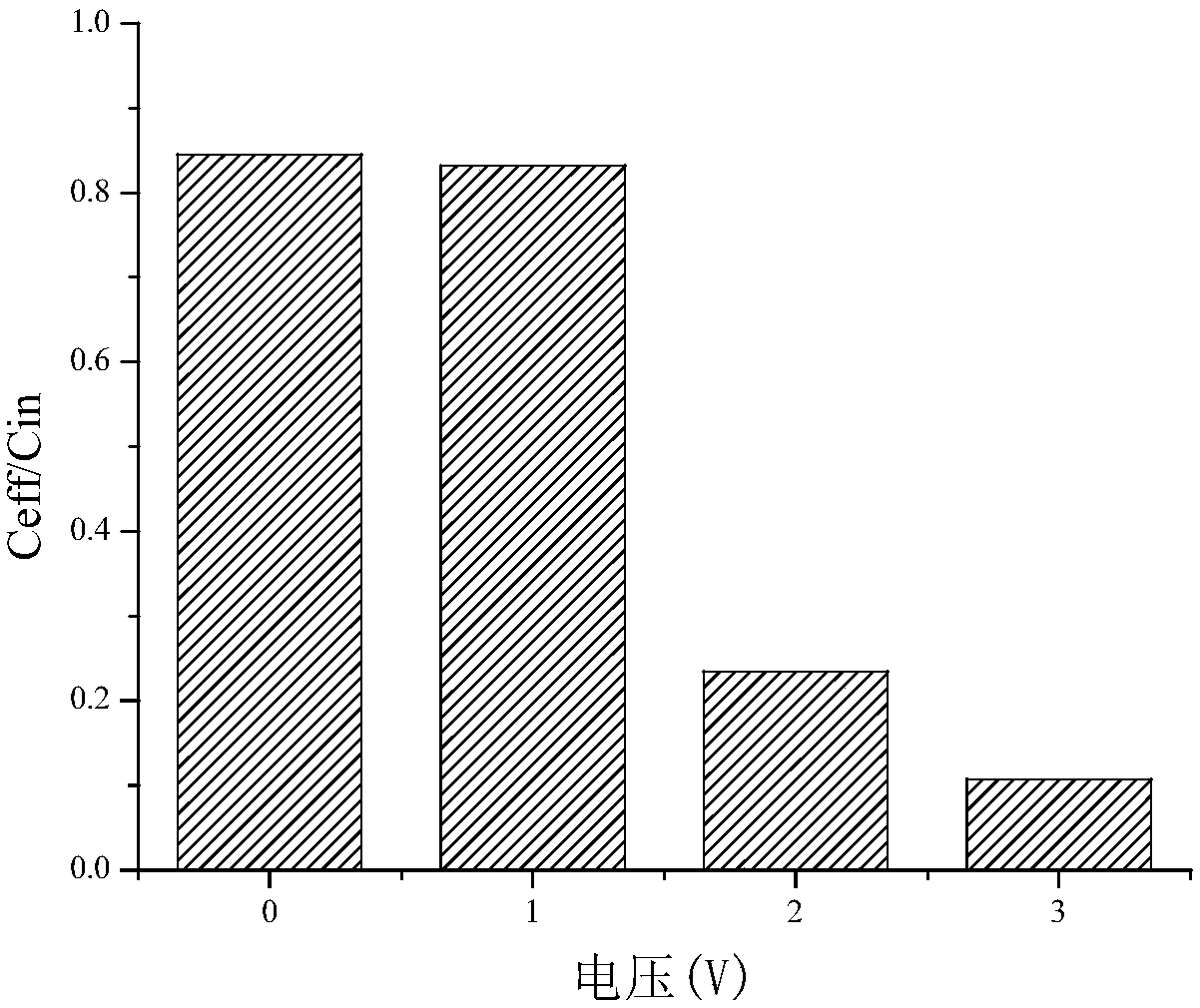
[0046] (2) Connect the filter-type electrochemical reactor to the power supply, set the external DC voltage to 0; according to the feed rate of 1.5mL / min, continuously pass the mixed solution in step (1) into the filter-type electrochemical reactor The electrochemical oxidation degradation is carried out at a temperature of 25°C, and the feeding time is 1h. Specifically, the mixed solution in step (1) is continuously fed into the reactor through the water inlet of the filter-type electrochemical reactor, and sequentially passed through The cathode and the anode, the adsorption reaction...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for removing antibiotics in water, using the filtering electrochemical reactor in embodiment 1 to process antibiotics, comprising the following steps:
[0052] (1) Mix sulfamethoxazole wastewater with an initial concentration of 50 mg / L and a pH of 7 with sodium chloride to obtain a mixed solution, wherein the concentration of sodium chloride in the mixed solution is 20 mmol / L.
[0053] (2) Connect the filter-type electrochemical reactor to the power supply, and set the external DC voltage to 3V; according to the feed rate of 1.5mL / min, continuously pass the mixed solution in step (1) into the filter-type electrochemical reactor The electrochemical oxidation degradation is carried out at a temperature of 25 ° C, and the feeding time is 1 h. Specifically, the mixed solution in step (1) is continuously fed into the reactor through the water inlet of the filter type electrochemical reactor, and sequentially passed through the cathode And the anode, the adsorption ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com