Method for treating antibiotic wastewater by utilizing visible light response semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photoelectrocatalytic material electrode
A technology of antibiotic wastewater and photoelectric catalysis, applied in chemical instruments and methods, special compound water treatment, light water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of stability and repeatability decline, limited promotion and application, weak light utilization ability, etc. , achieving the effects of simple and easy-to-obtain reagents, high cycle efficiency, and improved degradation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A method for treating antibiotic wastewater by using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode, specifically using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode as an anode to treat sulfamethazine in wastewater through a photoelectric catalytic reaction processing, including the following steps:
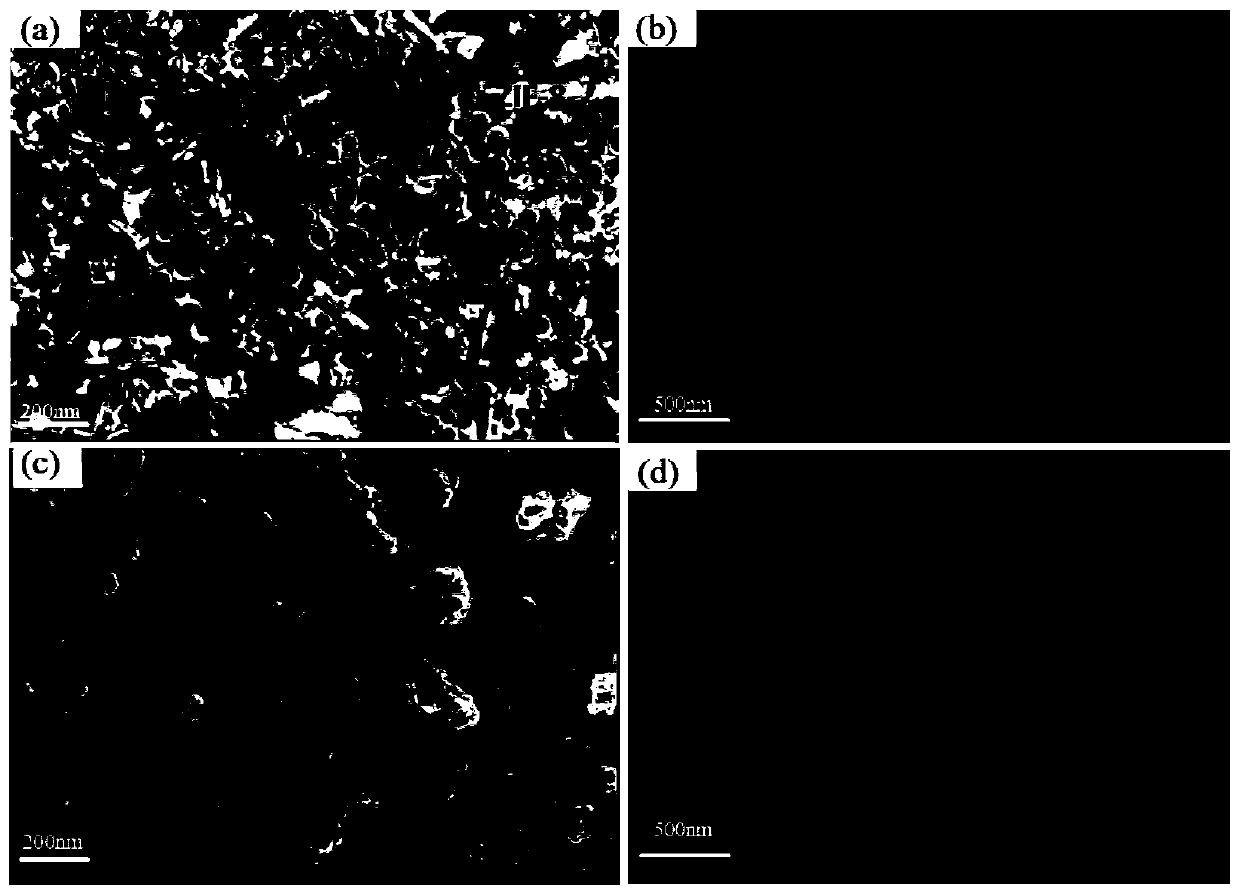
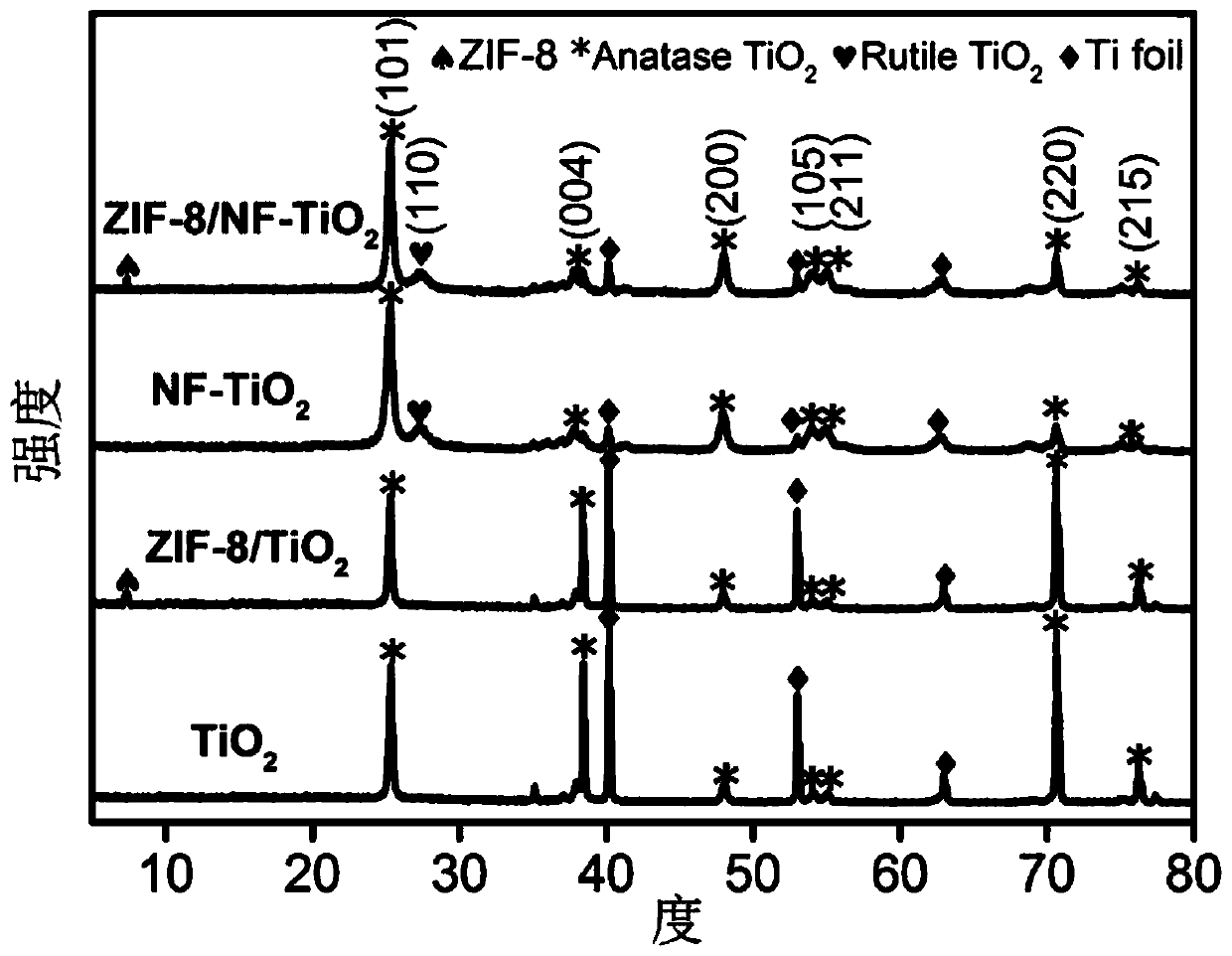
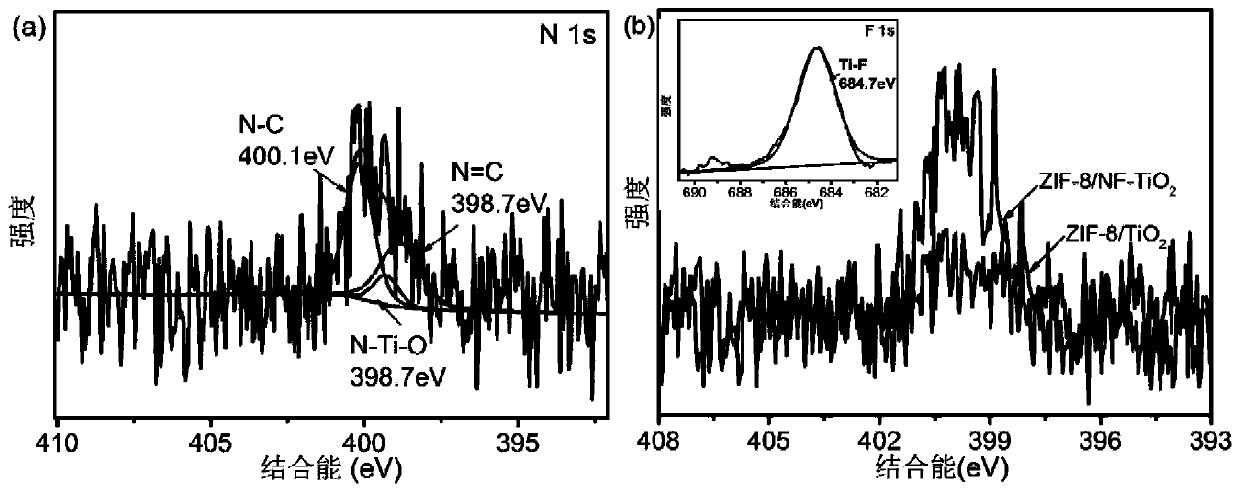
[0042] With material electrode (TiO 2 -NTs, ZIF-8 / TiO 2 , NF-TiO 2 、ZIF-8 / NF-TiO 2 ) as anode, Cu sheet as counter electrode, Ag / AgCl electrode as reference electrode, put into 100ml sulfamethazine wastewater containing sodium sulfate (the concentration of sodium sulfate in this wastewater is 0.5mol / L, sulfamethazine Concentration of 10mg / L, pH=3.5) for 3h in the photocatalytic reaction, wherein the photocatalytic reaction is carried out under the visible light source, the voltage is 2.0V, to complete the treatment of sulfamethazine.
[0043] In this example, the visible light responsive ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] A method for treating antibiotic wastewater by using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode, specifically using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode as an anode to treat sulfamethazine in wastewater through a photoelectric catalytic reaction processing, including the following steps:
[0064] With the visible light response semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode (ZIF-8 / NF-TiO 2 ) as anode, Cu sheet as counter electrode, Ag / AgCl electrode as reference electrode, put into 100ml sulfamethazine wastewater containing sodium sulfate (the concentration of sodium sulfate in this wastewater is 0.5mol / L, sulfamethazine The concentration is 10mg / L, pH=3.5), carry out photoelectric catalytic reaction under different conditions, complete the treatment of sulfamethazine.
[0065] Condition 1: Apply visible light source and 2V voltage for 3h.
[0066] Condition 2: A...
Embodiment 3
[0073] A method for treating antibiotic wastewater by using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode, specifically using a visible light responsive semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode as an anode to treat sulfamethazine in wastewater through a photoelectric catalytic reaction processing, including the following steps:
[0074] With the visible light response semiconductor-MOFs hybrid photocatalytic material electrode (ZIF-8 / NF-TiO 2 ) as anode, Cu sheet as counter electrode, Ag / AgCl electrode as reference electrode, put into 100ml sulfamethazine wastewater containing sodium sulfate (the concentration of sodium sulfate in this wastewater is 0.5mol / L, sulfamethazine concentration of 10 mg / L, pH=3.5), the photocatalytic reaction was carried out at voltages of 1.0V, 1.5V, 2.0V, 2.5V, and 3.0V for 3 hours, wherein the photocatalytic reaction was carried out under a visible light source, and the Treatment of sulf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com